LoadBalancer SPI 代码分析
网关应用需要支持多种负载均衡的方案,包括随机选择、Hash、轮询等方式。Apache Shenyu网关中不仅实现了传统网关的这些均衡策略,还通过流量预热(warmup)等细节处理,对服务器节点的加入,做了更平滑的流量处理,获得了更好的整体稳定性。让我们来看看Shenyu是是如何设计和实现这部分功能的。
本文基于
shenyu-2.5.0版本进行源码分析.
[TOC]
LoadBalancer SPI
LoadBalancer SPI 定义在shenyu-loadbalancer模组中,以下是这个核心接口的代码,这个接口很好的诠释了这样一个理念:负载均衡是在一系列服务器节点中选出最合适的节点,也就是选择策略。做流量转发、路由和负载均衡是LoadBalance SPI的基本功能
@SPI
public interface LoadBalancer {
/**
* this is select one for upstream list.
*
* @param upstreamList upstream list
* @param ip ip
* @return upstream
*/
Upstream select(List<Upstream> upstreamList, String ip);
}
接口中,upstreamList是可选路由的一组服务器节点,Upstream 是服务器节点的数据结构,它包括的重要元素有:协议、url 、权重、时间戳,warmup,健康状态等。
public class Upstream {
/**
* protocol.
*/
private final String protocol;
/**
* url.
*/
private String url;
/**
* weight.
*/
private final int weight;
/**
* false close, true open.
*/
private boolean status;
/**
* startup time.
*/
private final long timestamp;
/**
* warmup.
*/
private final int warmup;
/**
* healthy.
*/
private boolean healthy;
/**
* lastHealthTimestamp.
*/
private long lastHealthTimestamp;
/**
* lastUnhealthyTimestamp.
*/
private long lastUnhealthyTimestamp;
/**
* group.
*/
private String group;
/**
* version.
*/
private String version;
}
