Nacos数据同步源码分析
Apache ShenYu 是一个异步的,高性能的,跨语言的,响应式的
API网关。
在ShenYu网关中,数据同步是指,当在后台管理系统中,数据发送了更新后,如何将更新的数据同步到网关中。Apache ShenYu 网关当前支持ZooKeeper、WebSocket、Http长轮询、Nacos 、Etcd 和 Consul 进行数据同步。本文的主要内容是基于Nacos的数据同步源码分析。
本文基于
shenyu-2.4.0版本进行源码分析,官网的介绍请参考 数据同步原理 。
1. 关于Nacos
Nacos 平台用于动态服务发现,以及配置和服务管理。 Shenyu网关可选择使用Nacos进行数据同步。
2. Admin数据同步
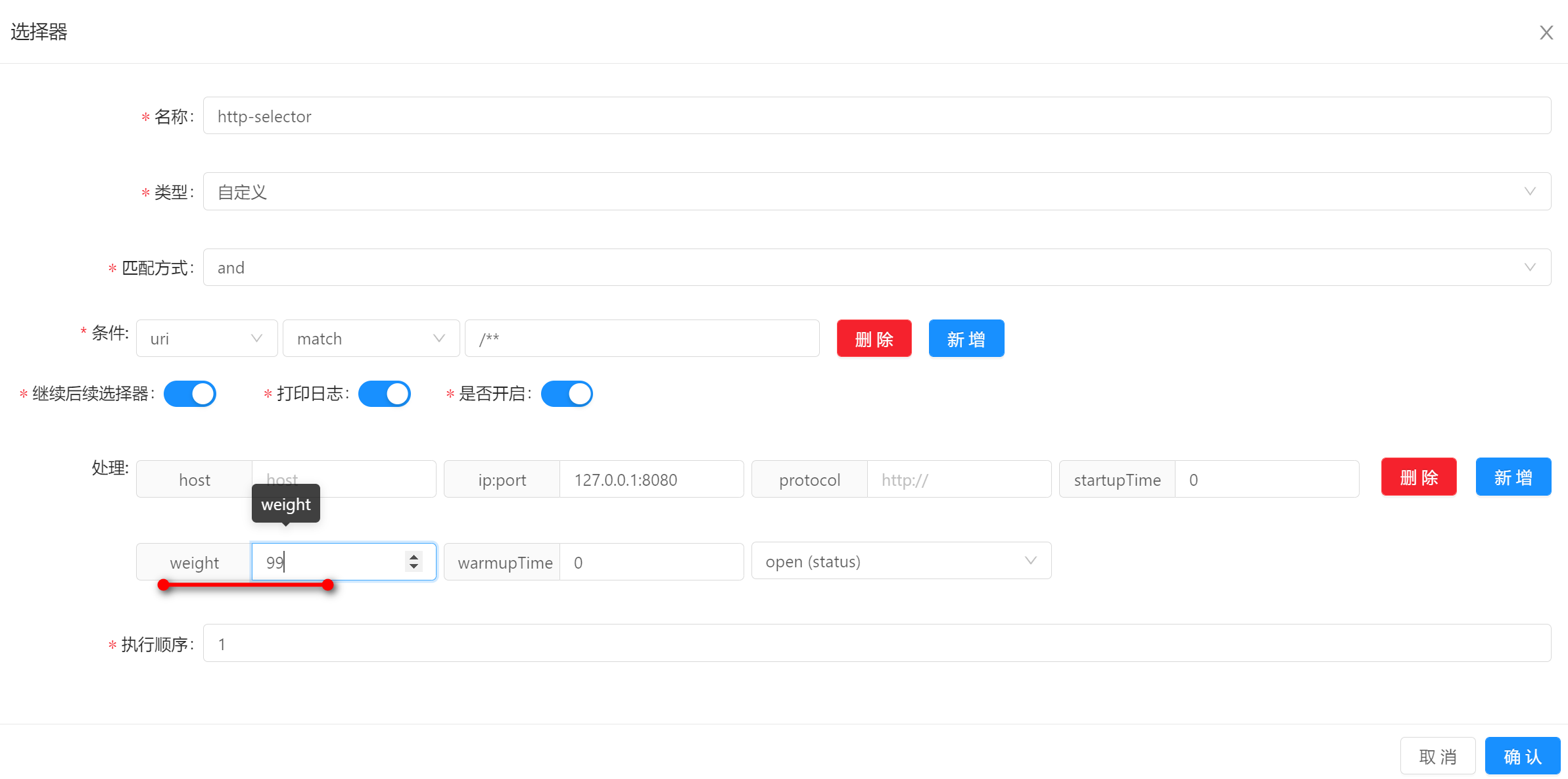
我们从一个实际案例进行源码追踪,比如在后台管理系统中,对Divide插件中的一条选择器数据进行更新,将权重更新为90:
2.1 接收数据
- SelectorController.updateSelector()
进入SelectorController类中的updateSelector()方法,它负责数据的校验,添加或更新数据,返回结果信息。
@Validated
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/selector")
public class SelectorController {
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public ShenyuAdminResult updateSelector(@PathVariable("id") final String id, @Valid @RequestBody final SelectorDTO selectorDTO) {
// 设置当前选择器数据id
selectorDTO.setId(id);
// 创建或更新操作
Integer updateCount = selectorService.createOrUpdate(selectorDTO);
// 返回结果信息
return ShenyuAdminResult.success(ShenyuResultMessage.UPDATE_SUCCESS, updateCount);
}
// ......
