注册中心实现原理之Http注册
Apache ShenYu 是一个异步的,高性能的,跨语言的,响应式的
API网关。
在ShenYu网关中,注册中心是用于将客户端信息注册到shenyu-admin,admin再通过数据同步将这些信息同步到网关,网关通过这些数据完成流量筛选。客户端信息主要包括接口信息和URI信息。
本文基于
shenyu-2.5.0版本进行源码分析,官网的介绍请参考 客户端接入原理 。
1. 注册中心原理
当客户端启动时,读取接口信息和uri信息,通过指定的注册类型,将数据发送到shenyu-admin。
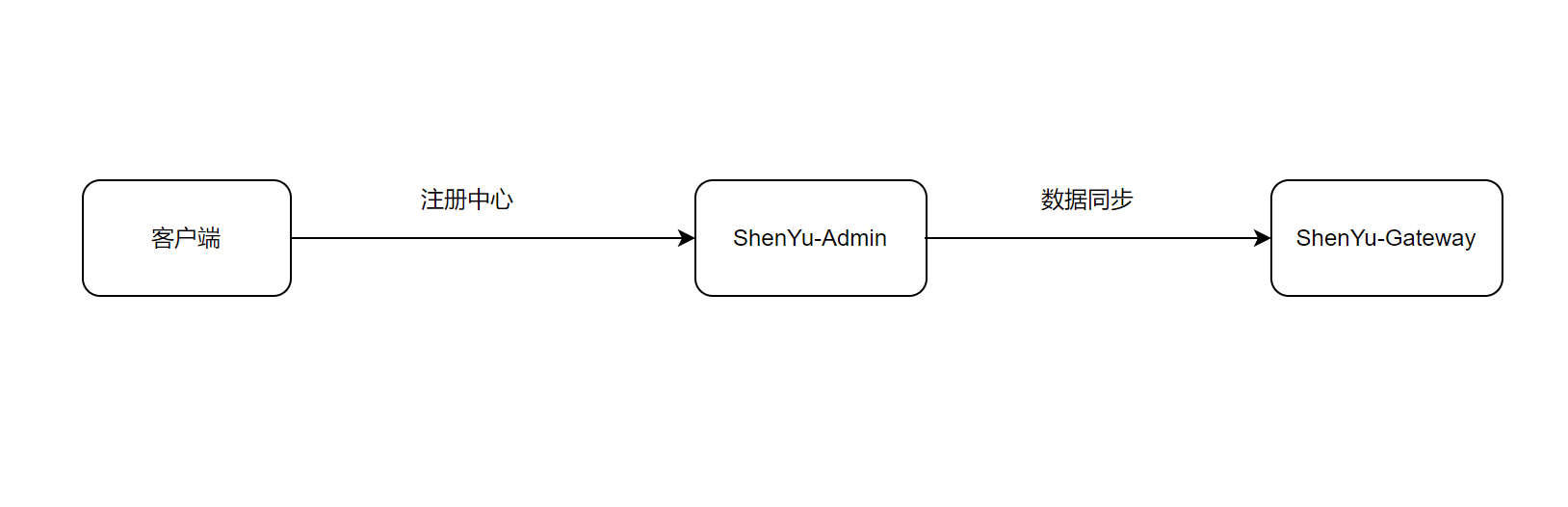
图中的注册中心需要用户指定使用哪种注册类型,ShenYu当前支持Http、Zookeeper、Etcd、Consul和Nacos进行注册。具体如何配置请参考 客户端接入配置 。
ShenYu在注册中心的原理设计上引入了Disruptor,Disruptor队列在其中起到数据与操作解耦,利于扩展。如果注册请求过多,导致注册异常,也有数据缓冲作用。
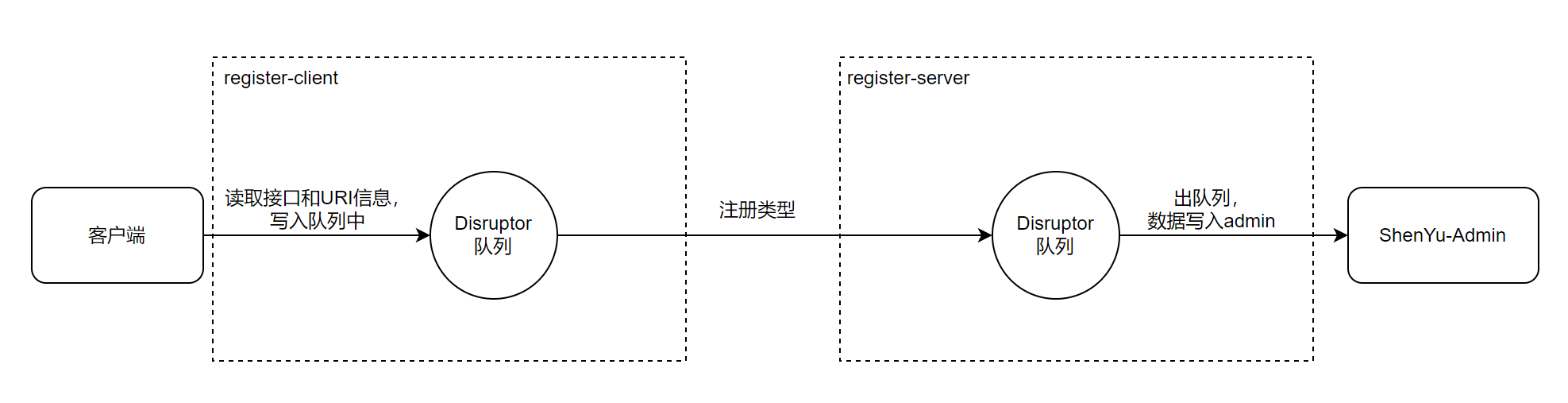
如图所示,注册中心分为两个部分,一是注册中心客户端register-client,负责处理客户端数据读取。另一个是注册中心服务端register-server,负责处理服务端(就是shenyu-admin)数据写入。通过指定注册类型进行数据发送和接收。
- 客户端:通常来说就是一个微服务,可以是
springmvc,spring-cloud,dubbo,grpc等。 register-client:注册中心客户端,读取客户接口和uri信息。Disruptor:数据与操作解耦,数据缓冲作用。register-server:注册中心服务端,这里就是shenyu-admin,接收数据,写入数据库,发数据同步事件。- 注册类型:指定注册类型,完成数据注册,当前支持
Http、Zookeeper、Etcd、Consul和Nacos。
本文分析的是使用Http的方式进行注册,所以具体的处理流程如下:
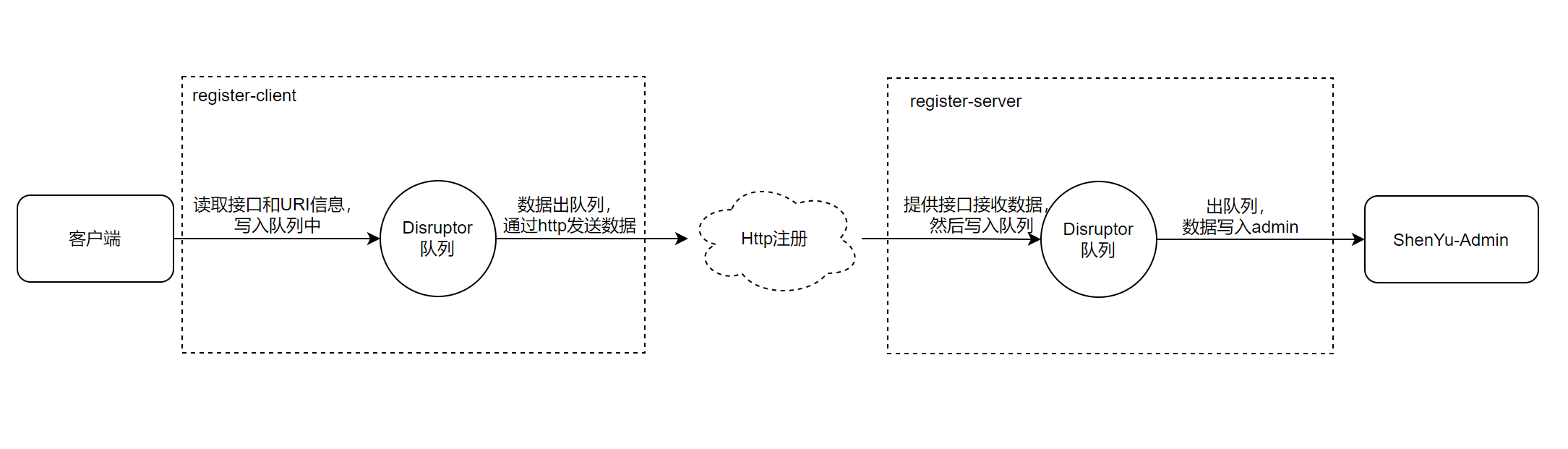
在客户端,数据出队列后,通过http传输数据,在服务端,提供相应的接口,接收数据,然后写入队列。
2. 客户端注册流程
当客户端启动后,根据相关配置,读取属性信息,然后写入队列。以官方提供的 shenyu-examples-http 为例,开始源码分析。官方提供的例子是一个由springboot构建的微服务。注册中心的相关配置可以参考官网 客户端接入配置 。
2.1 加载配置,读取属性
先用一张图串联下注册中心客户端初始化流程:
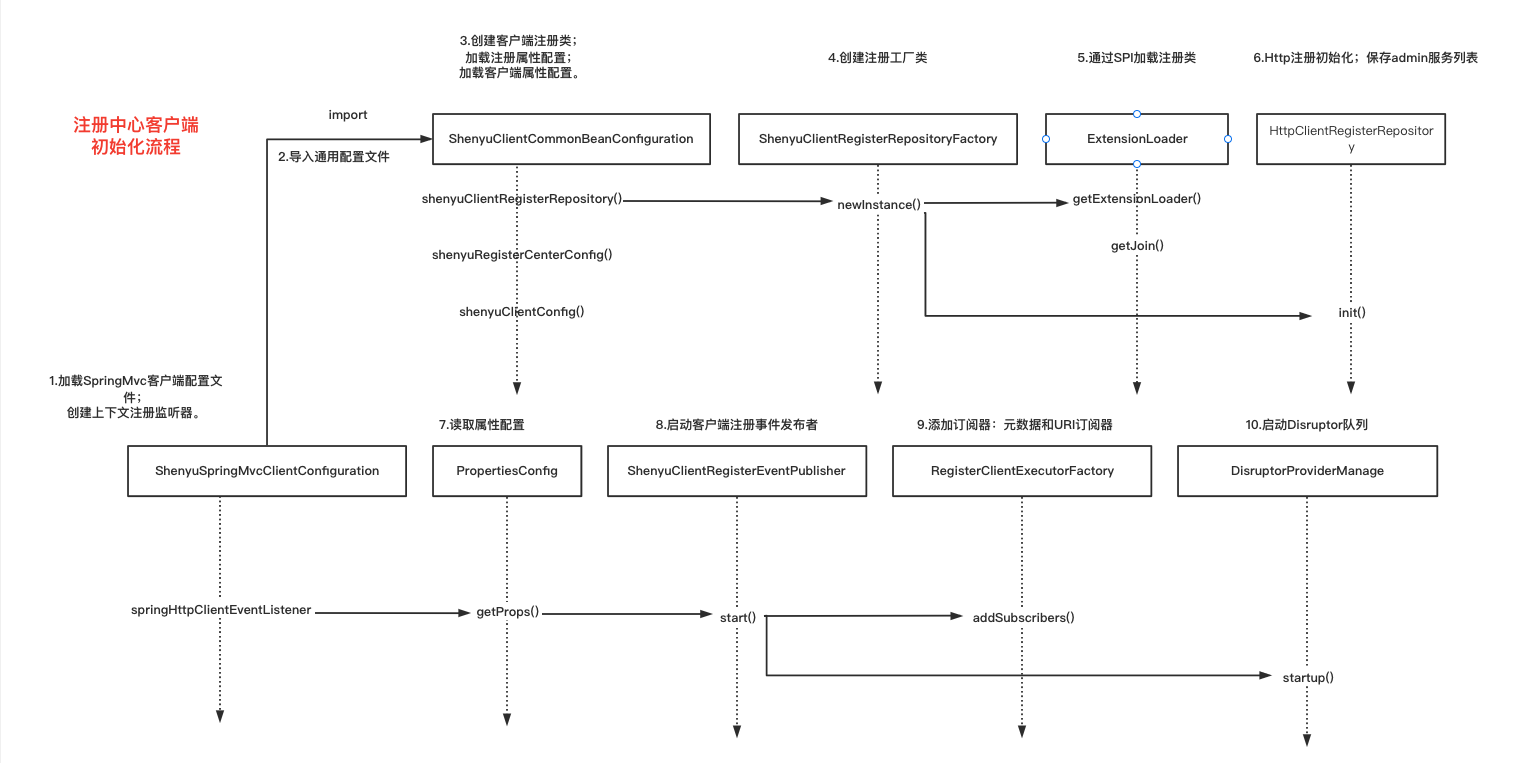
我们分析的是通过http的方式进行注册,所以需要进行如下配置:
shenyu:
register:
registerType: http
serverLists: http://localhost:9095
props:
username: admin
password: 123456
client:
http:
props:
contextPath: /http
appName: http
port: 8189
isFull: false
每个属性表示的含义如下:
registerType: 服务注册类型,填写http。serverList: 为http注册类型时,��填写Shenyu-Admin项目的地址,注意加上http://,多个地址用英文逗号分隔。username:Shenyu-Admin用户名password:Shenyu-Admin用户对应的密码port: 你本项目的启动端口,目前springmvc/tars/grpc需要进行填写。contextPath: 为你的这个mvc项目在shenyu网关的路由前缀, 比如/order,/product等等,网关会根据你的这个前缀来进行路由。appName:你的应用名称,不配置的话,会默认取spring.application.name的值。isFull: 设置true代表代理你的整个服务,false表示代理你其中某几个controller;目前适用于springmvc/springcloud。
项目启动后,会先加载配置文件,读取属性信息,生成相应的Bean。
首先读取到的配置文件是 ShenyuSpringMvcClientConfiguration,它是shenyu 客户端http注册配置类,通过@Configuration表示这是一个配置类,通过@ImportAutoConfiguration引入其他配置类。创建SpringMvcClientEventListener,主要处理元数据和 URI 信息。
/**
* shenyu 客户端http注册配置类
*/
@Configuration
@ImportAutoConfiguration(ShenyuClientCommonBeanConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "shenyu.register.enabled", matchIfMissing = true, havingValue = "true")
public class ShenyuSpringMvcClientConfiguration {
// 创建SpringMvcClientEventListener,主要处理元数据和URI信息
@Bean
public SpringMvcClientEventListener springHttpClientEventListener(final ShenyuClientConfig clientConfig,
final ShenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository) {
return new SpringMvcClientEventListener(clientConfig.getClient().get(RpcTypeEnum.HTTP.getName()), shenyuClientRegisterRepository);
}
}
ShenyuClientCommonBeanConfiguration是shenyu客户端通用配置类,会创建注册中心客户端通用的bean。
- 创建
ShenyuClientRegisterRepository,通过工厂类创建而成。 - 创建
ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig,读取shenyu.register属性配置。 - 创建
ShenyuClientConfig,读取shenyu.client属性配置。
/**
* shenyu客户端通用配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class ShenyuClientCommonBeanConfiguration {
// 创建ShenyuClientRegisterRepository,通过工厂类创建而成。
@Bean
public ShenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository(final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig config) {
return ShenyuClientRegisterRepositoryFactory.newInstance(config);