Design of LoadBalance module`
图1是LoadBalancer模组的类图:
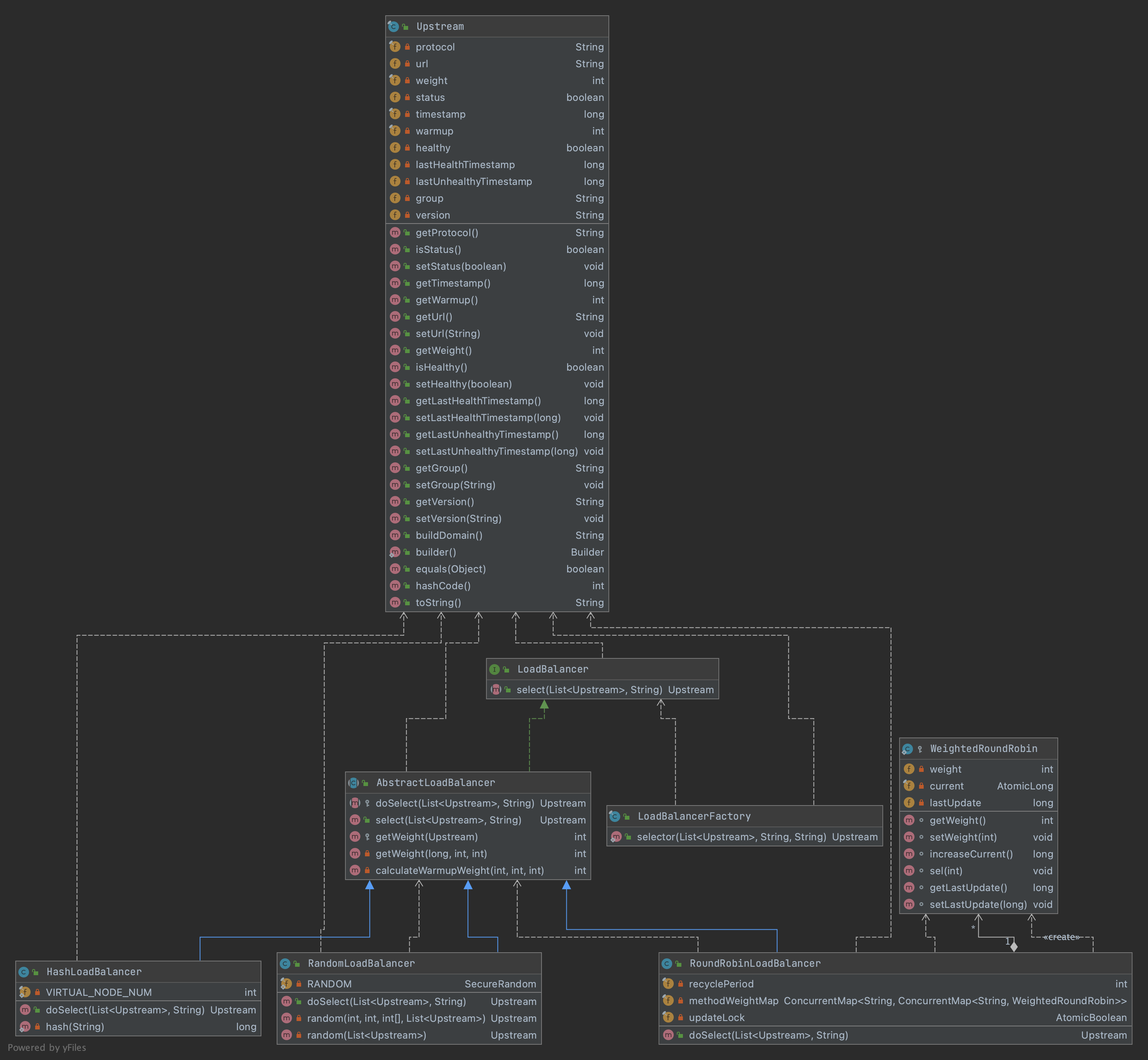
从类图上可以看出LoadBalance的设计概要:
-
抽象类
AbstractLoadBalancer继承自LoadBalancerSPI接口,并提供选择的模板方法,及权重计算。 -
三个实做类继承
AbstractLoadBalancer, 实现各自的逻辑处理。RandomLoadBalancer-加权随机选择 Weight RandomHashLoadBalancer- 一致性HashRoundRobinLoadBalancer-加权轮询(Weight Round Robin per-packet)
-
由工厂类
LoadBalancerFactory实现对外的静态调用方法。另外根据
Apache Sheny SPI规范,在SHENYU_DIERECTORY中的添加profile,配置LoadBalance的实现类,配置key=class形式,左边的operator要和LoadBalanceEnum中的定义一致。
random=org.apache.shenyu.loadbalancer.spi.RandomLoadBalancer
roundRobin=org.apache.shenyu.loadbalancer.spi.RoundRobinLoadBalancer
hash=org.apache.shenyu.loadbalancer.spi.HashLoadBalancer
LoadBalanceEnum的定义如下:
public enum LoadBalanceEnum {
/**
* Hash load balance enum.
*/
HASH(1, "hash", true),
/**
* Random load balance enum.
*/
RANDOM(2, "random", true),
/**
* Round robin load balance enum.
*/
ROUND_ROBIN(3, "roundRobin", true);
private final int code;
private final String name;
private final boolean support;
}
AbstractLoadBalancer
这个抽象类实做了LoadBalancer接口, 定义了抽象方法doSelect()留给实作类处理,在模板方法select() 中先进行校验,之后调用由实作类实现的doSelect()方法。
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalancer implements LoadBalancer {
/**
* Do select divide upstream.
