Http长轮询数据同步源码分析
Apache ShenYu 是一个异步的,高性能的,跨语言的,响应式的
API网关。
在ShenYu网关中,数据同步是指,当在后台管理系统中,数据发送了更新后,如何将更新的数据同步到网关中。Apache ShenYu 网关当前支持ZooKeeper、WebSocket、Http长轮询、Nacos 、Etcd 和 Consul 进行数据同步。本文的主要内容是基于Http长轮询的数据同步源码分析。
本文基于
shenyu-2.5.0版本进行源码分析,官网的介绍请参考 数据同步原理 。
1. Http长轮询
这里直接引用官网的相关描述:
Zookeeper和WebSocket数据同步的机制比较简单,而Http长轮询则比较复杂。Apache ShenYu借鉴了Apollo、Nacos的设计思想,取其精华,自己实现了Http长轮询数据同步功能。注意,这里并非传统的ajax长轮询!
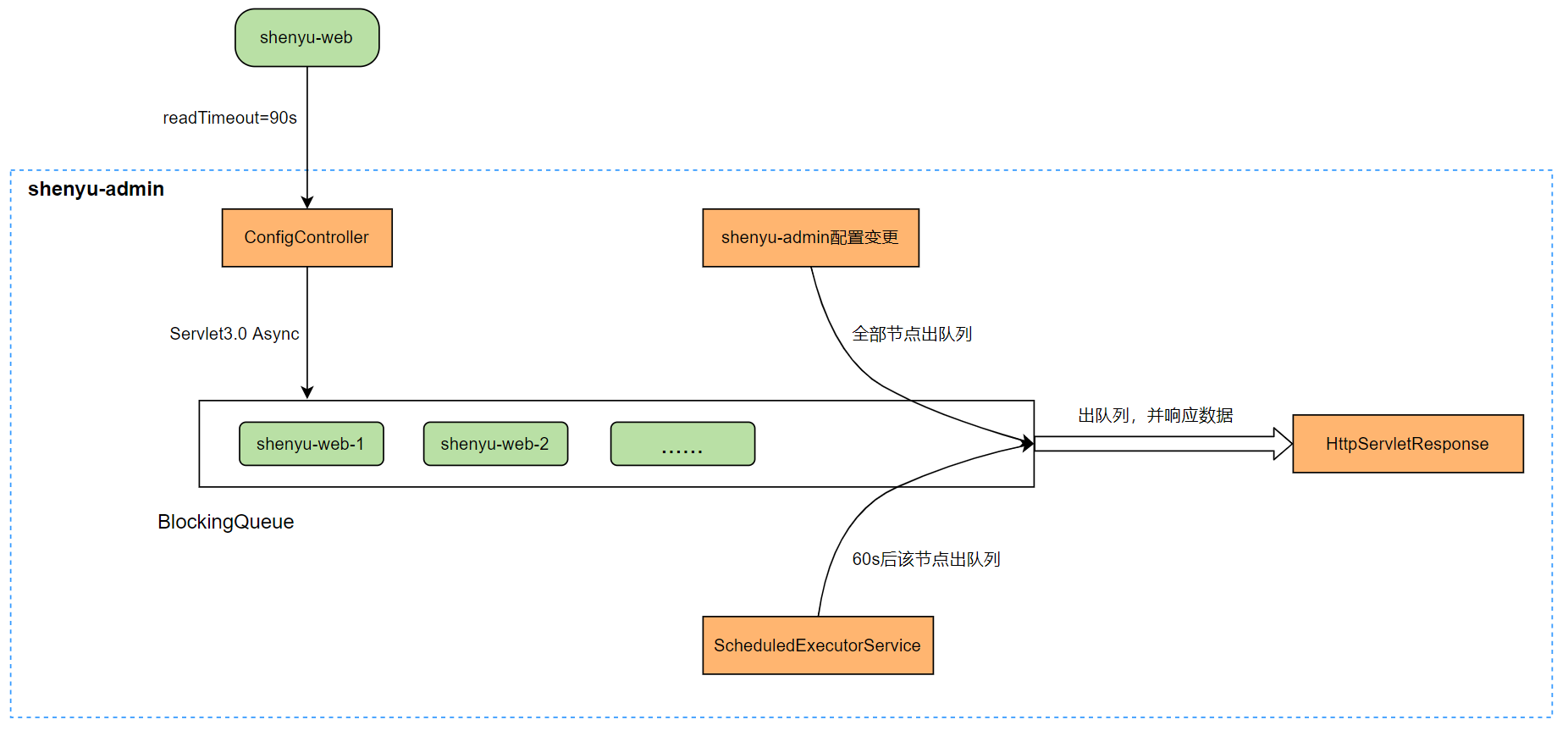
Http长轮询 机制如上所示,Apache ShenYu网关主动请求 shenyu-admin 的配置服务,读取超时时间为 90s,意味着网关层请求配置服务最多会等待 90s,这样便于 shenyu-admin 配置服务及时响应变更数据,从而实现准实时推送。
Http长轮询 机制是由网关主动请求 shenyu-admin ,所以这次的源码分析,我们从网关这一侧开始。
2. 网关数据同步
2.1 加载配置
Http长轮询 数据同步配置的加载是通过spring boot的starter机制,当我们引入相关依赖和在配置文件中有如下配置时,就会加载。
在pom文件中引入依赖:
<!--shenyu data sync start use http-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shenyu</groupId>
<artifactId>shenyu-spring-boot-starter-sync-data-http</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
在application.yml配置文件中添加配置:
shenyu:
sync:
http:
url : http://localhost:9095
当网关启动时,配置类HttpSyncDataConfiguration就会执行,加载相应的Bean。
/**
* Http sync data configuration for spring boot.
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(HttpSyncDataService.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "shenyu.sync.http", name = "url")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = HttpConfig.class)
public class HttpSyncDataConfiguration {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpSyncDataConfiguration.class);
/**
* Rest template.
* 创建RestTemplate
* @param httpConfig the http config http配置
* @return the rest template
*/
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(final HttpConfig httpConfig) {
OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory();
factory.setConnectTimeout(Objects.isNull(httpConfig.getConnectionTimeout()) ? (int) HttpConstants.CLIENT_POLLING_CONNECT_TIMEOUT : httpConfig.getConnectionTimeout());
factory.setReadTimeout(Objects.isNull(httpConfig.getReadTimeout()) ? (int) HttpConstants.CLIENT_POLLING_READ_TIMEOUT : httpConfig.getReadTimeout());
factory.setWriteTimeout(Objects.isNull(httpConfig.getWriteTimeout()) ? (int) HttpConstants.CLIENT_POLLING_WRITE_TIMEOUT : httpConfig.getWriteTimeout());
return new RestTemplate(factory);
}
/**
* AccessTokenManager.
* 创建AccessTokenManager,专门用户对admin进行http请求时access token的处理
* @param httpConfig the http config.
* @param restTemplate the rest template.
* @return the access token manager.
*/
@Bean
public AccessTokenManager accessTokenManager(final HttpConfig httpConfig, final RestTemplate restTemplate) {
return new AccessTokenManager(restTemplate, httpConfig);
}
/**
* Http sync data service.