}
// 创建ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig,读取shenyu.register属性配置
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shenyu.register")
public ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig shenyuRegisterCenterConfig() {
return new ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig();
}
// 创建ShenyuClientConfig,读取shenyu.client属性配置
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shenyu")
public ShenyuClientConfig shenyuClientConfig() {
return new ShenyuClientConfig();
}
}
2.2 用于注册的 HttpClientRegisterRepository
上面的配置文件中生成的ShenyuClientRegisterRepository是客户端注册的具体实现,它是一个接口,它的实现类如下。
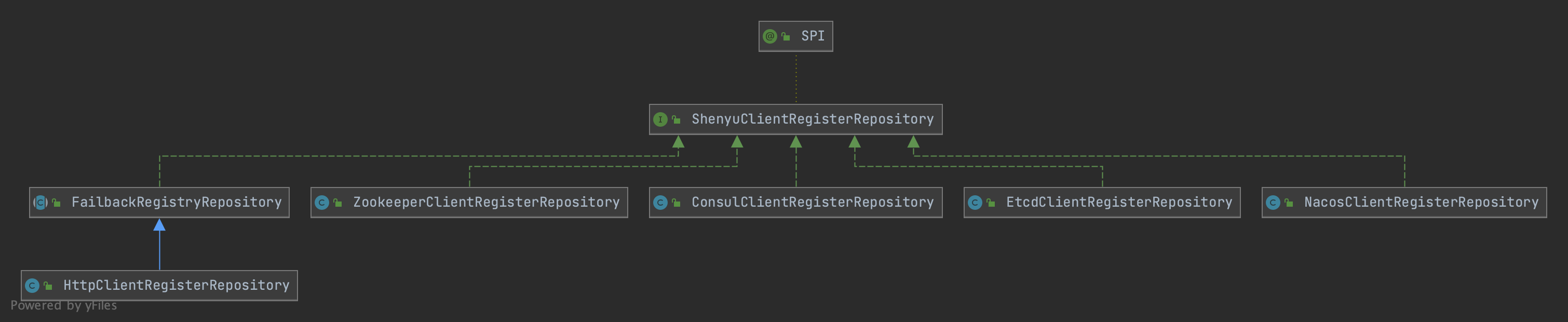
HttpClientRegisterRepository:通过http进行注册;ConsulClientRegisterRepository:通过Consul进行注册;EtcdClientRegisterRepository:通过Etcd进行注册;NacosClientRegisterRepository:通过nacos进行注册;ZookeeperClientRegisterRepository通过Zookeeper进行注册。
具体是哪一种方式,是通过SPI进行加载实现的,实现逻辑如下:
/**
* 加载 ShenyuClientRegisterRepository
*/
public final class ShenyuClientRegisterRepositoryFactory {
private static final Map<String, ShenyuClientRegisterRepository> REPOSITORY_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 创建 ShenyuClientRegisterRepository
*/
public static ShenyuClientRegisterRepository newInstance(final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig shenyuRegisterCenterConfig) {
if (!REPOSITORY_MAP.containsKey(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType())) {
// 通过SPI的方式进行加载,类型由registerType决定
ShenyuClientRegisterRepository result = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ShenyuClientRegisterRepository.class).getJoin(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType());
//执行初始化操作
result.init(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig);
ShenyuClientShutdownHook.set(result, shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getProps());
REPOSITORY_MAP.put(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType(), result);
return result;
}
return REPOSITORY_MAP.get(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType());
}
}
加载类型通过registerType指定,也就是我们在配置文件中指定的类型:
shenyu:
register:
registerType: http
serverLists: http://localhost:9095
我们指定的是http,所以会去加载HttpClientRegisterRepository。对象创建成功后,执行的初始化方法init()如下:
@Join
public class HttpClientRegisterRepository implements ShenyuClientRegisterRepository {
@Override
public void init(final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig config) {
this.username = config.getProps().getProperty(Constants.USER_NAME);
this.password = config.getProps().getProperty(Constants.PASS_WORD);
this.serverList = Lists.newArrayList(Splitter.on(",").split(config.getServerLists()));
this.setAccessToken();
}
// 暂时省略其他逻辑
}
读取配置文件中的username、password和serverLists,即sheenyu-admin的访问账号、密码和地址信息,为后续数据发送做准备。类注解@Join用于SPI的加载。
SPI全称为Service Provider Interface, 是JDK内置的一种服务提供发现功能, 一种动态替换发现的机制。shenyu-spi 是
Apache ShenYu网关自定义的SPI扩展实现,设计和实现原理参考了Dubbo的 SPI扩展实现 。
2.3 构建 元数据 和 URI信息 的 SpringMvcClientEventListener
创建 SpringMvcClientEventListener,负责客户端 元数据 和 URI 数据的构建和注册,它的创建是在配置文件中完成。
@Configuration
@ImportAutoConfiguration(ShenyuClientCommonBeanConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "shenyu.register.enabled", matchIfMissing = true, havingValue = "true")
public class ShenyuSpringMvcClientConfiguration {
// ......