*
* @param upstreamList the upstream list
* @param ip the ip
* @return the divide upstream
*/
protected abstract Upstream doSelect(List<Upstream> upstreamList, String ip);
@Override
public Upstream select(final List<Upstream> upstreamList, final String ip) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(upstreamList)) {
return null;
}
if (upstreamList.size() == 1) {
return upstreamList.get(0);
}
return doSelect(upstreamList, ip);
}
}
权重的处理方法getWeight()的逻辑是:当有时间戳,并且当前时间与时间戳间隔在流量预热warmup时间内,权重计算的公式为:
$$ 0
ww = min(1,uptime/(warmup/weight))
$$
从公式可以看出,最终的权值,与设置的weight成正比,时间间隔越接近warmup时间,权重就越大。也就是说等待�的时间越长,被分派的权重越高。没有时间戳时等其他情况下,返回Upstream设置的weight值。
考虑流量预热(warmup)的核心思想是避免在添加新服务器和启动新JVM时网关性能不佳。
下面我们看一下三个实做类的实现。
RandomLoadBalancer
这里随机LoadBalancer 可以处理两种情况:
- 没有权重:所有服务器都没有设定权重,或者权重都一样, 会随机选择一个。
- 有权重:服务器设定有不同的权重,会根据权重,进行随机选择。
下面是有权重时的随机选择代码random(): 遍历全部服务器列表,当随机值小于某个服务器权重时,这个服务器被选中(这里提前计算了前一半服务器的权重和,如果随机值大于halfLengthTotalWeight,则遍历从(weights.length + 1) / 2开始,提高了小效率)。 若遍历后没有满足条件,就在全部服务器列表中随机选择一个返回。这里getWeight(final Upstream upstream) 方法是在AbstractLoadBalancer 中定义的,按公式计算权重。
@Override
public Upstream doSelect(final List<Upstream> upstreamList, final String ip) {
int length = upstreamList.size();
// every upstream has the same weight?
boolean sameWeight = true;
// the weight of every upstream
int[] weights = new int[length];
int firstUpstreamWeight = getWeight(upstreamList.get(0));
weights[0] = firstUpstreamWeight;
// init the totalWeight
int totalWeight = firstUpstreamWeight;
int halfLengthTotalWeight = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
int currentUpstreamWeight = getWeight(upstreamList.get(i));
if (i <= (length + 1) / 2) {
halfLengthTotalWeight = totalWeight;
}
weights[i] = currentUpstreamWeight;
totalWeight += currentUpstreamWeight;
if (sameWeight && currentUpstreamWeight != firstUpstreamWeight) {
// Calculate whether the weight of ownership is the same.
sameWeight = false;
}
}
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
return random(totalWeight, halfLengthTotalWeight, weights, upstreamList);
}
return random(upstreamList);
}
private Upstream random(final int totalWeight, final int halfLengthTotalWeight, final int[] weights, final List<Upstream> upstreamList) {
// If the weights are not the same and the weights are greater than 0, then random by the total number of weights.
int offset = RANDOM.nextInt(totalWeight);
int index = 0;
int end = weights.length;
if (offset >= halfLengthTotalWeight) {
index = (weights.length + 1) / 2;
offset -= halfLengthTotalWeight;
} else {
end = (weights.length + 1) / 2;
}
// Determine which segment the random value falls on
for (; index < end; index++) {
offset -= weights[index];
if (offset < 0) {
return upstreamList.get(index);
}
}
return random(upstreamList);
}
因此,当采用RandomLoadBalancer时,是按权重随机分派服务器的。
HashLoadBalancer
Apache Shenyu的HashLoadBalancer 中采用了一致性hash算法,使用有序hash环,将key与服务器节点的hash映射缓存起�来。对于请求的ip地址,计算出其hash值, 在hash环上顺时针查找距离这个key的hash值最近的节点,将其作为要路由的节点。一致性hash解决了传统取余hash算法的可伸缩性差的问题。
HashLoadBalancer中的采用的是加密的单向MD5散列函数,这个hash函数会hash后产生不可预期但确定性的()的结果,输出为32-bit的长整数。hash代码如下:
private static long hash(final String key) {
// md5 byte
MessageDigest md5;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new ShenyuException("MD5 not supported", e);
}
md5.reset();
byte[] keyBytes;
keyBytes = key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
md5.update(keyBytes);
byte[] digest = md5.digest();
// hash code, Truncate to 32-bits
long hashCode = (long) (digest[3] & 0xFF) << 24