* 创建 HttpSyncDataService
* @param httpConfig the http config
* @param pluginSubscriber the plugin subscriber
* @param restTemplate the rest template
* @param metaSubscribers the meta subscribers
* @param authSubscribers the auth subscribers
* @param accessTokenManager the access token manager
* @return the sync data service
*/
@Bean
public SyncDataService httpSyncDataService(final ObjectProvider<HttpConfig> httpConfig,
final ObjectProvider<PluginDataSubscriber> pluginSubscriber,
final ObjectProvider<RestTemplate> restTemplate,
final ObjectProvider<List<MetaDataSubscriber>> metaSubscribers,
final ObjectProvider<List<AuthDataSubscriber>> authSubscribers,
final ObjectProvider<AccessTokenManager> accessTokenManager) {
LOGGER.info("you use http long pull sync shenyu data");
return new HttpSyncDataService(
Objects.requireNonNull(httpConfig.getIfAvailable()),
Objects.requireNonNull(pluginSubscriber.getIfAvailable()),
Objects.requireNonNull(restTemplate.getIfAvailable()),
metaSubscribers.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList),
authSubscribers.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList),
Objects.requireNonNull(accessTokenManager.getIfAvailable())
);
}
}
HttpSyncDataConfiguration是Http长轮询数据同步的配置类,负责创建HttpSyncDataService(负责http数据同步的具体实现)、RestTemplate和AccessTokenManager (负责与adminhttp调用时access token的处理)。它的注解如下:
@Configuration:表示这是一个配置类;@ConditionalOnClass(HttpSyncDataService.class):条件注解,表示要有HttpSyncDataService这个类;@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "shenyu.sync.http", name = "url"):条件注解,要有shenyu.sync.http.url这个属性配置。@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = HttpConfig.class):表示让HttpConfig上的注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shenyu.sync.http")生效,将HttpConfig这个配置类注入Ioc容器中。
2.2 属性初始化
- HttpSyncDataService
在HttpSyncDataService的构造函数中,完成属性初始化。
public class HttpSyncDataService implements SyncDataService {
// 省略了属性字段......
public HttpSyncDataService(final HttpConfig httpConfig,
final PluginDataSubscriber pluginDataSubscriber,
final RestTemplate restTemplate,
final List<MetaDataSubscriber> metaDataSubscribers,
final List<AuthDataSubscriber> authDataSubscribers,
final AccessTokenManager accessTokenManager) {
// 1.设置accessTokenManager
this.accessTokenManager = accessTokenManager;
// 2.创建数据处理器
this.factory = new DataRefreshFactory(pluginDataSubscriber, metaDataSubscribers, authDataSubscribers);
// 3.shenyu-admin的url, 多个用逗号(,)分割
this.serverList = Lists.newArrayList(Splitter.on(",").split(httpConfig.getUrl()));
// 4.只用于http长轮询的restTemplate
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
// 5.开始执行长轮询任务
this.start();
}
//......
}
上面代码中省略了其他函数和相关字段,在构造函数中完成属性的初始化,主要是:
-
设置
accessTokenManager,定时向admin请求更新accessToken的值。然后每次向admin发起请求时都必须将header的X-Access-Token属性设置成accessToken对应的值; -
创建数据处理器,用于后续缓存各种类型的数据(插件、选择器、规则、元数据和认证数据);
-
获取
admin属性配置,主要是获取admin的url,admin有可能是集群,多个用逗号(,)分割; -
设置
RestTemplate,用于向admin发起请求; -
开始执行长轮询任务。
2.3 开始长轮询
- HttpSyncDataService#start()
在start()方法中,干了两件事情,一个是获取全量数据,即请求admin端获取所有需要同步的数据,然后将获取到的数据缓存到网关内存中。另一个是开启多线程执行长轮询任务。
public class HttpSyncDataService implements SyncDataService {
// ......
private void start() {
// // 只初始化一次,通过原子类实现。
if (RUNNING.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 初次启动,获取全量数据
this.fetchGroupConfig(ConfigGroupEnum.values());
// 一个后台服务,一个��线程
int threadSize = serverList.size();
// 自定义线程池
this.executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadSize, threadSize, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),
ShenyuThreadFactory.create("http-long-polling", true));
// 开始长轮询,一个admin服务,创建一个线程用于数据同步
this.serverList.forEach(server -> this.executor.execute(new HttpLongPollingTask(server)));
} else {
LOG.info("shenyu http long polling was started, executor=[{}]", executor);
}
}
// ......
}
2.3.1 获取全量数据
- HttpSyncDataService#fetchGroupConfig()
ShenYu将所有需要同步的数据进行了分组,一共有5种数据类型,分别是插件、选择器、规则、元数据和认证数据。
public enum ConfigGroupEnum {
APP_AUTH, // 认证数据
PLUGIN, //插件
RULE, // 规则
SELECTOR, // 选择器
META_DATA; // 元数据
}
admin有可能是集群,这里通过循环的方式向每个admin发起请求,有一个执行成功了,那么向admin获取全量数据并缓存到网关的操作就执行成功。如果出现了异常,就向下一个admin发起请求。
public class HttpSyncDataService implements SyncDataService {
// ......
private void fetchGroupConfig(final ConfigGroupEnum... groups) throws ShenyuException {
// admin有可能是集群,这里通过循环的方式向每个admin发起请求
for (int index = 0; index < this.serverList.size(); index++) {
String server = serverList.get(index);
try {
// 真正去执行
this.doFetchGroupConfig(server, groups);
// 有一个成功,就成功了,可以退出循环
break;
} catch (ShenyuException e) {
// 出现异常,尝试执行下一个
// 最后一个也执行失败了,抛出异常
if (index >= serverList.size() - 1) {
throw e;
}
LOG.warn("fetch config fail, try another one: {}", serverList.get(index + 1));
}
}
}
// ......
}
- HttpSyncDataService#doFetchGroupConfig()
在此方法中,首先拼装请求参数,然后通过httpClient发起请求,到admin中获取数据,最后将获取到的数据更新到网关内存中。
public class HttpSyncDataService implements SyncDataService {
private void doFetchGroupConfig(final String server, final ConfigGroupEnum... groups) {
// 1. 拼请求参数,所有分组枚举类型
StringBuilder params = new StringBuilder();
for (ConfigGroupEnum groupKey : groups) {
params.append("groupKeys").append("=").append(groupKey.name()).append("&");
}
// admin端提供的接口 /configs/fetch
String url = server + Constants.SHENYU_ADMIN_PATH_CONFIGS_FETCH + "?" + StringUtils.removeEnd(params.toString(), "&");
LOG.info("request configs: [{}]", url);
String json;
try {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
// 设置accessToken
headers.set(Constants.X_ACCESS_TOKEN, this.accessTokenManager.getAccessToken());
HttpEntity<String> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(headers);
// 2. 发起请求,获取变更数据
json = this.restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, httpEntity, String.class).getBody();
} catch (RestClientException e) {
String message = String.format("fetch config fail from server[%s], %s", url, e.getMessage());
LOG.warn(message);
throw new ShenyuException(message, e);
}
// 3. 更新网关内存中数据
boolean updated = this.updateCacheWithJson(json);
if (updated) {
LOG.debug("get latest configs: [{}]", json);
return;
}
// 更新成功,此方法就执行完成了
LOG.info("The config of the server[{}] has not been updated or is out of date. Wait for 30s to listen for changes again.", server);
// 服务端没有数据更新,就等30s
ThreadUtils.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS, 30);
}
}
从代码中,可以看到 admin端�提供的获取全量数据接口是 /configs/fetch,这里先不进一步深入,放在后文再分析。
获取到admin返回结果数据,并成功更新,那么此方法就执行结束了。如果没有更新成功,那么有可能是服务端没有数据更新,就等待30s。
这里需要提前说明一下,网关在判断是否更新成功时,有比对数据的操作,马上就会提到。
- HttpSyncDataService#updateCacheWithJson()
更新网关内存中的数据。使用GSON进行反序列化,从属性data中拿真正的数据,然后交给DataRefreshFactory去做更新。
private boolean updateCacheWithJson(final String json) {
// 使用GSON进行反序列化
JsonObject jsonObject = GSON.fromJson(json, JsonObject.class);
// if the config cache will be updated?