// 创建 SpringMvcClientEventListener
@Bean
public SpringMvcClientEventListener springHttpClientEventListener(final ShenyuClientConfig clientConfig,
final ShenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository) {
return new SpringMvcClientEventListener(clientConfig.getClient().get(RpcTypeEnum.HTTP.getName()), shenyuClientRegisterRepository);
}
}
SpringMvcClientEventListener继承了AbstractContextRefreshedEventListener
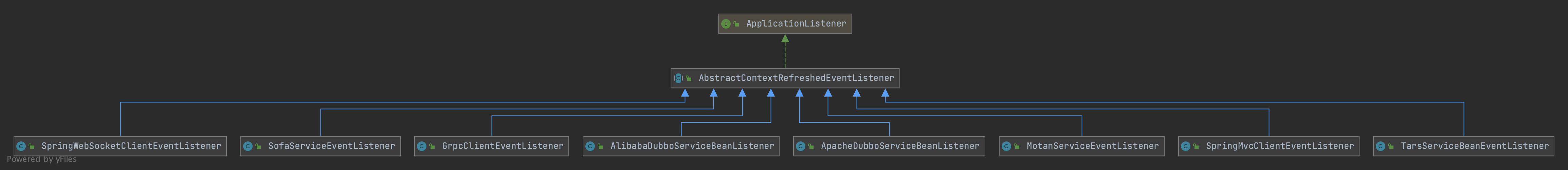
AbstractContextRefreshedEventListener是一个抽象类,它实现了ApplicationListener接口,并重写了onApplicationEvent()方法,当有Spring事件发生后,该方法会执行。它的实现目前有八种,每一种表示对应的RPC调用协议的 元数据 和URI 信息的注册。
AlibabaDubboServiceBeanListener:处理使用Alibaba Dubbo协议;ApacheDubboServiceBeanListener:处理使用Apacge Dubbo协议;GrpcClientEventListener:处理使用grpc协议;MotanServiceEventListener:处理使用Mortan协议;SofaServiceEventListener:处理使用Sofa协议;SpringMvcClientEventListener:处理使用http协议;SpringWebSocketClientEventListener:处理使用websocket协议;TarsServiceBeanEventListener:处理使用Tars注册类型;
// 实现了ApplicationListener接口
public abstract class AbstractContextRefreshedEventListener<T, A extends Annotation> implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
//......
//构造函数
public AbstractContextRefreshedEventListener(final PropertiesConfig clientConfig,
final ShenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository) {
// 读取 shenyu.client.http 配置信息
Properties props = clientConfig.getProps();
// appName 应用名称
this.appName = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.APP_NAME);
// contextPath上下文路径
this.contextPath = Optional.ofNullable(props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.CONTEXT_PATH)).map(UriUtils::repairData).orElse("");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(appName) && StringUtils.isBlank(contextPath)) {
String errorMsg = "client register param must config the appName or contextPath";
LOG.error(errorMsg);
throw new ShenyuClientIllegalArgumentException(errorMsg);
}
this.ipAndPort = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.IP_PORT);
// host信息
this.host = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.HOST);
// port 客户端端口信息
this.port = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.PORT);
// 开始事件发布
publisher.start(shenyuClientRegisterRepository);
}
// 当有上下文刷新事件ContextRefreshedEvent发生时,该方法会执行
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(@NonNull final ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
//保证该方法的内容只执行一次
if (!registered.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return;
}
final ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
// 获取声明RPC调用的类
Map<String, T> beans = getBeans(context);
if (MapUtils.isEmpty(beans)) {
return;
}
// 构建URI数据并注册
publisher.publishEvent(buildURIRegisterDTO(context, beans));
// 构建元数据并注册
beans.forEach(this::handle);
}
// 交给不同的子类实现
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected abstract URIRegisterDTO buildURIRegisterDTO(ApplicationContext context,
Map<String, T> beans);
protected void handle(final String beanName, final T bean) {
Class<?> clazz = getCorrectedClass(bean);
// 获取当前bean的对应shenyu客户端的注解(对应不同的RPC调用注解不一样,像http的就是@ShenyuSpringMvcClient,而像SpringCloud的则是@ShenyuSpringCloudClient)
final A beanShenyuClient = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(clazz, getAnnotationType());
// 根据bean获取对应的path(不同子类实现不一样)
final String superPath = buildApiSuperPath(clazz, beanShenyuClient);
// 如果包含Shenyu客户端注解或者path中包括'*',表示注册整个类的接口
if (Objects.nonNull(beanShenyuClient) && superPath.contains("*")) {
// 构建类的元数据,发送注册事件
handleClass(clazz, bean, beanShenyuClient, superPath);
return;
}
// 获取当前bean的所有方法
final Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(clazz);
// 遍历方法
for (Method method : methods) {
// 注册符合条件的方法
handleMethod(bean, clazz, beanShenyuClient, method, superPath);
}
}
// 构建类元数据并注册的默认实现
protected void handleClass(final Class<?> clazz,
final T bean,
@NonNull final A beanShenyuClient,
final String superPath) {
publisher.publishEvent(buildMetaDataDTO(bean, beanShenyuClient, pathJoin(contextPath, superPath), clazz, null));
}
// 构建方法元数据并注册的默认实现
protected void handleMethod(final T bean,
final Class<?> clazz,
@Nullable final A beanShenyuClient,
final Method method,
final String superPath) {
// 如果方法上有Shenyu客户端注解,就表示该方法需要注册
A methodShenyuClient = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, getAnnotationType());
if (Objects.nonNull(methodShenyuClient)) {
// 构建元数据,发送注册事件
publisher.publishEvent(buildMetaDataDTO(bean, methodShenyuClient, buildApiPath(method, superPath, methodShenyuClient), clazz, method));
}
}
// 交给不同子类实现
protected abstract MetaDataRegisterDTO buildMetaDataDTO(T bean,
@NonNull A shenyuClient,
String path,
Class<?> clazz,
Method method);
}
在构造函数中主要是读取属性配置。
shenyu:
client:
http:
props:
contextPath: /http
appName: http
port: 8189
isFull: false
最后,执行了publisher.start(),开始事件发布,为注册做准备。
- ShenyuClientRegisterEventPublisher
ShenyuClientRegisterEventPublisher通过单例模式实现,主要是生成元数据和URI订阅器(后续用于数据发布),然后启动Disruptor队列。提供了一个共有方法publishEvent(),发布事件,向Disruptor队列发数据。
public class ShenyuClientRegisterEventPublisher {
// 私有变量
private static final ShenyuClientRegisterEventPublisher INSTANCE = new ShenyuClientRegisterEventPublisher();
private DisruptorProviderManage<DataTypeParent> providerManage;
/**
* 公开静态方法
*
* @return ShenyuClientRegisterEventPublisher instance
*/
public static ShenyuClientRegisterEventPublisher getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
/**
* Start方法执行
*
* @param shenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository
*/
public void start(final ShenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository) {
// 创建客户端注册工厂类
RegisterClientExecutorFactory factory = new RegisterClientExecutorFactory();
// 添加元数据订阅器
factory.addSubscribers(new ShenyuClientMetadataExecutorSubscriber(shenyuClientRegisterRepository));
// 添加URI订阅器
factory.addSubscribers(new ShenyuClientURIExecutorSubscriber(shenyuClientRegisterRepository));
// 启动Disruptor队列
providerManage = new DisruptorProviderManage(factory);
providerManage.startup();
}
/**
* 发布事件,向Disruptor队列发数据
*
* @param data the data
*/
public <T> void publishEvent(final DataTypeParent data) {
DisruptorProvider<DataTypeParent> provider = providerManage.getProvider();
provider.onData(data);
}
}
AbstractContextRefreshedEventListener的构造函数逻辑分析完成了,主要是读取属性配置,创建元数据和URI订阅器,启动Disruptor队列。
onApplicationEvent()方法是有Spring事件发生时会执行,这里的参数是ContextRefreshedEvent,表示上下文刷新事件。当Spring容器就绪后执行此处逻辑:先构建URI数据并注册,再构建元数据并注册,
ContextRefreshedEvent是Spring内置事件。ApplicationContext被初始化或刷新时,该事件被触发。这也可以在ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中使用refresh()方法来发生。此处的初始化是指:所有的Bean被成功装载,后处理Bean被检测并激活,所有Singleton Bean被预实例化,ApplicationContext容器已就绪可用。
再来看AbstractContextRefreshedEventListener的http实现SpringMvcClientEventListener。
public class SpringMvcClientEventListener extends AbstractContextRefreshedEventListener<Object, ShenyuSpringMvcClient> {
private final List<Class<? extends Annotation>> mappingAnnotation = new ArrayList<>(3);
private final Boolean isFull;
private final String protocol;
// 构造函数
public SpringMvcClientEventListener(final PropertiesConfig clientConfig,
final ShenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository) {
super(clientConfig, shenyuClientRegisterRepository);
Properties props = clientConfig.getProps();
// 获取 isFull
this.isFull = Boolean.parseBoolean(props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.IS_FULL, Boolean.FALSE.toString()));
// 表示是http协议的实现
this.protocol = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.PROTOCOL, ShenyuClientConstants.HTTP);
mappingAnnotation.add(ShenyuSpringMvcClient.class);
mappingAnnotation.add(RequestMapping.class);
}
@Override
protected Map<String, Object> getBeans(final ApplicationContext context) {
// 配置属性,如果 isFull=true 的话,表示注册整个微服务
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(isFull)) {
getPublisher().publishEvent(MetaDataRegisterDTO.builder()
.contextPath(getContextPath())
.appName(getAppName())
.path(PathUtils.decoratorPathWithSlash(getContextPath()))
.rpcType(RpcTypeEnum.HTTP.getName())
.enabled(true)
.ruleName(getContextPath())
.build());
return null;
}
// 否则获取带Controller注解的bean
return context.getBeansWithAnnotation(Controller.class);
}
// 构造URI数据
@Override
protected URIRegisterDTO buildURIRegisterDTO(final ApplicationContext context,
final Map<String, Object> beans) {
// ...