| ((long) (digest[2] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((long) (digest[1] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (digest[0] & 0xFF);
return hashCode & 0xffffffffL;
}
再看一下HashLoadBalancer的选择函数doSelect()的实现:
private static final int VIRTUAL_NODE_NUM = 5;
@Override
public Upstream doSelect(final List<Upstream> upstreamList, final String ip) {
final ConcurrentSkipListMap<Long, Upstream> treeMap = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
upstreamList.forEach(upstream -> IntStream.range(0, VIRTUAL_NODE_NUM).forEach(i -> {
long addressHash = hash("SHENYU-" + upstream.getUrl() + "-HASH-" + i);
treeMap.put(addressHash, upstream);
}));
long hash = hash(ip);
SortedMap<Long, Upstream> lastRing = treeMap.tailMap(hash);
if (!lastRing.isEmpty()) {
return lastRing.get(lastRing.firstKey());
}
return treeMap.firstEntry().getValue();
}
这个方法中,生成带虚拟服务器节点的hash环, 一个实际节点会生成5个虚拟节点,因此整个hash环的均匀性大大增加,降低数据倾斜的发生。
为了实现hash环的有序性及顺时针查找功能,代码中使用Java 的ConcurrentSkipListMap 来存储带虚拟节点的服务器节点及其hash值, 它既能保证线程安全,又能保证数据的有序性,支持高并发。 另外,ConcurrentSkipListMap提供了一个tailMap(K fromKey)方法,可从map中查找比fromKey大的值的集合,但并不需要遍历整个数据结构。
上述代码中,生成hash环之后,就是调用ConcurrentSkipListMap的tailMap()方法,找到大于等于请求的ip的hash值的子集,这个子集的第一个就是要路由的服务器节点。采用了合适的数据结构,这里的代码看上去是不是特别的简洁流畅?
RoundRobinLoadBalancer
Round-robin轮询方法的原始定义是顺序循环将请求依次循环地连接到每个服务器。当某个服务器发生故障(例如:一分钟连接不上的服务器),从候选队列中取出,不参与下一次的轮询,直到其恢复正常。在 RoundRobinLoadBalancer中实现的是组内加权轮询(Weight Round Robin per-packet)方法:
为了计算和存储每个服务器节点的轮询次数,在这个类中定义了一个静态内部类WeigthRoundRobin,我们先看一下它的主要代码(去掉了注释):
protected static class WeightedRoundRobin {
private int weight;
private final AtomicLong current = new AtomicLong(0);
private long lastUpdate;
void setWeight(final int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
current.set(0);
}
long increaseCurrent() {
return current.addAndGet(weight);
}
void sel(final int total) {
current.addAndGet(-1 * total);
}
void setLastUpdate(final long lastUpdate) {
this.lastUpdate = lastUpdate;
}
}
请重点关注这几个方法:
-
setWeight(final int weight),为对象设定权重,并将current重置为0. -
increaseCurrent(): 对AtomicLong类型的对象current,累加其权重值。 -
sel(final int total):current减去传入的total值。
下面我们看一下带权重的轮询过程是如何实现的。
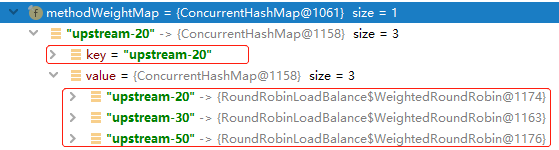
首先定义了一个ConcurrentMap类型对象methodWeightMap 两层对象来存储服务器列表与其各个明细节点的轮询资料。
private final ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>> methodWeightMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
这个map对象第一层的key为当前服务器列表的第一个节点的upstreamUrl, 第二个对象ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>存储了组内各个服务器节点的轮询情况,内层Map的key为组内每个服务器的upstreamUrl。Map对象使用JUC的ConcurrentHashMap,不仅存取高效,而且线程安全,支持高并发。
内层map的每个节点对应的WeighedRoundRobin作为静态内部类能确保线程安全,并实现组内的加权轮询选择功能。下面是这个类的doSelect()方法的代码。
@Override
public Upstream doSelect(final List<Upstream> upstreamList, final String ip) {
String key = upstreamList.get(0).getUrl();
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = methodWeightMap.get(key);
if (Objects.isNull(map)) {
methodWeightMap.putIfAbsent(key, new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
map = methodWeightMap.get(key);
}
int totalWeight = 0;
long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Upstream selectedInvoker = null;
WeightedRoundRobin selectedWeightedRoundRobin = null;
for (Upstream upstream : upstreamList) {
String rKey = upstream.getUrl();
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = map.get(rKey);
int weight = getWeight(upstream);
if (Objects.isNull(weightedRoundRobin)) {
weightedRoundRobin = new WeightedRoundRobin();
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
map.putIfAbsent(rKey, weightedRoundRobin);
}
if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) {
// weight changed.