return factory.executor(jsonObject.getAsJsonObject("data"));
}
- DataRefreshFactory#executor()
根据不同数据类型去更新数据,返回更新结果。具体更新逻辑交给了dataRefresh.refresh()方法。在更新结果中,有一种数据类型进行了更新,就表示此次操作发生了更新。
public boolean executor(final JsonObject data) {
//并行更新数据
List<Boolean> result = ENUM_MAP.values().parallelStream()
.map(dataRefresh -> dataRefresh.refresh(data))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//有一个更新就表示此次发生了更新操作
return result.stream().anyMatch(Boolean.TRUE::equals);
}
- AbstractDataRefresh#refresh()
数据更新逻辑采用的是模板方法设计模式,通用操作在抽象方法中完成,不同的实现逻辑由子类完成。5种数据类型具体的更新逻辑有些差异,但是也存在通用的更新逻辑,类图关系如下:
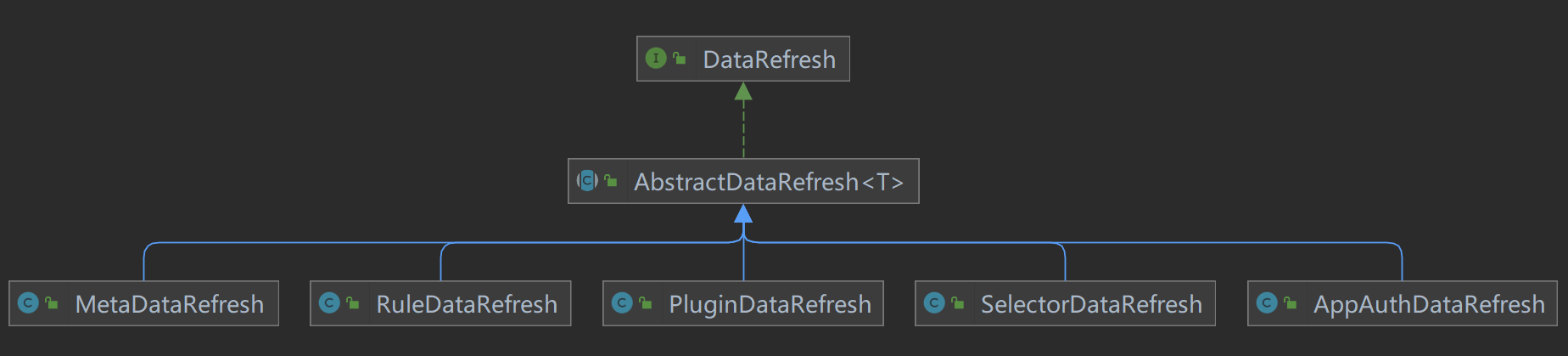
在通用的refresh()方法中,负责数据类型转换,判断是否需要更新,和实际的数据刷新操作。
public abstract class AbstractDataRefresh<T> implements DataRefresh {
// ......
@Override
public Boolean refresh(final JsonObject data) {
// 数据类型转换
JsonObject jsonObject = convert(data);
if (Objects.isNull(jsonObject)) {
return false;
}
boolean updated = false;
// 得到数据类型
ConfigData<T> result = fromJson(jsonObject);
// 是否需要更新
if (this.updateCacheIfNeed(result)) {
updated = true;
// 真正的更新逻辑,数据刷新操作
refresh(result.getData());
}
return updated;
}
// ......
}
- AbstractDataRefresh#updateCacheIfNeed()
数据转换的过程,就是根据不同的数据类型进行转换,我们就不再进一步追踪了,看看数据是否需要更新的逻辑。方法名是updateCacheIfNeed(),通过方法重载实现。
public abstract class AbstractDataRefresh<T> implements DataRefresh {
// ......
// result是数据
protected abstract boolean updateCacheIfNeed(ConfigData<T> result);
// newVal是获取到的最新的值
// groupEnum 是哪种数据类型
protected boolean updateCacheIfNeed(final ConfigData<T> newVal, final ConfigGroupEnum groupEnum) {
// 如果是第一次,那么直接放到cache中,返回 true,表示此次进行了更新
if (GROUP_CACHE.putIfAbsent(groupEnum, newVal) == null) {
return true;
}
ResultHolder holder = new ResultHolder(false);
GROUP_CACHE.merge(groupEnum, newVal, (oldVal, value) -> {
// md5 值相同,不需要更新
if (StringUtils.equals(oldVal.getMd5(), newVal.getMd5())) {
LOG.info("Get the same config, the [{}] config cache will not be updated, md5:{}", groupEnum, oldVal.getMd5());
return oldVal;
}
// 当前缓存的数据修改时间大于 新来的数据,不需要更新
// must compare the last update time
if (oldVal.getLastModifyTime() >= newVal.getLastModifyTime()) {
LOG.info("Last update time earlier than the current configuration, the [{}] config cache will not be updated", groupEnum);
return oldVal;
}
LOG.info("update {} config: {}", groupEnum, newVal);
holder.result = true;
return newVal;
});
return holder.result;
}
// ......
}
从上面的源码中可以看到,有两种情况不需要更新:
- 两个的数据的
md5值相同,不需要更新; - 当前缓存的数据修改时间大于 新来的数据,不需要更新。
其他情况需要更新数据。
分析到这里,就将start() 方法中初次启动,获取全量数据的逻辑分析完了,接下来是长轮询的操作。为了方便,我将start()方法再粘贴一次:
public class HttpSyncDataService implements SyncDataService {
// ......
private void start() {
// // 只初始化一次,通过原子类实现。
if (RUNNING.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 初次启动,获取全量数据
this.fetchGroupConfig(ConfigGroupEnum.values());
// 一个后台服务,一个线程
int threadSize = serverList.size();
// 自定义线程池
this.executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadSize, threadSize, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),
ShenyuThreadFactory.create("http-long-polling", true));
// 开始长轮询,一个admin服务,创建一个线程用于数据同步
this.serverList.forEach(server -> this.executor.execute(new HttpLongPollingTask(server)));
} else {
LOG.info("shenyu http long polling was started, executor=[{}]", executor);
}
}
// ......