}
@Override
protected String buildApiSuperPath(final Class<?> clazz, @Nullable final ShenyuSpringMvcClient beanShenyuClient) {
// 如果有带上Shenyu客户端注解,则优先取注解中的不为空的path属性
if (Objects.nonNull(beanShenyuClient) && StringUtils.isNotBlank(beanShenyuClient.path())) {
return beanShenyuClient.path();
}
// 如果有带上RequestMapping注解,且path属性不为空,则返回path数组的第一个值
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(clazz, RequestMapping.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(requestMapping) && ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(requestMapping.path()) && StringUtils.isNotBlank(requestMapping.path()[0])) {
return requestMapping.path()[0];
}
return "";
}
// 声明http实现的客户端注解是ShenyuSpringMvcClient
@Override
protected Class<ShenyuSpringMvcClient> getAnnotationType() {
return ShenyuSpringMvcClient.class;
}
@Override
protected void handleMethod(final Object bean, final Class<?> clazz,
@Nullable final ShenyuSpringMvcClient beanShenyuClient,
final Method method, final String superPath) {
// 获取当前bean的RequestMapping注解
final RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
// 获取当前bean的 ShenyuSpringMvcClient 注解
ShenyuSpringMvcClient methodShenyuClient = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, ShenyuSpringMvcClient.class);
methodShenyuClient = Objects.isNull(methodShenyuClient) ? beanShenyuClient : methodShenyuClient;
//如果有 ShenyuSpringMvcClient 注解并且包含RequestMapping注解(表示是一个接口),则进行注册
if (Objects.nonNull(methodShenyuClient) && Objects.nonNull(requestMapping)) {
getPublisher().publishEvent(buildMetaDataDTO(bean, methodShenyuClient, buildApiPath(method, superPath, methodShenyuClient), clazz, method));
}
}
//...
// 构造元数据
@Override
protected MetaDataRegisterDTO buildMetaDataDTO(final Object bean,
@NonNull final ShenyuSpringMvcClient shenyuClient,
final String path, final Class<?> clazz,
final Method method) {
//...
}
}
注册逻辑都是通过 publisher.publishEvent()完成。
Controller注解和RequestMapping注解是由Spring提供的,这个大家应该很熟悉,不过多赘述。ShenyuSpringMvcClient 注解是由Apache ShenYu提供的,用于注册SpringMvc客户端,它的定义如下:
/**
* shenyu 客户端接口,用于方法上或类上
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface ShenyuSpringMvcClient {
// path 注册路径
@AliasFor(attribute = "path")
String value() default "";
// path 注册路径
@AliasFor(attribute = "value")
String path();
// ruleName 规则名称
String ruleName() default "";
// desc 描述信息
String desc() default "";
// enabled是否启用
boolean enabled() default true;
// registerMetaData 注册元数据
boolean registerMetaData() default false;
}
它的使用如下:
- 注册整个接口
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
@ShenyuSpringMvcClient(path = "/test/**") // 表示整个接口注册
public class HttpTestController {
//......
}
- 注册当前方法
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/order")
@ShenyuSpringMvcClient(path = "/order")
public class OrderController {
/**
* Save order dto.
*
* @param orderDTO the order dto
* @return the order dto
*/
@PostMapping("/save")
@ShenyuSpringMvcClient(path = "/save", desc = "Save order") // 注册当前方法
public OrderDTO save(@RequestBody final OrderDTO orderDTO) {
orderDTO.setName("hello world save order");
return orderDTO;
}
}
- publisher.publishEvent() 发布注册事件
该方法会将数据发送到Disruptor队列中,关于Disruptor队列更多细节这里不做更多介绍,这不影响分析注册的流程。
当数据发送后,Disruptor队列的消费者会处理数据,进行消费。
- QueueConsumer 消费数据
QueueConsumer是一个消费者,它实现了WorkHandler接口,它��的创建过程在providerManage.startup()逻辑中。WorkHandler接口是disruptor的数据消费接口,只有一个方法是onEvent()。
package com.lmax.disruptor;
public interface WorkHandler<T> {
void onEvent(T event) throws Exception;
}
QueueConsumer重写了onEvent()方法,主要逻辑是生成消费任务,然后在线程池中去执行。
/**
*
* 队列消费者
*/
public class QueueConsumer<T> implements WorkHandler<DataEvent<T>> {
// 省略了其他逻辑
@Override
public void onEvent(final DataEvent<T> t) {
if (t != null) {
// 根据事件类型使用不同的线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = orderly(t);
// 通过工厂创建队列消费任务
QueueConsumerExecutor<T> queueConsumerExecutor = factory.create();
// 保存数据
queueConsumerExecutor.setData(t.getData());
// help gc
t.setData(null);
// 放在线程池中执行 消费任务
executor.execute(queueConsumerExecutor);
}
}
}
QueueConsumerExecutor是在线程池中被执行的任务,它实现了Runnable接口,具体的实现类有两个:
RegisterClientConsumerExecutor:客户端消费者执行器;RegisterServerConsumerExecutor:服务端消费者执行器。
顾名思义,一个负责处理客户端任务,一个负责处理服务端任务(服务端就是admin,在下文进行分析)。
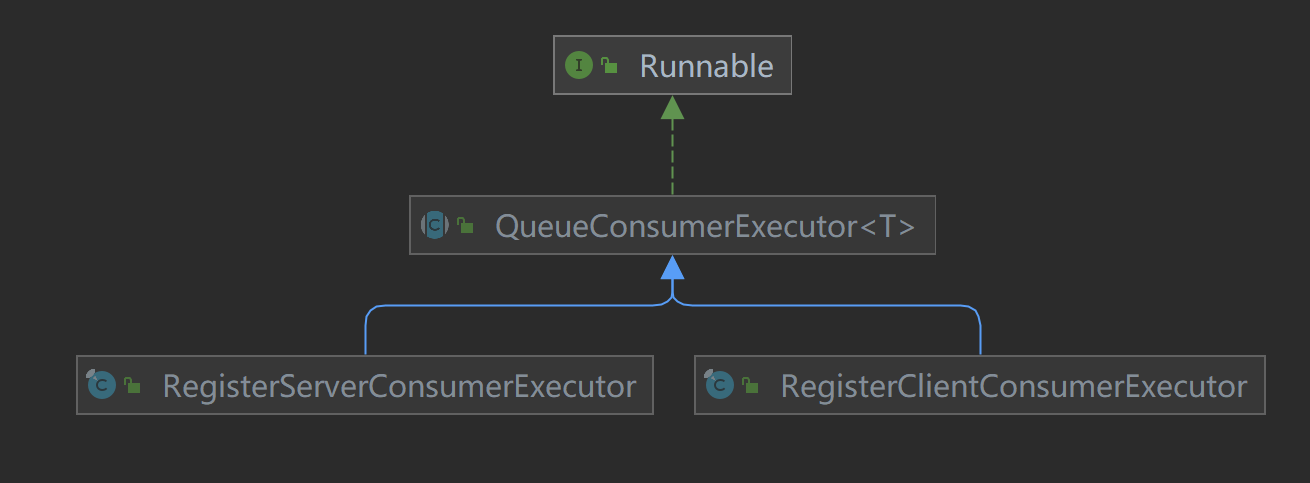
- RegisterClientConsumerExecutor 消费者执行器
重写的run()逻辑如下:
public final class RegisterClientConsumerExecutor<T extends DataTypeParent> extends QueueConsumerExecutor<T> {
//......
@Override
public void run() {
// 获取数据
final T data = getData();
// 根据数据类型调用相应的处理器进行处理
subscribers.get(data.getType()).executor(Lists.newArrayList(data));
}
}
根据不同的数据类型调用不同的处理器去执行相应的任务。数据类型有两种,一个是元数据,记录客户端注册信息。一个是URI数据,记录客户端服务信息。
//数据类型
public enum DataType {
// 元数据
META_DATA,
// URI数据
URI,
}
- ExecutorSubscriber#executor() 执行器订阅者
执行器订阅者也分为两类,一个是处理元数据,一个是处理URI。在客户端和服务端分别有两个,所以一共是四个。
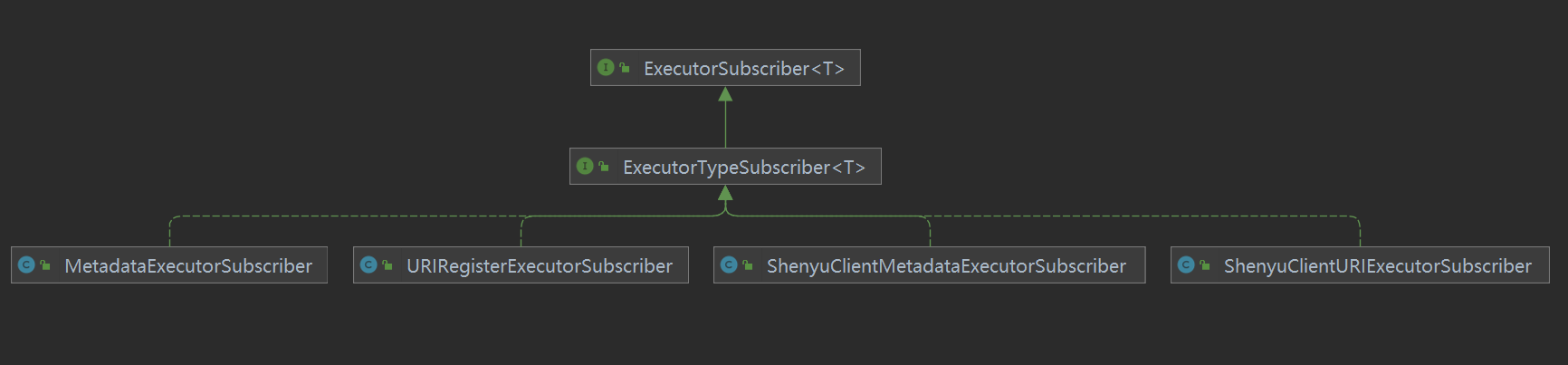
先看元数据处理
- ShenyuClientMetadataExecutorSubscriber#executor()
客户端这边对元数据处理逻辑是:遍历元数据信息,调用接口方法persistInterface()完成数据的发布。
public class ShenyuClientMetadataExecutorSubscriber implements ExecutorTypeSubscriber<MetaDataRegisterDTO> {
//......