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
}
long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent();
weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now);
if (cur > maxCurrent) {
maxCurrent = cur;
selectedInvoker = upstream;
selectedWeightedRoundRobin = weightedRoundRobin;
}
totalWeight += weight;
}
...... //erase the section which handles the time-out upstreams.
if (selectedInvoker != null) {
selectedWeightedRoundRobin.sel(totalWeight);
return selectedInvoker;
}
// should not happen here
return upstreamList.get(0);
}
举例,若服务器组upstreamUrl 分别为: LIST = [upstream-20, upstream-50, upstream-30]时,经过一轮执行后,建立的methodWeightMap 资料如下:
假设上述的LIST中,各个服务器节点的权重数组为: [20,50,30], 下图是内部类current 值变化和轮询选择过程:
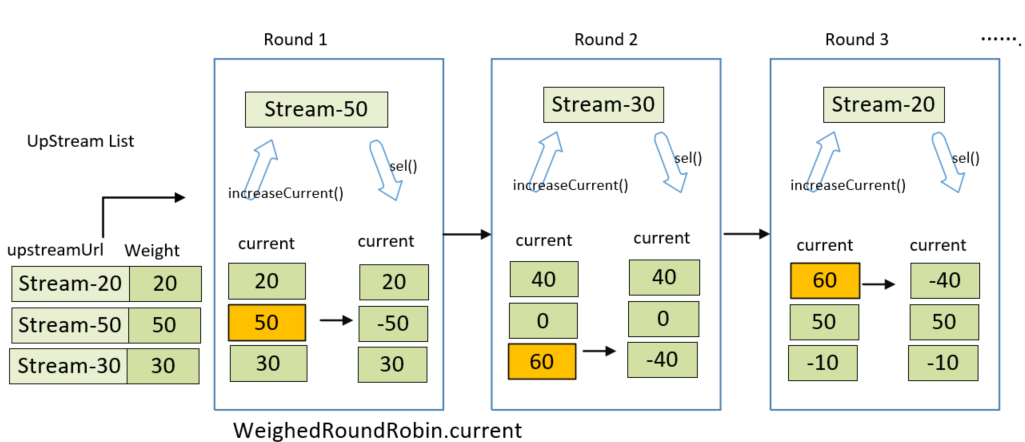
每一轮,选择值current最大的服务器节点:
- Round1:
- 对当前服务器LIST做遍历,当服务器节点的weightedRoundRobin 为null时,current被置为各自的权重; 不为null时,累加各自的权重。
- 即:遍历后current 分别为 [20, 50,30] , 会选择Stream-50, Stream-50对应的WeightRoundRobin静态类做 sel(-total)处理,current 更新为[20,-50, 30].
- Round 2 遍历后的current是[40,0,60], 会选择Stream-30, current分别更新为[40,0,-40].