}
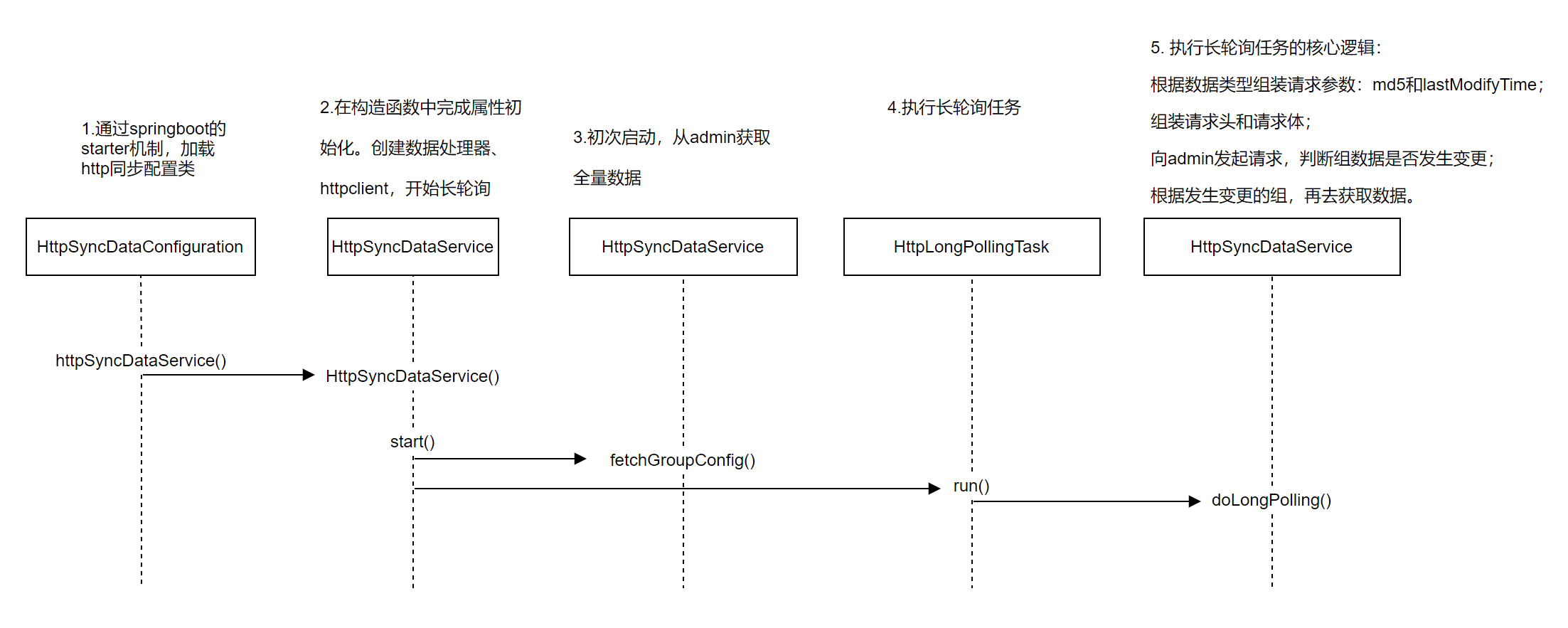
2.3.2 执行长轮询任务
- HttpLongPollingTask#run()
长轮询任务是HttpLongPollingTask,它实现了Runnable接口,任务逻辑在run()方法中。通过while()循环实现不断执行任务,即长轮询。在每一次的轮询中有三次重试逻辑,一次轮询任务失败了,等 5s 再继续,3 次都失败了,等5 分钟再试。
开始长轮询,一个admin服务,创建一个线程用于数据同步。
class HttpLongPollingTask implements Runnable {
private final String server;
HttpLongPollingTask(final String server) {
this.server = server;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 一直轮询
while (RUNNING.get()) {
// 默认重试 3 次
int retryTimes = 3;
for (int time = 1; time <= retryTimes; time++) {
try {
doLongPolling(server);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (time < retryTimes) {
LOG.warn("Long polling failed, tried {} times, {} times left, will be suspended for a while! {}",
time, retryTimes - time, e.getMessage());
// 长轮询失败了,等 5s 再继续
ThreadUtils.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS, 5);
continue;
}
LOG.error("Long polling failed, try again after 5 minutes!", e);
// 3 次都失败了,等 5 分钟再试
ThreadUtils.sleep(TimeUnit.MINUTES, 5);
}
}
}
LOG.warn("Stop http long polling.");
}
}
- HttpSyncDataService#doLongPolling()
执行长轮询任务的核心逻辑:
- 根据数据类型组装请求参数:
md5和lastModifyTime; - 组装请求头和请求体;
- 向
admin发起请求,判断组数据是否发生变更; - 根据发生变更的组,再去获取数据。
public class HttpSyncDataService implements SyncDataService {
private void doLongPolling(final String server) {
// 组装请求参数:md5 和 lastModifyTime
MultiValueMap<String, String> params = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(8);
for (ConfigGroupEnum group : ConfigGroupEnum.values()) {
ConfigData<?> cacheConfig = factory.cacheConfigData(group);
if (cacheConfig != null) {
String value = String.join(",", cacheConfig.getMd5(), String.valueOf(cacheConfig.getLastModifyTime()));
params.put(group.name(), Lists.newArrayList(value));
}
}
// 组装请求头和请求体
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
// 设置accessToken
headers.set(Constants.X_ACCESS_TOKEN, this.accessTokenManager.getAccessToken());
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, String>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(params, headers);
String listenerUrl = server + Constants.SHENYU_ADMIN_PATH_CONFIGS_LISTENER;
JsonArray groupJson;
//向admin发起请求,判断组数据是否发生变更
//这里只是判断了某个组是否发生变更
try {
String json = this.restTemplate.postForEntity(listenerUrl, httpEntity, String.class).getBody();
LOG.info("listener result: [{}]", json);
JsonObject responseFromServer = GsonUtils.getGson().fromJson(json, JsonObject.class);
groupJson = responseFromServer.getAsJsonArray("data");
} catch (RestClientException e) {
String message = String.format("listener configs fail, server:[%s], %s", server, e.getMessage());
throw new ShenyuException(message, e);
}
// 根据发生变更的组,再去获取数据
/**
* 官网对此处的解释:
* 网关收到响应信息之后,只知道是哪个 Group 发生了配置变更,还需要再次请求该 Group 的配置数据。
* 这里可能会存在一个疑问:为什么不是直接将变更的数据写出?
* 我们在开发的时候,也深入讨论过该问题,因为 http 长轮询机制只能保证准实时,如果在网关层处理不及时,
* 或者管理员频繁更新配置,很有可能便错过了某个配置变更的推送,安全起见,我们只告知某个 Group 信息发生了变更。
*
* 个人理解:
* 如果将变更数据直接写出,当管理员频繁更新配置时,第一次更新了,将client移除阻塞队列,返回响应信息给网关。
* 如果这个时候进行了第二次更新,那么当前的client是不在阻塞队列中,所以这一次的变更就会错过。
* 网关层处理不及时,也是同理。
* 这是一个长轮询,一个网关一个同步线程,可能存在耗时的过程。
* 如果admin有数据变更,当前网关client是没有在阻塞队列中,就不到数据。
*/
if (Objects.nonNull(groupJson) && groupJson.size() > 0) {
// fetch group configuration async.