}
2.2 处理数据
- SelectorServiceImpl.createOrUpdate()
在SelectorServiceImpl类中通过createOrUpdate()方法完成数据的转换,保存到数据库,发布事件,更新upstream。
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class SelectorServiceImpl implements SelectorService {
// 负责事件发布的eventPublisher
private final ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int createOrUpdate(final SelectorDTO selectorDTO) {
int selectorCount;
// 构建数据 DTO --> DO
SelectorDO selectorDO = SelectorDO.buildSelectorDO(selectorDTO);
List<SelectorConditionDTO> selectorConditionDTOs = selectorDTO.getSelectorConditions();
// 判断是添加还是更新
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(selectorDTO.getId())) {
// 插入选择器数据
selectorCount = selectorMapper.insertSelective(selectorDO);
// 插入选择器中的条件数据
selectorConditionDTOs.forEach(selectorConditionDTO -> {
selectorConditionDTO.setSelectorId(selectorDO.getId());
selectorConditionMapper.insertSelective(SelectorConditionDO.buildSelectorConditionDO(selectorConditionDTO));
});
// check selector add
// 权限检查
if (dataPermissionMapper.listByUserId(JwtUtils.getUserInfo().getUserId()).size() > 0) {
DataPermissionDTO dataPermissionDTO = new DataPermissionDTO();
dataPermissionDTO.setUserId(JwtUtils.getUserInfo().getUserId());
dataPermissionDTO.setDataId(selectorDO.getId());
dataPermissionDTO.setDataType(AdminConstants.SELECTOR_DATA_TYPE);
dataPermissionMapper.insertSelective(DataPermissionDO.buildPermissionDO(dataPermissionDTO));
}
} else {
// 更新数据,先删除再新增
selectorCount = selectorMapper.updateSelective(selectorDO);
//delete rule condition then add
selectorConditionMapper.deleteByQuery(new SelectorConditionQuery(selectorDO.getId()));
selectorConditionDTOs.forEach(selectorConditionDTO -> {
selectorConditionDTO.setSelectorId(selectorDO.getId());
SelectorConditionDO selectorConditionDO = SelectorConditionDO.buildSelectorConditionDO(selectorConditionDTO);
selectorConditionMapper.insertSelective(selectorConditionDO);
});
}
// 发布事件
publishEvent(selectorDO, selectorConditionDTOs);
// 更新upstream
updateDivideUpstream(selectorDO);
return selectorCount;
}
// ......
}
在Service类完成数据的持久化操作,��即保存数据到数据库,这个比较简单,就不深入追踪了。关于更新upstream操作,放到后面对应的章节中进行分析,重点关注发布事件的操作,它会执行数据同步。
publishEvent()方法的逻辑是:找到选择器对应的插件,构建条件数据,发布变更数据。
private void publishEvent(final SelectorDO selectorDO, final List<SelectorConditionDTO> selectorConditionDTOs) {
// 找到选择器对应的插件
PluginDO pluginDO = pluginMapper.selectById(selectorDO.getPluginId());
// 构建条件数据
List<ConditionData> conditionDataList = selectorConditionDTOs.stream().map(ConditionTransfer.INSTANCE::mapToSelectorDTO).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 发布变更数据
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DataChangedEvent(ConfigGroupEnum.SELECTOR, DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE,
Collections.singletonList(SelectorDO.transFrom(selectorDO, pluginDO.getName(), conditionDataList))));
}
发布变更数据通过eventPublisher.publishEvent()完成,这个eventPublisher对象是一个ApplicationEventPublisher类,这个类的全限定名是org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher。看到这儿,我们知道了发布数据是通过Spring相关的功能来完成的。
关于
ApplicationEventPublisher:当有状态发生变化时,发布者调用
ApplicationEventPublisher的publishEvent方法发布一个事件,Spring容器广播事件给所有观察者,调用观察者的onApplicationEvent方法把事件对象传递给观察者。调用publishEvent方法有两种途径,一种是实现接口由容器注入ApplicationEventPublisher对象然后调用其方法,另一种是直接调用容器的方法,两种方法发布事件没有太大区别。
ApplicationEventPublisher:发布事件;ApplicationEvent:Spring事件,记录事件源、时间和数据;ApplicationListener:事件监听者,观察者;
在Spring的事件发布机制中,有三个对象,
一个是发布事件的ApplicationEventPublisher,在ShenYu中通过构造器注入了一个eventPublisher。
另一个对象是ApplicationEvent,在ShenYu中通过DataChangedEvent继承了它,表示事件对象。
public class DataChangedEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
//......