@Override
public DataType getType() {
return DataType.META_DATA; // 元数据
}
@Override
public void executor(final Collection<MetaDataRegisterDTO> metaDataRegisterDTOList) {
for (MetaDataRegisterDTO metaDataRegisterDTO : metaDataRegisterDTOList) {
// 调用接口方法persistInterface()完成数据的发布
shenyuClientRegisterRepository.persistInterface(metaDataRegisterDTO);
}
}
}
- ShenyuClientRegisterRepository#persistInterface()
ShenyuClientRegisterRepository是一个接口,用于表示客户端数据注册,它的实现类目前有五种,每一种就表示一种注册方法。
ConsulClientRegisterRepository:通过Consul实现客户端注册;EtcdClientRegisterRepository:通过Etcd实现客户端注册;HttpClientRegisterRepository:通过Http实现客户端注册;NacosClientRegisterRepository:通过Nacos实现客户端注册;ZookeeperClientRegisterRepository:通过Zookeeper实现客户端注册;
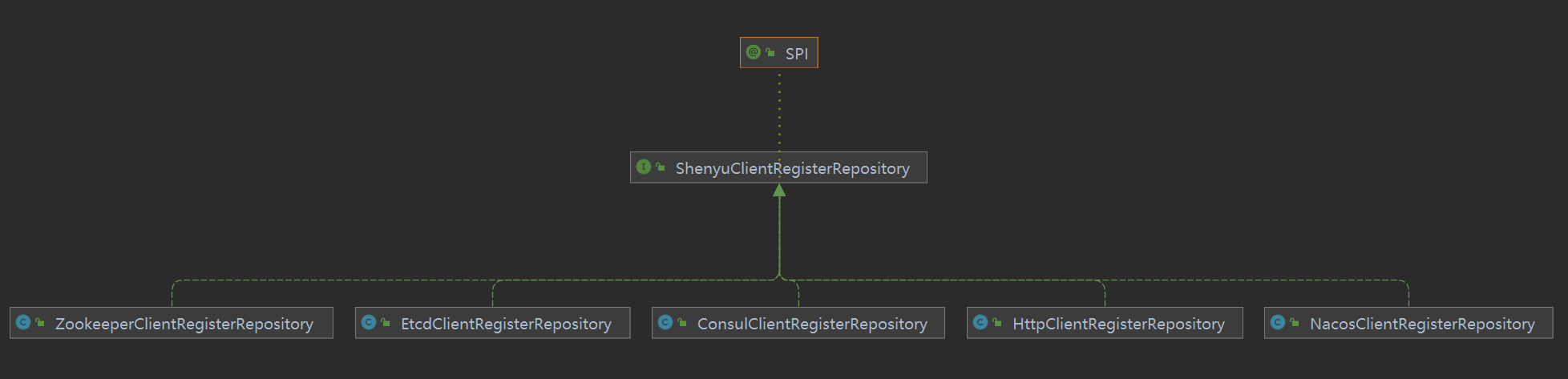
从图中可以看出,注册中心的加载是通过SPI的方式完成的。这个在前面提到过了,在客户端通用配置文件中,通过指定配置文件中的属性完成具体的类加载。
/**
* 加载 ShenyuClientRegisterRepository
*/
public final class ShenyuClientRegisterRepositoryFactory {
private static final Map<String, ShenyuClientRegisterRepository> REPOSITORY_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 创建 ShenyuClientRegisterRepository
*/
public static ShenyuClientRegisterRepository newInstance(final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig shenyuRegisterCenterConfig) {
if (!REPOSITORY_MAP.containsKey(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType())) {
// 通过SPI的方式进行加载,类型由registerType决定
ShenyuClientRegisterRepository result = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ShenyuClientRegisterRepository.class).getJoin(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType());
//执行初始化操作
result.init(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig);
ShenyuClientShutdownHook.set(result, shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getProps());
REPOSITORY_MAP.put(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType(), result);
return result;
}
return REPOSITORY_MAP.get(shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType());
}
}
本文的源码分析是基于Http的方式进行注册,所以我们先分析HttpClientRegisterRepository,其他的注册方式后续再分析。HttpClientRegisterRepository继承了FailbackRegistryRepository,而FailbackRegistryRepository本身主要用于对Http注册过程中的失败异常的处理,这里就省略了。
通过http的方式注册很简单,就是调用工具类发送http请求。注册元数据和URI都是调用的同一个方法doRegister(),指定接口和类型就好。
Constants.URI_PATH的值/shenyu-client/register-metadata:服务端提供的接口用于注册元数据。Constants.META_PATH的值/shenyu-client/register-uri: 服务端提供的接口用于注册URI。
@Join
public class HttpClientRegisterRepository extends FailbackRegistryRepository {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpClientRegisterRepository.class);
private static URIRegisterDTO uriRegisterDTO;
private String username;
private String password;
private List<String> serverList;
private String accessToken;
public HttpClientRegisterRepository() {
}
public HttpClientRegisterRepository(final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig config) {
init(config);
}
@Override
public void init(final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig config) {
// admin的用户名
this.username = config.getProps().getProperty(Constants.USER_NAME);
// admin的用户名对应的密码
this.password = config.getProps().getProperty(Constants.PASS_WORD);
// admin服务列表
this.serverList = Lists.newArrayList(Splitter.on(",").split(config.getServerLists()));
// 设置访问的token
this.setAccessToken();
}
/**
* Persist uri.
*
* @param registerDTO the register dto
*/
@Override
public void doPersistURI(final URIRegisterDTO registerDTO) {
if (RuntimeUtils.listenByOther(registerDTO.getPort())) {
return;
}
doRegister(registerDTO, Constants.URI_PATH, Constants.URI);
uriRegisterDTO = registerDTO;
}
@Override
public void doPersistInterface(final MetaDataRegisterDTO metadata) {
doRegister(metadata, Constants.META_PATH, Constants.META_TYPE);
}
@Override
public void close() {
if (uriRegisterDTO != null) {
uriRegisterDTO.setEventType(EventType.DELETED);
doRegister(uriRegisterDTO, Constants.URI_PATH, Constants.URI);
}
}
private void setAccessToken() {
for (String server : serverList) {
try {
Optional<?> login = RegisterUtils.doLogin(username, password, server.concat(Constants.LOGIN_PATH));
login.ifPresent(v -> this.accessToken = String.valueOf(v));
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Login admin url :{} is fail, will retry. cause: {} ", server, e.getMessage());
}
}
}
private <T> void doRegister(final T t, final String path, final String type) {
int i = 0;
// 遍历admin服务列表(admin可能是集群)
for (String server : serverList) {
i++;
String concat = server.concat(path);
try {
// 设置访问token
if (StringUtils.isBlank(accessToken)) {
this.setAccessToken();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(accessToken)) {
throw new NullPointerException("accessToken is null");
}
}
// 调用工具类发送 http 请求
RegisterUtils.doRegister(GsonUtils.getInstance().toJson(t), concat, type, accessToken);
return;
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Register admin url :{} is fail, will retry. cause:{}", server, e.getMessage());
if (i == serverList.size()) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
将数据序列化后,通过OkHttp发送数据。
public final class RegisterUtils {
//......
// 通过OkHttp发送数据
public static void doRegister(final String json, final String url, final String type) throws IOException {
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(accessToken)) {
LOGGER.error("{} client register error accessToken is null, please check the config : {} ", type, json);
return;
}
Headers headers = new Headers.Builder().add(Constants.X_ACCESS_TOKEN, accessToken).build();
String result = OkHttpTools.getInstance().post(url, json, headers);
if (Objects.equals(SUCCESS, result)) {
LOGGER.info("{} client register success: {} ", type, json);
} else {
LOGGER.error("{} client register error: {} ", type, json);
}
}
}
至此,客户端通过http的方式注册元数据的逻辑就分析完了。小结一下:通过读取自定义的注解信息构造元数据,将数据发到Disruptor队列,然后从队列中消费数据,将消费者放到线程池中去执行,最终通过发送http请求到admin。
再来看看 URI 数据的处理
- ShenyuClientURIExecutorSubscriber#executor()
主要逻辑是遍历URI数据集合,通过persistURI()方法实现数据注册。
public class ShenyuClientURIExecutorSubscriber implements ExecutorTypeSubscriber<URIRegisterDTO> {
//......