ConfigGroupEnum[] changedGroups = GsonUtils.getGson().fromJson(groupJson, ConfigGroupEnum[].class);
LOG.info("Group config changed: {}", Arrays.toString(changedGroups));
this.doFetchGroupConfig(server, changedGroups);
}
}
}
这里需要特别解释一点的是:在长轮询任务中,为什么不直接拿到变更的数据?而是先判断哪个分组数据发生了变更,然后再次请求admin,获取变更数据?
官网对此处的解释是:
网关收到响应信息之后,只知道是哪个 Group 发生了配置变更,还需要再次请求该 Group 的配置数据。 这里可能会存在一个疑问:为什么不是直接将变更的数据写出? 我们在开发的时候,也深入讨论过该问题,因为
http长轮询机制只能保证准实时,如果在网关层处理不及时, 或者管理员频繁更新配置,很有可能便错过了某个配置变更的推送,安全起见,我们只告知某个 Group 信息发生了变更。
个人理解是:
如果将变更数据直接写出,管理员频繁更新配置时,第一次更新了,将
client移除阻塞队列,返回响应信息给网关。如果这个时候进行了第二次更新,那么当前的client是不在阻塞队列中,所以这一次的变更就会错过。网关层处理不及时,也是同理。 这是一个长轮询,一个网关一个同步线程,可能存在耗时的过程。如果admin有数据变更,当前网关client是没有在阻塞队列中,就会更新不到数据。
我们还没有分析到admin端的处理逻辑,先大概说一下。在admin端,会将网关client放到阻塞队列,有数据变更,网关client就会出队列,发送变更数据。所以,如果有数据变更时,网关client不在阻塞队列,那么就无法得到当前变更的数据。
知道哪个分组数据发生变更时,主动再向admin获取变更的数据,根据分组不同,全量拿数据。调用方法是doFetchGroupConfig(),这个在前面已经分析过了。
分析到这里,网关端的数据同步操作就完成了。长轮询任务就是不断向admin发起请求,看看数据是否发生变更,如果有分组数据发生变更,那么就再主动向admin发起请求,获取变更数据,然后更新网关内存中的数据。
网关端长轮询任务流程:
3. admin数据同步
从前面分析的过程中,可以看到,网关端主要调用admin的两个接口:
/configs/listener:判断组数据是否发生变更;/configs/fetch:获取变更组数据。
直接从这两个接口分析的话,可能有的地方不好理解,所以我们还是从admin启动流程开始分析数据同步过程。
3.1 加载配置
如果在配置文件application.yml中,进行了如下配置,就表示通过http长轮询的方式进行数据同步。
shenyu:
sync:
http:
enabled: true
程序启动时,通过springboot条件装配实现数据同步类的配置加载。在这个过程中,会创建HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener,负责处理长轮询的相关实现逻辑。
/**
* 数据同步配置类
* 通过springboot条件装配实现
* The type Data sync configuration.
*/
@Configuration
public class DataSyncConfiguration {
/**
* http长轮询
* http long polling.
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "shenyu.sync.http.enabled", havingValue = "true")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpSyncProperties.class)
static class HttpLongPollingListener {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener.class)
public HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener httpLongPollingDataChangedListener(final HttpSyncProperties httpSyncProperties) {
return new HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener(httpSyncProperties);
}
}
}
3.2 数据变更监听器实例化
- HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener
数据变更监听器通过构造函数的方式完成实例化和初始化操作。在构造函数中会创建阻塞队列,用于存放客户端;创建线程池,用于执行延迟任务,周期任务;保存长轮询相关属性信息。
public HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener(final HttpSyncProperties httpSyncProperties) {
// 默认客户端(这里是网关)1024个
this.clients = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1024);
// 创建线程池
// ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 可以执行延迟任务,周期任务,普通任务
this.scheduler = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1,
ShenyuThreadFactory.create("long-polling", true));
// 长轮询的属性信息
this.httpSyncProperties = httpSyncProperties;
}
另外,它的类图关系如下:
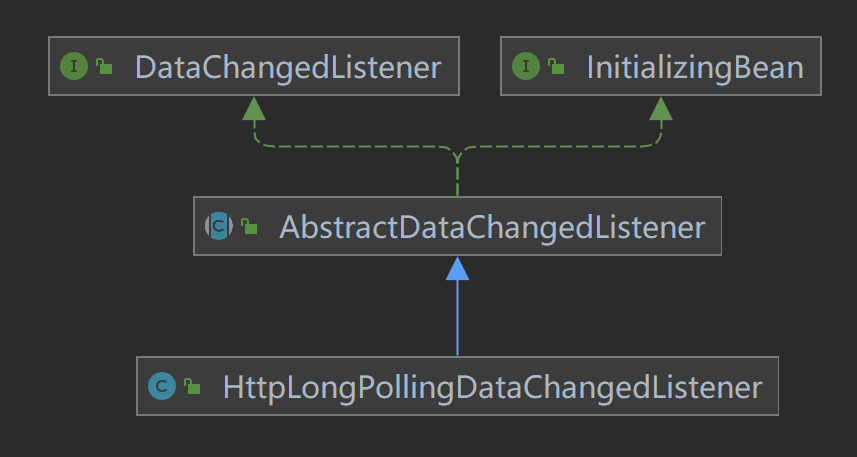
实现了InitializingBean接口,所以在bean的初始化过程中执行afterInitialize()方法。通过线程池执行周期任务:更新内存中(CACHE)的数据每隔5分钟执行一次,5分钟后开始执行。刷新本地缓存就是从数据库读取数据到本地缓存(这里就是内存),通过refreshLocalCache()完成。
public class HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener extends AbstractDataChangedListener {
// ......
/**
* 在 InitializingBean接口中的afterPropertiesSet()方法中被调用,即在bean的初始化过程中执行
*/
@Override
protected void afterInitialize() {
long syncInterval = httpSyncProperties.getRefreshInterval().toMillis();
// 执行周期任务:更新内存中(CACHE)的数据每隔5分钟执行一次,5分钟后开始执行
// 防止admin先启动一段时间后,产生了数据;然后网关初次连接时,没有拿到全量数据
scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
LOG.info("http sync strategy refresh config start.");
try {
// 从数据库读取数据到本地缓存(这里就是内存)
this.refreshLocalCache();
LOG.info("http sync strategy refresh config success.");
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("http sync strategy refresh config error!", e);
}
}, syncInterval, syncInterval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
LOG.info("http sync strategy refresh interval: {}ms", syncInterval);
}
// ......
}
- refreshLocalCache()
分别对5种数据类型进行更新。
public abstract class AbstractDataChangedListener implements DataChangedListener, InitializingBean {
// ......
// 从数据库读取数据到本地缓存(这里就是内存)
private void refreshLocalCache() {
//更新认证数据
this.updateAppAuthCache();
//更新插件数据
this.updatePluginCache();
//更新规则数据
this.updateRuleCache();
//更新选择器数据
this.updateSelectorCache();
//更新元数据
this.updateMetaDataCache();
}
// ......
}
5个更新方法的逻辑是类似的,调用service方法获取数据,然后放到内存CACHE中。以更新规则数据方法updateRuleCache()为例,传入规则枚举类型,调用ruleService.listAll()从数据库获取所有规则数据。
/**
* Update rule cache.
*/
protected void updateRuleCache() {
this.updateCache(ConfigGroupEnum.RULE, ruleService.listAll());
}
- updateCache()
使用数据库中的数据更新内存中的数据。
public abstract class AbstractDataChangedListener implements DataChangedListener, InitializingBean {
// ......