- Round 3 遍历后的current是[60,50,-10], 会选择Stream-20,current分别更新为[-40,50,-10].
中间进行了容错处理, 当服务器的个数与map个数不一样,就对methodWeightMap 加锁做处理。 用先copy 后modify的方式, 把超时的服务器remove掉,即移除掉发生故障的服务器,并更新Map资料。如下是异常时的处理代码:
if (!updateLock.get() && upstreamList.size() != map.size() && updateLock.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
// copy -> modify -> update reference.
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> newMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(map);
newMap.entrySet().removeIf(item -> now - item.getValue().getLastUpdate() > recyclePeriod);
methodWeightMap.put(key, newMap);
} finally {
updateLock.set(false);
}
}
if (Objects.nonNull(selectedInvoker)) {
selectedWeightedRoundRobin.sel(totalWeight);
return selectedInvoker;
}
// should not happen here.
return upstreamList.get(0);
LoadBalancerFactory
在这个工厂类中,提供了调用LoadBalancer的静态方法, 其中ExtensionLoader 是Apache Shenyu的SPI执行入口。也就是说,LoadBalancer模组是可配置、可扩展的。这个静态方法中的algorithm变量是LoadBalanceEnum中定义name��枚举类型。
/**
* Selector upstream.
*
* @param upstreamList the upstream list
* @param algorithm the loadBalance algorithm
* @param ip the ip
* @return the upstream
*/
public static Upstream selector(final List<Upstream> upstreamList, final String algorithm, final String ip) {
LoadBalancer loadBalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalancer.class).getJoin(algorithm);
return loadBalance.select(upstreamList, ip);
}
Using of LoadBalancer module
上面说明了LoadBalancer SPI接口及三个实作类。下面看一下LoadBalancer在Apache Shenyu中是如何被调用的。DividePlugin是路由选择插件,所有的Http请求都由该插件进行负载均衡处理。当请求头rpcType = http, 且开启该插件时,它将根据请求参数匹配规则,最终交由下游插件进行响应式代理调用。
在DividePlugin的doExecute方法中,先对要转发的请求的Header大小、content长度等做校验,
@Override
protected Mono<Void> doExecute(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ShenyuPluginChain chain, final SelectorData selector, final RuleData rule) {
......
}
接口方法的第二个参数是ShenyuPluginChain 类型,代表plugin的调用链,具体可参见Apache Sheyu 的plugin的调用机制。第三个SelectorData类型的参数是选择器, 第四个是RuldData类型,代表规则。分别请查看对应的代码。
下面给出了doExecute()方法中,有关LoadBalancer调用的代码片段:
//取到要路由的服务器节点列表。
List<Upstream> upstreamList = UpstreamCacheManager.getInstance().findUpstreamListBySelectorId(selector.getId());
...
//取到请求的ip
String ip = Objects.requireNonNull(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress()).getAddress().getHostAddress();
//调用Util方法,执行LoadBalancer处理
Upstream upstream = LoadBalancerFactory.selector(upstreamList, ruleHandle.getLoadBalance(), ip);
这里UpstreamCacheManager 是缓存的要路由的服务器节点 , ruleHandle.getLoadBalance()取到的是LoadBalanceEnum定义的枚举name, 如random, hash, roundRobin等.
经过封装,调用负载均衡功能非常的方便。 未来增加新的LoadBalancer类,这些调用的Plugin代码完全不需要变更。
Summary
经过上面的代码解读,从设计角度总结LoadBalancer 模组具有如下的特点:
-
可扩展性:面向接口的设计,及基于Apache Shenyu SPI的实现,使得系统具有良好的可扩展性。可以方便的扩展为其他的动态的负载均衡算法,��如最少连接方式(least connection)、最快模式( fastest)。并支持集群处理,具有良好的可扩展性。
-
可伸缩性:采用的一致性hash、权重随机和权重轮询算法,都可以无缝支持集群扩容或缩容。
-
流量预热等更细致的设计,能带来整体上更为平滑的负载均衡。