@Override
public DataType getType() {
return DataType.URI; //数据类型是URI
}
// 注册URI数据
@Override
public void executor(final Collection<URIRegisterDTO> dataList) {
for (URIRegisterDTO uriRegisterDTO : dataList) {
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted();
while (true) {
try (Socket ignored = new Socket(uriRegisterDTO.getHost(), uriRegisterDTO.getPort())) {
break;
} catch (IOException e) {
long sleepTime = 1000;
// maybe the port is delay exposed
if (stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) > 5) {
LOG.error("host:{}, port:{} connection failed, will retry",
uriRegisterDTO.getHost(), uriRegisterDTO.getPort());
// If the connection fails for a long time, Increase sleep time
if (stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.SECONDS) > 180) {
sleepTime = 10000;
}
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(sleepTime);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//添加hook,优雅停止客户端
ShenyuClientShutdownHook.delayOtherHooks();
// 注册URI
shenyuClientRegisterRepository.persistURI(uriRegisterDTO);
}
}
}
代码中的while(true)循环是为了保证客户端已经成功启动了,通过host和port可以连接上。
后面的逻辑是:添加hook函数,用于优雅停止客户端 。
通过persistURI()方法实现数据注册。整个逻辑也在前面分析过了,最终就是通过OkHttp客户端向shenyu-admin发起http,通过http的方式注册URI。
分析到这里就将客户端的注册逻辑分析完了,将构建的元数据和URI数据发送到Disruptor队列,再从中消费,读取数据,通过http向admin发送数据。
客户端元数据和URI注册流程的源码分析完成了,流程图如下:
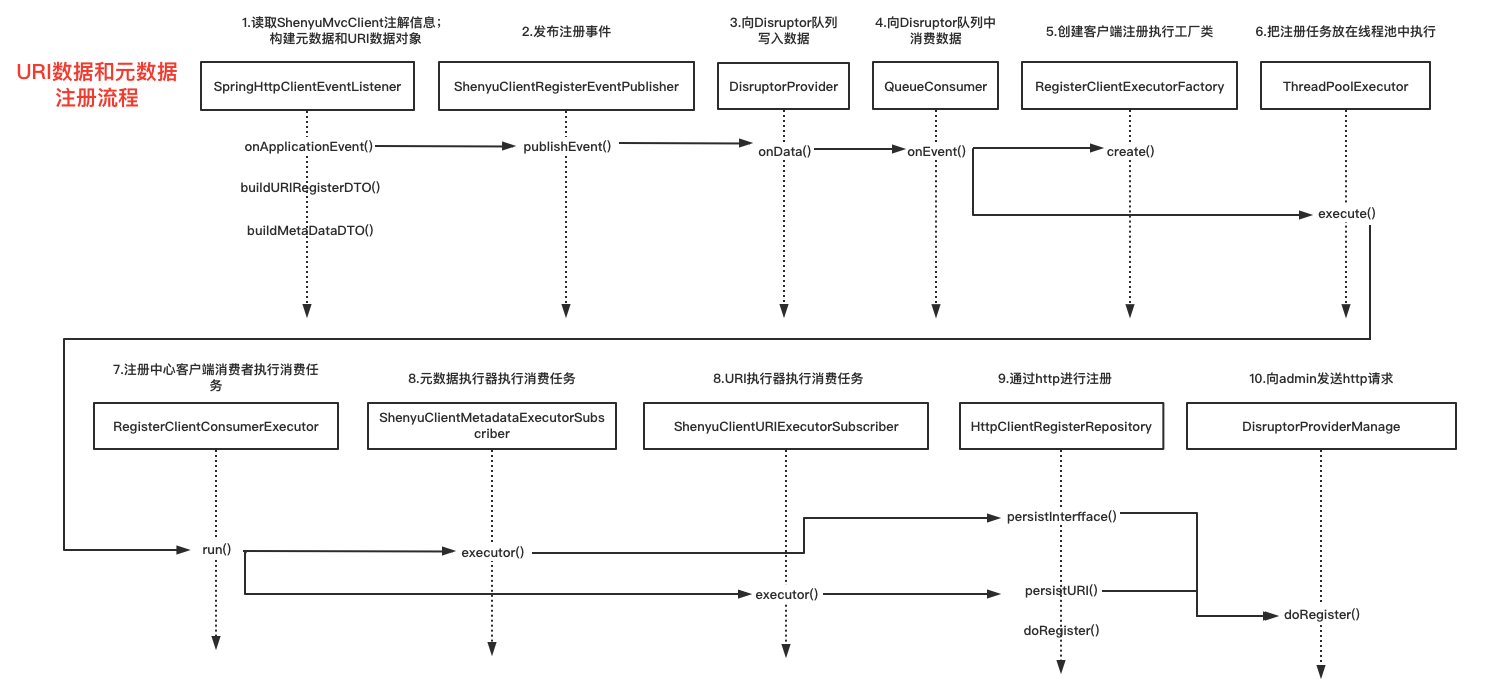
3. 服务端注册流程
3.1 注册接口ShenyuClientHttpRegistryController
从前面的分析可以知道,服务端提供了注册的两个接口:
/shenyu-client/register-metadata:服务端提供的接口用于注册元数据。/shenyu-client/register-uri: 服务端提供的接口用于注册URI。
这两个接口位于ShenyuClientHttpRegistryController中,它实现了ShenyuClientServerRegisterRepository接口,是服务端注册的实现类。它用@Join标记,表示通过SPI进行加载。
// shenuyu客户端接口
@RequestMapping("/shenyu-client")
@Join
public class ShenyuClientHttpRegistryController implements ShenyuClientServerRegisterRepository {
private ShenyuClientServerRegisterPublisher publisher;
@Override
public void init(final ShenyuClientServerRegisterPublisher publisher, final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig config) {
this.publisher = publisher;
}
@Override
public void close() {
publisher.close();
}
// 注册元数据
@PostMapping("/register-metadata")
@ResponseBody
public String registerMetadata(@RequestBody final MetaDataRegisterDTO metaDataRegisterDTO) {
publisher.publish(metaDataRegisterDTO);
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
// 注册URI
@PostMapping("/register-uri")
@ResponseBody
public String registerURI(@RequestBody final URIRegisterDTO uriRegisterDTO) {
publisher.publish(uriRegisterDTO);
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
}
两个注册接口获取到数据好,就调用了publisher.publish()方法,把数据发布到Disruptor队列中。
ShenyuClientServerRegisterRepository接口
ShenyuClientServerRegisterRepository接口是服务注册接口,它有五个实现类,表示有五种注册方式:
ConsulClientServerRegisterRepository:通过Consul实现注册;EtcdClientServerRegisterRepository:通过Etcd实现注册;NacosClientServerRegisterRepository:通过Nacos实现注册;ShenyuClientHttpRegistryController:通过Http实现注册;ZookeeperClientServerRegisterRepository:通过Zookeeper实现注册。
具体用哪一种方式,是通过配置文件指定的,然后通过SPI进行加载。
在shenyu-admin中的application.yml文件中配置注册方式,registerType指定注册类型,当用http进行注册时,serverLists不需要填写,更多配置说明可以参考官网 客户端接入配置 。
shenyu:
register:
registerType: http
serverLists:
- RegisterCenterConfiguration 加载配置
在引入相关依赖和属性配置后,启动shenyu-admin时,会先加载配置文件,和注册中心相关的配置文件类是RegisterCenterConfiguration。
// 注册中心配置类
@Configuration
public class RegisterCenterConfiguration {
// 读取配置属性
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shenyu.register")
public ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig shenyuRegisterCenterConfig() {
return new ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig();
}
//创建ShenyuServerRegisterRepository,用于服务端注册
@Bean(destroyMethod = "close")
public ShenyuServerRegisterRepository shenyuServerRegisterRepository(final ShenyuRegisterCenterConfig shenyuRegisterCenterConfig, final List<ShenyuClientRegisterService> shenyuClientRegisterService) {
// 1.从配置属性中获取注册类型
String registerType = shenyuRegisterCenterConfig.getRegisterType();
// 2.通过注册类型,以SPI的方法加载实现类
ShenyuClientServerRegisterRepository registerRepository = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ShenyuClientServerRegisterRepository.class).getJoin(registerType);
// 3.获取publisher,向Disruptor队列中写数据
RegisterClientServerDisruptorPublisher publisher = RegisterClientServerDisruptorPublisher.getInstance();
// 4.注册Service, rpcType -> registerService
Map<String, ShenyuClientRegisterService> registerServiceMap = shenyuClientRegisterService.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(ShenyuClientRegisterService::rpcType, e -> e));
// 5.事件发布的准备工作
publisher.start(registerServiceMap);
// 6.注册的初始化操作
registerRepository.init(publisher, shenyuRegisterCenterConfig);
return registerRepository;
}
}
在配置类中生成了两个bean:
-
shenyuRegisterCenterConfig:读取属性配置; -
shenyuClientServerRegisterRepository:用于服务端注册。
在创建shenyuClientServerRegisterRepository的过程中,也进行了一系列的准备工作:
-
1.从配置属性中获取注册类型。
-
2.通过注册类型,以
SPI的方法加载实现类:比如指定的类型是http,就会加载ShenyuClientHttpRegistryController。 -
3.获取
publisher,向Disruptor队列中写数据。 -
4.注册
Service,rpcType -> registerService:获取注册的Service,每种rpc都有对应的Service。本文的客户端构建是通过springboot,属于http类型,还有其他客户端类型:dubbo,Spring Cloud,gRPC等。 -
5.事件发布的准备工作:添加服务端元数据和
URI订阅器,处理数据。并且启动Disruptor队列。 -
6.注册的初始化操作:
http类型的注册初始化操作就是保存publisher。 -
RegisterServerDisruptorPublisher#publish()
服务端向Disruptor队列写入数据的发布者 ,通过单例模式构建。
public class RegisterClientServerDisruptorPublisher implements ShenyuClientServerRegisterPublisher {
//私有属性
private static final RegisterClientServerDisruptorPublisher INSTANCE = new RegisterClientServerDisruptorPublisher();
private DisruptorProviderManage<Collection<DataTypeParent>> providerManage;
//公开静态方法获取实例
public static RegisterServerDisruptorPublisher getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
//事件发布的准备工作,添加服务端元数据和URI订阅器,处理数据。并且启动Disruptor队列。
public void start(final Map<String, ShenyuClientRegisterService> shenyuClientRegisterService) {