// 缓存数据的 Map
protected static final ConcurrentMap<String, ConfigDataCache> CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* if md5 is not the same as the original, then update lcoal cache.
* 更新缓存中的数据
* @param group ConfigGroupEnum
* @param <T> the type of class
* @param data the new config data
*/
protected <T> void updateCache(final ConfigGroupEnum group, final List<T> data) {
//数据序列化
String json = GsonUtils.getInstance().toJson(data);
//传入md5值和修改时间
ConfigDataCache newVal = new ConfigDataCache(group.name(), json, Md5Utils.md5(json), System.currentTimeMillis());
//更新分组数据
ConfigDataCache oldVal = CACHE.put(newVal.getGroup(), newVal);
LOG.info("update config cache[{}], old: {}, updated: {}", group, oldVal, newVal);
}
// ......
}
初始化的过程就是启动周期性任务,定时从数据库获取数据更新内存数据。
接下来开始对两个接口开始分析:
/configs/listener:判断组数据是否发生变更;/configs/fetch:获取变更组数据。
3.3 数据变更轮询接口
/configs/listener:判断组数据是否发生变更;
接口类是ConfigController,只有使用http长轮询进行数据同步时才会生效。接口方法listener()没有其他逻辑,直接调用doLongPolling()方法。
/**
* This Controller only when HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener exist, will take effect.
*/
@ConditionalOnBean(HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener.class)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/configs")
public class ConfigController {
private final HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener longPollingListener;
public ConfigController(final HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener longPollingListener) {
this.longPollingListener = longPollingListener;
}
// 省略其他逻辑
/**
* Listener.
* 监听数据变更,执行长轮询
* @param request the request
* @param response the response
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/listener")
public void listener(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) {
longPollingListener.doLongPolling(request, response);
}
}
- HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener#doLongPolling()
执行长轮询任务:如果有数据变更,将会立即响应给客户端(这里就是网关端)。否则,客户端会一直被阻塞,直到有数据变更或者超时。
public class HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener extends AbstractDataChangedListener {
// ......
/**
* 执行长轮询:如果有数据变更,会立即响应给客户端(这里就是网关端)。
* 否则,否则客户端会一直被阻塞,直到有数据变更或者超时。
* @param request
* @param response
*/
public void doLongPolling(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) {
// compare group md5
// 比较md5,判断网关的数据和admin端的数据是否一致,得到发生变更的数据组
List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroup = compareChangedGroup(request);
String clientIp = getRemoteIp(request);
// response immediately.
// 有变更的数据,则立即向网关响应
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(changedGroup)) {
this.generateResponse(response, changedGroup);
Log.info("send response with the changed group, ip={}, group={}", clientIp, changedGroup);
return;
}
// 没有变更,则将客户端(这里就是网关)放进阻塞队列
final AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync();
asyncContext.setTimeout(0L);
scheduler.execute(new LongPollingClient(asyncContext, clientIp, HttpConstants.SERVER_MAX_HOLD_TIMEOUT));
}
// ......
}
- HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener#compareChangedGroup()
判断组数据是否发生变更,判断逻辑是比较网关端和admin端的md5值和lastModifyTime。
- 如果
md5值不一样,那么需要更新; - 如果
admin端的lastModifyTime大于网关端的lastModifyTime,那么需要更新。
/**
* 判断组数据是否发生变更
* @param request
* @return
*/
private List<ConfigGroupEnum> compareChangedGroup(final HttpServletRequest request) {
List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroup = new ArrayList<>(ConfigGroupEnum.values().length);
for (ConfigGroupEnum group : ConfigGroupEnum.values()) {
// 网关端数据的md5值和lastModifyTime
String[] params = StringUtils.split(request.getParameter(group.name()), ',');
if (params == null || params.length != 2) {
throw new ShenyuException("group param invalid:" + request.getParameter(group.name()));
}
String clientMd5 = params[0];
long clientModifyTime = NumberUtils.toLong(params[1]);
ConfigDataCache serverCache = CACHE.get(group.name());
// do check. 判断组数据是否发生变更
if (this.checkCacheDelayAndUpdate(serverCache, clientMd5, clientModifyTime)) {
changedGroup.add(group);
}
}
return changedGroup;
}
- LongPollingClient
没有变更数据,则将客户端(这里就是网关)放进阻塞队列。阻塞时间是60秒,即60秒后移除,并响应客户端。
class LongPollingClient implements Runnable {
// 省略了其他逻辑
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 先设置定时任务:60秒后移除,并响应客户端
this.asyncTimeoutFuture = scheduler.schedule(() -> {
clients.remove(LongPollingClient.this);
List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroups = compareChangedGroup((HttpServletRequest) asyncContext.getRequest());
sendResponse(changedGroups);
}, timeoutTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 添加到阻塞队列
clients.add(this);
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("add long polling client error", ex);
}
}
/**
* Send response.
*
* @param changedGroups the changed groups
*/
void sendResponse(final List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroups) {
// cancel scheduler
if (null != asyncTimeoutFuture) {
asyncTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);
}
// 响应变更的组
generateResponse((HttpServletResponse) asyncContext.getResponse(), changedGroups);
asyncContext.complete();
}
}
3.4 获取变更数据接口
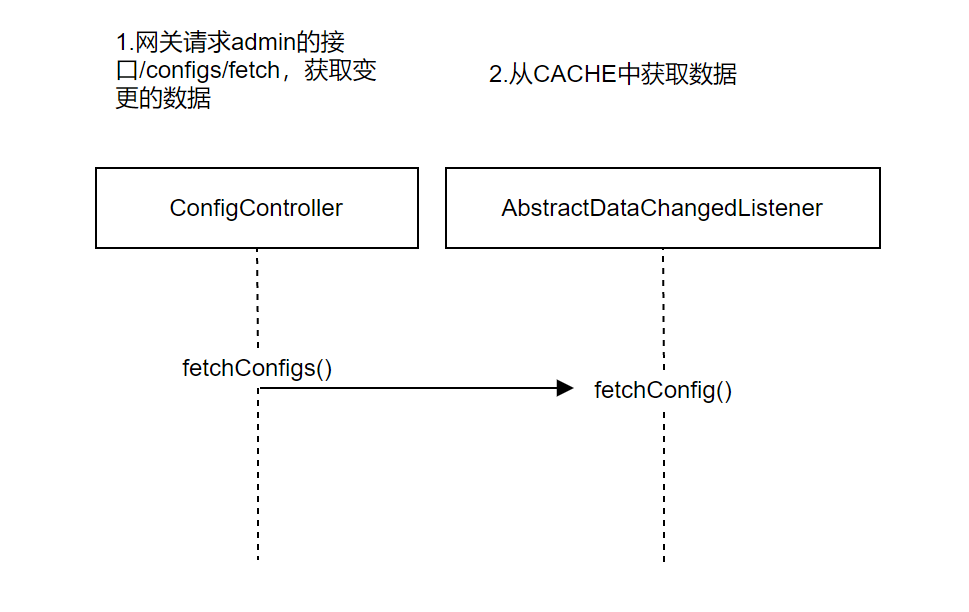
/configs/fetch:获取变更数据;
根据网关传入的参数,获取分组数据,返回结果。主要实现方法是longPollingListener.fetchConfig()。
@ConditionalOnBean(HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener.class)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/configs")
public class ConfigController {
private final HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener longPollingListener;
public ConfigController(final HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener longPollingListener) {
this.longPollingListener = longPollingListener;
}
/**
* Fetch configs shenyu result.