//服务端注册工厂
RegisterServerExecutorFactory factory = new RegisterServerExecutorFactory();
//添加URI数据订阅器
factory.addSubscribers(new URIRegisterExecutorSubscriber(shenyuClientRegisterService));
//添加元数据订阅器
factory.addSubscribers(new MetadataExecutorSubscriber(shenyuClientRegisterService));
//启动Disruptor队列
providerManage = new DisruptorProviderManage(factory);
providerManage.startup();
}
// 向队列中写入数据
@Override
public void publish(final DataTypeParent data) {
DisruptorProvider<Collection<DataTypeParent>> provider = providerManage.getProvider();
provider.onData(Collections.singleton(data));
}
// 批量向队列中写入数据
@Override
public void publish(final Collection<? extends DataTypeParent> dataList) {
DisruptorProvider<Collection<DataTypeParent>> provider = providerManage.getProvider();
provider.onData(dataList.stream().map(DataTypeParent.class::cast).collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Override
public void close() {
providerManage.getProvider().shutdown();
}
}
配置文件的加载,可看作是注册中心服务端初始化流程,用图描述如下:
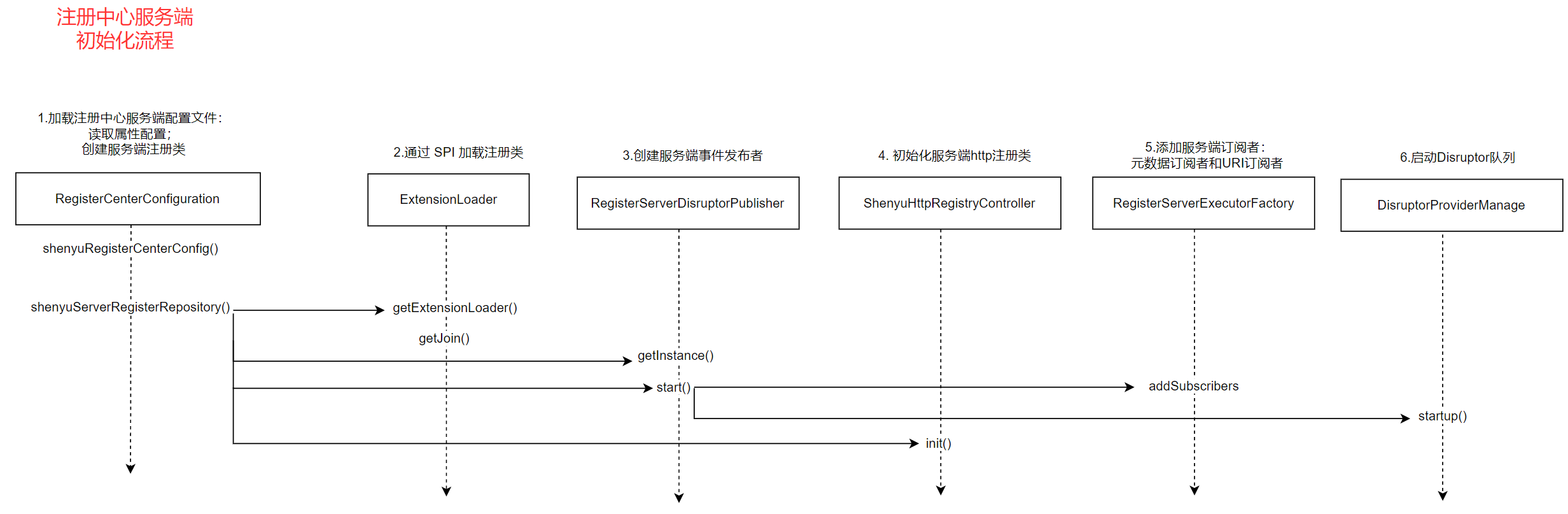
3.2 消费数据QueueConsumer
在前面分析了客户端disruptor队列消费数据的过。服务端也是一样的逻辑,只是其中执行任务的执行者变了。
QueueConsumer是一个消费者,它实现了WorkHandler接口,它的创建过程在providerManage.startup()逻辑中。WorkHandler接口是disruptor的数据消费接口,只有一个方法是onEvent()。
package com.lmax.disruptor;
public interface WorkHandler<T> {
void onEvent(T event) throws Exception;
}
QueueConsumer重写了onEvent()方法,主要逻辑是生成消费任务,然后在线程池中去执行。
/**
*
* 队列消费者
*/
public class QueueConsumer<T> implements WorkHandler<DataEvent<T>> {
// 省略了其他逻辑
@Override
public void onEvent(final DataEvent<T> t) {
if (t != null) {
// 根据事件类型获取相应的线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = orderly(t);
// 通过工厂创建队列消费任务
QueueConsumerExecutor<T> queueConsumerExecutor = factory.create();
// 保存数据
queueConsumerExecutor.setData(t.getData());
// help gc
t.setData(null);
// 放在线程池中执行 消费任务
executor.execute(queueConsumerExecutor);
}
}
}
QueueConsumerExecutor是在线程池中被执行的任务,它实现了Runnable接口,具体的实现类有两个:
RegisterClientConsumerExecutor:客户端消费者执行器;RegisterServerConsumerExecutor:服务端消费者执行器。
顾名思义,一个负责处理客户端任务,一个负责处理服务端任务。
RegisterServerConsumerExecutor#run()
RegisterServerConsumerExecutor是服务端消费者执行器,它通过QueueConsumerExecutor间接实现了Runnable接口,并重写了run()方法。
public final class RegisterServerConsumerExecutor extends QueueConsumerExecutor<Collection<DataTypeParent>> {
// ...
@Override
public void run() {
//获取从disruptor队列中拿到的数据
Collection<DataTypeParent> results = getData()
.stream()
.filter(this::isValidData)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(results)) {
return;
}
//根据类型执行操作
selectExecutor(results).executor(results);
}
// 根据类型获取订阅者
private ExecutorSubscriber<DataTypeParent> selectExecutor(final Collection<DataTypeParent> list) {
final Optional<DataTypeParent> first = list.stream().findFirst();
return subscribers.get(first.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("the data type is not found")).getType());
}
}
- ExecutorSubscriber#executor()
执行器订阅者分为两类,一个是处理元数据,一个是处理URI。在客户端和服务端分别有两个,所以一共是四个。

- MetadataExecutorSubscriber#executor()
如果是注册元数据,则通过MetadataExecutorSubscriber#executor()实现:根据类型获取注册Service,调用register()。
public class MetadataExecutorSubscriber implements ExecutorTypeSubscriber<MetaDataRegisterDTO> {
//......
@Override
public DataType getType() {
return DataType.META_DATA; // 元数据类型
}
@Override
public void executor(final Collection<MetaDataRegisterDTO> metaDataRegisterDTOList) {
// 遍历元数据列表
metaDataRegisterDTOList.forEach(meta -> {
Optional.ofNullable(this.shenyuClientRegisterService.get(meta.getRpcType())) // 根据类型获取注册Service
.ifPresent(shenyuClientRegisterService -> {
// 对元数据进行注册,加锁确保顺序执行,防止并发错误
synchronized (shenyuClientRegisterService) {
shenyuClientRegisterService.register(meta);
}
});
});
}
}
- URIRegisterExecutorSubscriber#executor()
如果是注册元数据,则通过URIRegisterExecutorSubscriber#executor()实现:构建URI数据,根据注册类型查找Service,通过registerURI方法实现注册。
public class URIRegisterExecutorSubscriber implements ExecutorTypeSubscriber<URIRegisterDTO> {
//......
@Override
public DataType getType() {
return DataType.URI; // URI数据类型
}
@Override
public void executor(final Collection<URIRegisterDTO> dataList) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(dataList)) {
return;
}
// 根据rpc调用类型聚集数据
final Map<String, List<URIRegisterDTO>> groupByRpcType = dataList.stream()
.filter(data -> StringUtils.isNotBlank(data.getRpcType()))
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(URIRegisterDTO::getRpcType));
for (Map.Entry<String, List<URIRegisterDTO>> entry : groupByRpcType.entrySet()) {
final String rpcType = entry.getKey();
// 根据类型查找Service
Optional.ofNullable(shenyuClientRegisterService.get(rpcType))
.ifPresent(service -> {
final List<URIRegisterDTO> list = entry.getValue();
// 构建URI数据类型,通过registerURI方法实现注册
Map<String, List<URIRegisterDTO>> listMap = buildData(list);
listMap.forEach(service::registerURI);
});
}
}
}
- ShenyuClientRegisterService#register()
ShenyuClientRegisterService是注册方法接口,它有多个实现类:
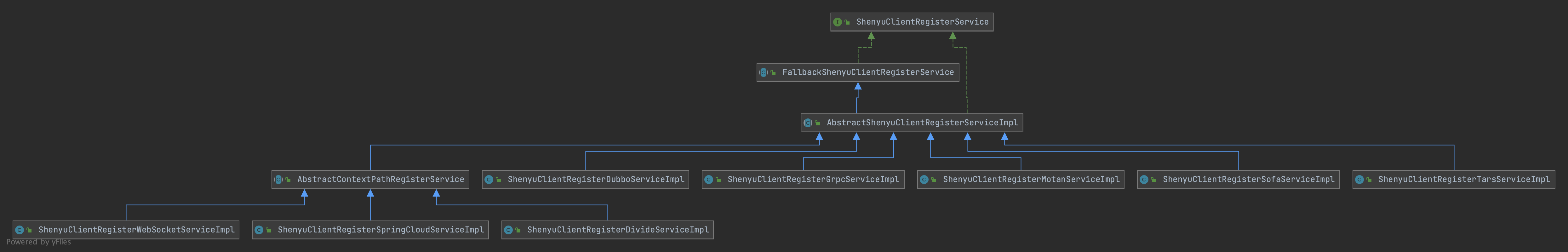
AbstractContextPathRegisterService:抽象类,处理部分公共逻辑;AbstractShenyuClientRegisterServiceImpl::抽象类,处理部分公共逻辑;ShenyuClientRegisterDivideServiceImpl:divide类,处理http注册类型;ShenyuClientRegisterDubboServiceImpl:dubbo类,处理dubbo注册类型;ShenyuClientRegisterGrpcServiceImpl:gRPC类,处理gRPC注册类型;ShenyuClientRegisterMotanServiceImpl:Motan类,处理Motan注册类型;ShenyuClientRegisterSofaServiceImpl:Sofa类,处理Sofa注册类型;ShenyuClientRegisterSpringCloudServiceImpl:SpringCloud类,处理SpringCloud注册类型;ShenyuClientRegisterTarsServiceImpl:Tars类,处理Tars注册类型;ShenyuClientRegisterWebSocketServiceImpl:Websocket类,处理Websocket注册类型;
从上面可以看出每种微服务都有对应的注册实现类,本文的源码分析是 以官方提供的 shenyu-examples-http 为例,是属http注册类型,所以元数据和URI数据的注册实现类是 ShenyuClientRegisterDivideServiceImpl:
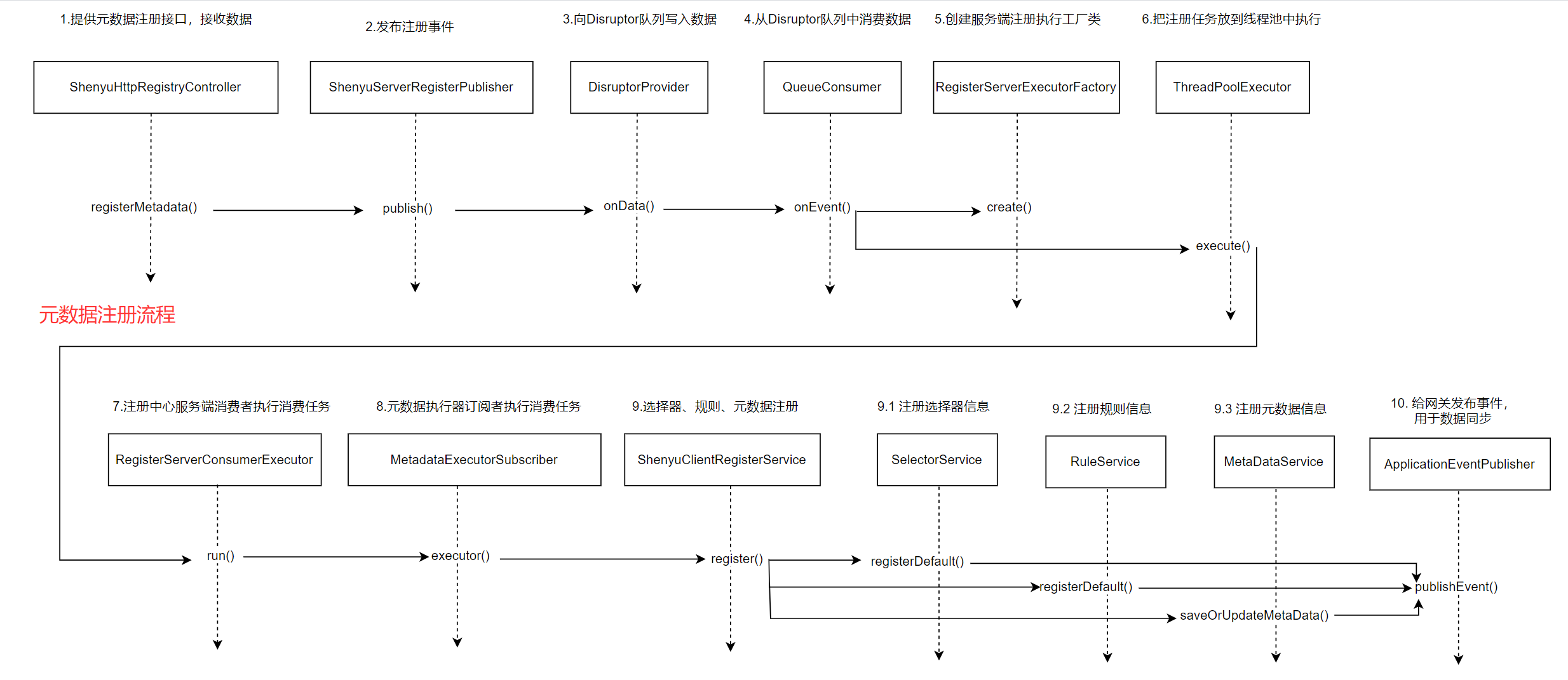
- register(): 注册元数据
public abstract class AbstractShenyuClientRegisterServiceImpl extends FallbackShenyuClientRegisterService implements ShenyuClientRegisterService {
//......