* 全量获取分组数据
* @param groupKeys the group keys
* @return the shenyu result
*/
@GetMapping("/fetch")
public ShenyuAdminResult fetchConfigs(@NotNull final String[] groupKeys) {
Map<String, ConfigData<?>> result = Maps.newHashMap();
for (String groupKey : groupKeys) {
ConfigData<?> data = longPollingListener.fetchConfig(ConfigGroupEnum.valueOf(groupKey));
result.put(groupKey, data);
}
return ShenyuAdminResult.success(ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS, result);
}
// 省略了其他接口
}
- AbstractDataChangedListener#fetchConfig()
数据获取直接从CACHE中拿,然后根据不同分组类型进行匹配,封装。
public abstract class AbstractDataChangedListener implements DataChangedListener, InitializingBean {
/**
* fetch configuration from cache.
* 获取分组下的全量数据
* @param groupKey the group key
* @return the configuration data
*/
public ConfigData<?> fetchConfig(final ConfigGroupEnum groupKey) {
// 直接从 CACHE 中拿数据
ConfigDataCache config = CACHE.get(groupKey.name());
switch (groupKey) {
case APP_AUTH: // 认证数据
return buildConfigData(config, AppAuthData.class);
case PLUGIN: // 插件数据
return buildConfigData(config, PluginData.class);
case RULE: // 规则数据
return buildConfigData(config, RuleData.class);
case SELECTOR: // 选择器数据
return buildConfigData(config, SelectorData.class);
case META_DATA: // 元数据
return buildConfigData(config, MetaData.class);
default: // 其他类型,抛出异常
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected groupKey: " + groupKey);
}
}
}
3.5 数据变更
在之前的websocket数据同步和zookeeper数据同步源码分析文章中,我们知道admin端数据同步设计结构如下:
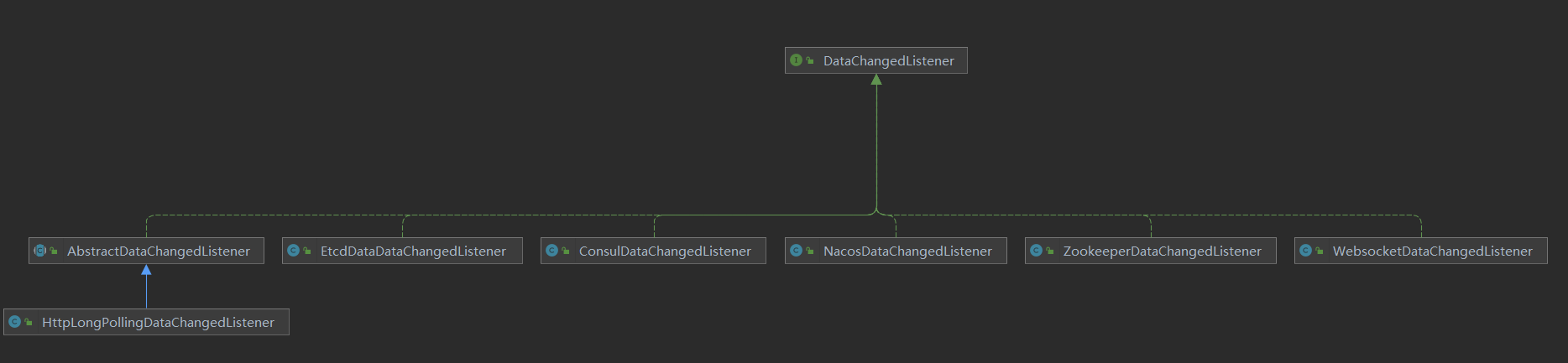
各种数据变更监听器都是DataChangedListener的子类。
当在admin端修改数据后,通过Spring的事件处理机制,发送事件通知。发送逻辑如下:
/**
* Event forwarders, which forward the changed events to each ConfigEventListener.
* 数据变更事件分发器:当admin端有数据发生变更时,将变更数据同步到 ShenYu 网关
* 数据变更依赖于Spring的事件监听机制:ApplicationEventPublisher --> ApplicationEvent --> ApplicationListener
*
*/
@Component
public class DataChangedEventDispatcher implements ApplicationListener<DataChangedEvent>, InitializingBean {
//省略了其他逻辑
/**
* 有数据变更时,调用此方法
* @param event
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void onApplicationEvent(final DataChangedEvent event) {
// 遍历数据变更监听器(一般使用一种数据同步的方式就好了)
for (DataChangedListener listener : listeners) {
// 哪种数据发生变更
switch (event.getGroupKey()) {
case APP_AUTH: // 认证信息
listener.onAppAuthChanged((List<AppAuthData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case PLUGIN: // 插件信息
listener.onPluginChanged((List<PluginData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case RULE: // 规则信息
listener.onRuleChanged((List<RuleData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case SELECTOR: // 选择器信息
listener.onSelectorChanged((List<SelectorData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
// 当选择器数据更新时,更新API文档信息
applicationContext.getBean(LoadServiceDocEntry.class).loadDocOnSelectorChanged((List<SelectorData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case META_DATA: // 元数据
listener.onMetaDataChanged((List<MetaData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
default: // 其他类型,抛出异常
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected value: " + event.getGroupKey());
}
}
}
}
假设,对插件信息进行了修改,通过http长轮询的方式进行数据同步,那么listener.onPluginChanged()的实际调用的是org.apache.shenyu.admin.listener.AbstractDataChangedListener#onPluginChanged:
/**
* 在admin的操作,有插件发生了更新
* @param changed the changed
* @param eventType the event type
*/
@Override
public void onPluginChanged(final List<PluginData> changed, final DataEventTypeEnum eventType) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(changed)) {
return;
}
// 更新内存CACHE
this.updatePluginCache();
// 执行变更任务
this.afterPluginChanged(changed, eventType);
}
有两个处理操作,一是更新内存CACHE,这个在前面分析过了;另一个是执行变更任务,在线程池中执行。
- HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener#afterPluginChanged()
@Override
protected void afterPluginChanged(final List<PluginData> changed, final DataEventTypeEnum eventType) {
// 在线程池中执行
scheduler.execute(new DataChangeTask(ConfigGroupEnum.PLUGIN));
}
- DataChangeTask
数据变更任务:将阻塞队列中的客户端依次移除,并发送响应,通知网关有组数据发生变更。
class DataChangeTask implements Runnable {
//省略了其他逻辑
@Override
public void run() {
// 阻塞队列中的客户端超过了给定的值100,则分批执行
if (clients.size() > httpSyncProperties.getNotifyBatchSize()) {
List<LongPollingClient> targetClients = new ArrayList<>(clients.size());
clients.drainTo(targetClients);
List<List<LongPollingClient>> partitionClients = Lists.partition(targetClients, httpSyncProperties.getNotifyBatchSize());
// 分批执行
partitionClients.forEach(item -> scheduler.execute(() -> doRun(item)));
} else {
// 执行任务
doRun(clients);
}
}
private void doRun(final Collection<LongPollingClient> clients) {
// 通知所有客户端发生了数据变更
for (Iterator<LongPollingClient> iter = clients.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
LongPollingClient client = iter.next();
iter.remove();
// 发送响应
client.sendResponse(Collections.singletonList(groupKey));
LOG.info("send response with the changed group,ip={}, group={}, changeTime={}", client.ip, groupKey, changeTime);
}
}
}
至此,admin端数据同步逻辑就分析完了。在基于http长轮询数据同步是,它主要有三个功能:
- 提供数据变更监听接口;
- 提供获取变更数据接口;
- 有数据变更时,移除阻塞队列中的客户端,并响应结果。
最后,用三张图描述下admin端长轮询任务流程:
/configs/listener数据变更监听接口:
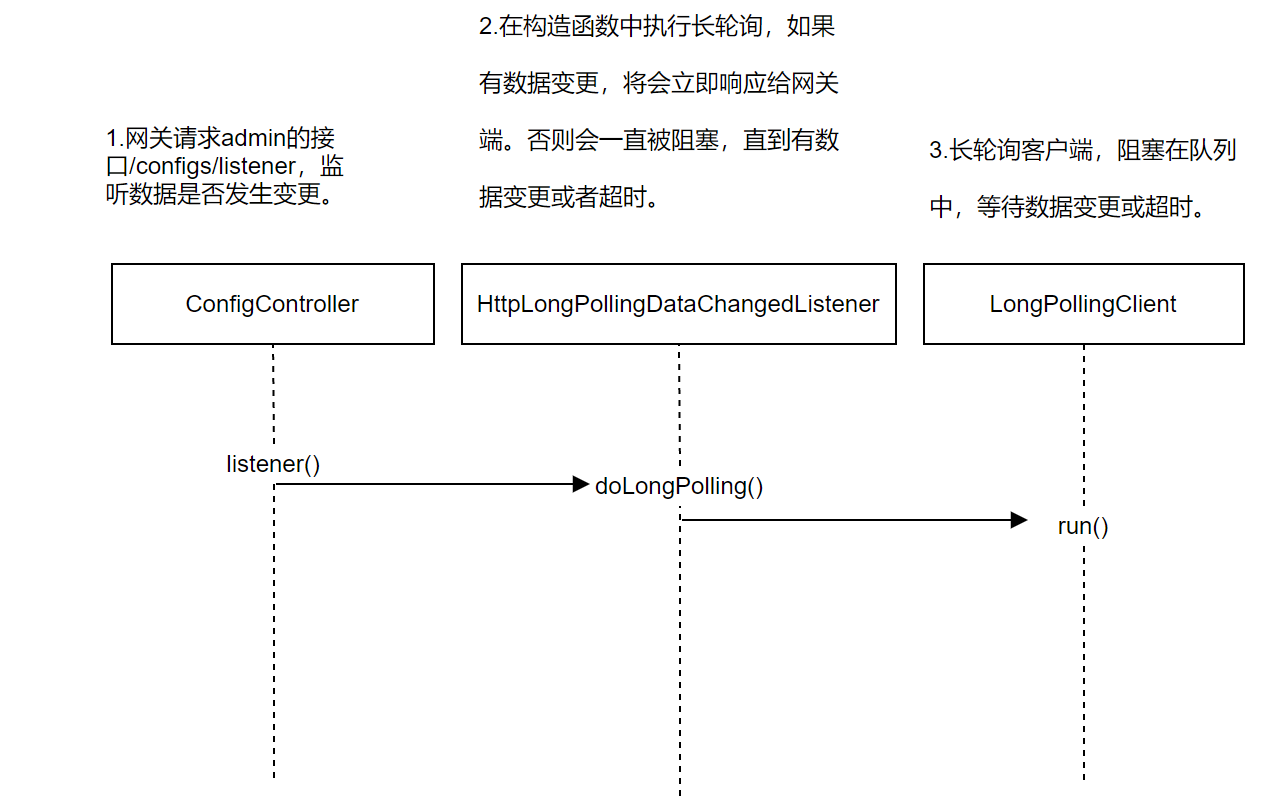
/configs/fetch获取变更数据接口:
- 在admin后台管理系统更新数据,进行数据同步:
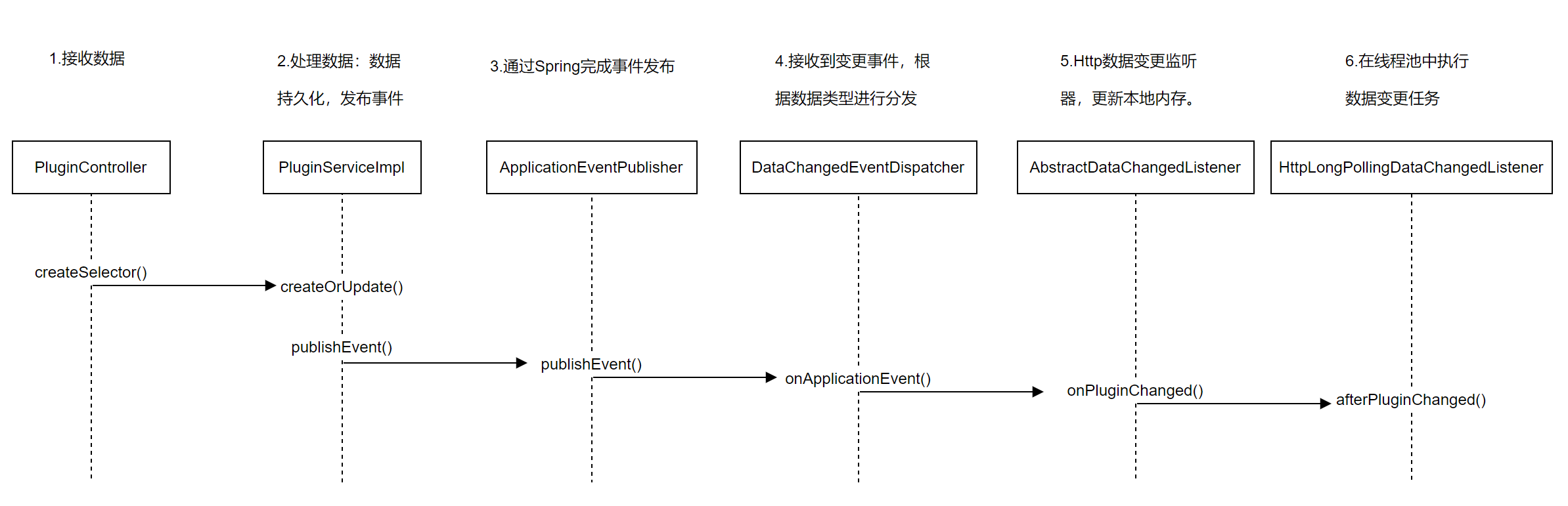
4. 总结
本文主要对ShenYu网关中的http长轮询数据同步进行了源码分析。涉�及到的主要知识点如下:
http长轮询由网关端主动发起请求,不断请求admin端;- 变更数据以组为粒度(认证信息、插件、选择器、规则、元数据);
http长轮询结果只拿到了变更组,还需要再次发起请求获取组数据;- 数据是否更新由
md5值和修改时间lastModifyTime决定。