public String register(final MetaDataRegisterDTO dto) {
// 1.注册选择器信息
String selectorHandler = selectorHandler(dto);
String selectorId = selectorService.registerDefault(dto, PluginNameAdapter.rpcTypeAdapter(rpcType()), selectorHandler);
// 2.注册规则信息
String ruleHandler = ruleHandler();
RuleDTO ruleDTO = buildRpcDefaultRuleDTO(selectorId, dto, ruleHandler);
ruleService.registerDefault(ruleDTO);
// 3.注册元数据信息
registerMetadata(dto);
// 4.注册contextPath
String contextPath = dto.getContextPath();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(contextPath)) {
registerContextPath(dto);
}
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
}
整个注册逻辑可以分为4个步骤:
- 1.注册选择器信息
- 2.注册规则信息
- 3.注册元数据信息
- 4.注册
contextPath
在admin这一侧通过客户端的元数据信息需要构建选择器、规则、元数据和ContextPath。具体的注册过程和细节处理跟rpc类型有关。我们就不再继续向下追踪了,对于注册中心的逻辑分析,跟踪到这里就够了。
服务端元数据注册流程的源码分析完了,流程图描述如下:
- registerURI(): 注册
URI数据
public abstract class AbstractShenyuClientRegisterServiceImpl extends FallbackShenyuClientRegisterService implements ShenyuClientRegisterService {
//......
public String doRegisterURI(final String selectorName, final List<URIRegisterDTO> uriList) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(uriList)) {
return "";
}
// 对应的选择器是否存在
SelectorDO selectorDO = selectorService.findByNameAndPluginName(selectorName, PluginNameAdapter.rpcTypeAdapter(rpcType()));
if (Objects.isNull(selectorDO)) {
throw new ShenyuException("doRegister Failed to execute,wait to retry.");
}
List<URIRegisterDTO> validUriList = uriList.stream().filter(dto -> Objects.nonNull(dto.getPort()) && StringUtils.isNotBlank(dto.getHost())).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 处理选择器中的handler信息
String handler = buildHandle(validUriList, selectorDO);
if (handler != null) {
selectorDO.setHandle(handler);
SelectorData selectorData = selectorService.buildByName(selectorName, PluginNameAdapter.rpcTypeAdapter(rpcType()));
selectorData.setHandle(handler);
// 更新数据库中的记录
selectorService.updateSelective(selectorDO);
// 发布事件
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DataChangedEvent(ConfigGroupEnum.SELECTOR, DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE, Collections.singletonList(selectorData)));
}
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
}
admin拿到URI数据后,主要是更新选择器中的handler信息,然后写入到数据库,最后发布事件通知网关。通知网关的逻辑是由数据同步操作完成,这在之前的文章中已经分析过了,就不再赘述。
服务端URI注册流程的源码分析完成了,用图描述如下:
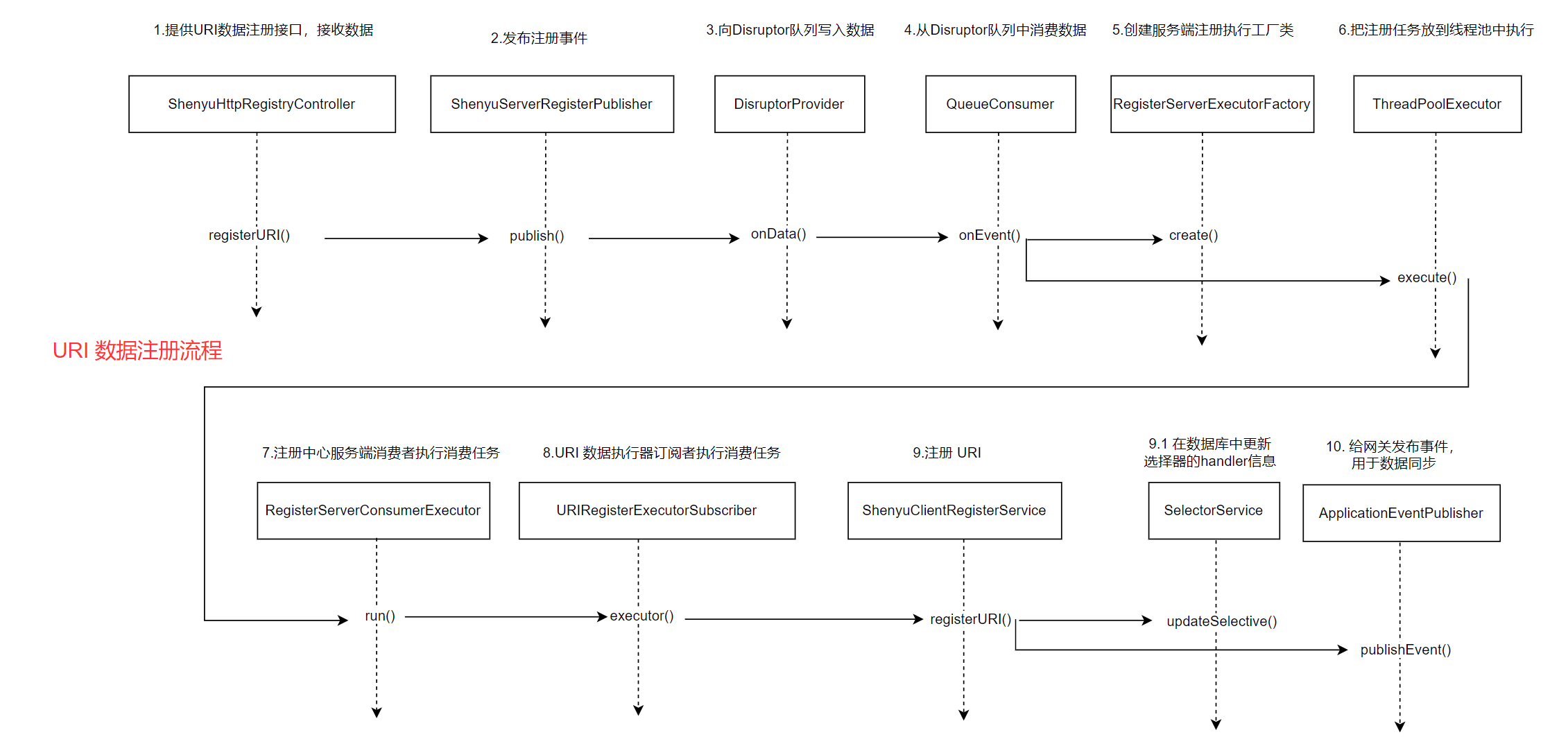
至此,服务端注册流程也就分析完了,主要通过对外提供的接口,接受客户端的注册信息,然后写入到Disruptor队列,再从中消费数据,根据接收到的元数据和URI数据更新admin的选择器、规则、元数据和选择器的handler。
4. 总结
本文主要对Apache ShenYu网关中的http注册模块进行了源码分析。涉及到的主要知识点,归纳如下:
- 注册中心是为了将客户端信息注册到
admin,方便流量筛选; http注册是将客户端元数据信息和URI信息注册到admin;http服务的接入通过注解@ShenyuSpringMvcClient标识;- 注册信息的构建主要通过
Spring应用监听器ApplicationListener; - 注册类型的加载通过
SPI完成; - 引入
Disruptor队列是为了数据与操作解耦,以及数据缓冲。 - 注册中心的实现采用了面向接口编程,使用模板方法、单例、观察者等设计模式。