}
最后一个是 ApplicationListener,在ShenYu中通过DataChangedEventDispatcher类实现了该接口,作为事件的监听者,负责处理事件对象。
@Component
public class DataChangedEventDispatcher implements ApplicationListener<DataChangedEvent>, InitializingBean {
//......
}
2.3 分发数据
- DataChangedEventDispatcher.onApplicationEvent()
当事件发布完成后,会自动进入到DataChangedEventDispatcher类中的onApplicationEvent()方法,进行事件处理。
@Component
public class DataChangedEventDispatcher implements ApplicationListener<DataChangedEvent>, InitializingBean {
/**
* 有数据变更时,调用此方法
* @param event
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void onApplicationEvent(final DataChangedEvent event) {
// 遍历数据变更监听器(一般使用一种数据同步的方式就好了)
for (DataChangedListener listener : listeners) {
// 哪种数据发生变更
switch (event.getGroupKey()) {
case APP_AUTH: // 认证信息
listener.onAppAuthChanged((List<AppAuthData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case PLUGIN: // 插件信息
listener.onPluginChanged((List<PluginData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case RULE: // 规则信息
listener.onRuleChanged((List<RuleData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case SELECTOR: // 选择器信息
listener.onSelectorChanged((List<SelectorData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case META_DATA: // 元数据
listener.onMetaDataChanged((List<MetaData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
default: // 其他类型,抛出异常
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected value: " + event.getGroupKey());
}
}
}
}
当有数据变更时,调用onApplicationEvent方法,然后遍历所有数据变更监听器,判断是哪种数据类型,交给相应的数据监听器进行处理。
ShenYu将所有数据进行了分组,一共是五种:认证信息、插件信息、规则信息、选择器信息和元数据。
这里的数据变更监听器(DataChangedListener),就是数据同步策略的抽象,它的具体实现有:
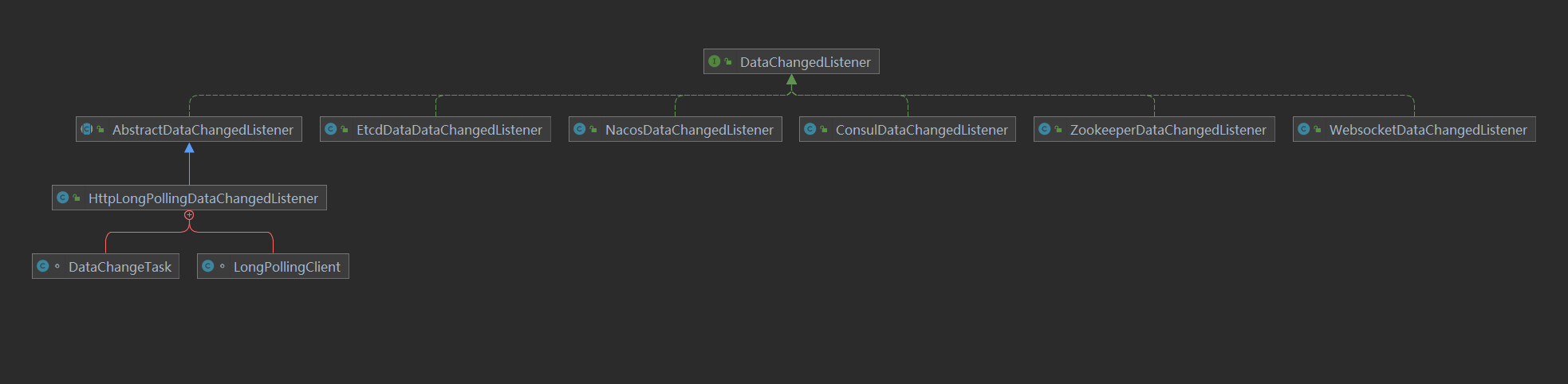
这几个实现类就是当前ShenYu支持的同步策略:
WebsocketDataChangedListener:基于websocket的数据同步;ZookeeperDataChangedListener:基于zookeeper的数据同步;ConsulDataChangedListener:基于consul的数据同步;EtcdDataDataChangedListener:基于etcd的数据同步;HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener:基于http长轮询的数据同步;NacosDataChangedListener:基于nacos的数据同步;
既然有这么�多种实现策略,那么如何确定使用哪一种呢?
因为本文是基于Nacos的数据同步源码分析,所以这里以NacosDataChangedListener为例,分析它是如何被加载并实现的。
通过查看对NacosDataChangedListener类的调用,可以发现,它是在DataSyncConfiguration类进行配置的。
/**
* 数据同步配置类
* 通过springboot条件装配实现
* The type Data sync configuration.
*/
@Configuration
public class DataSyncConfiguration {
//省略了其他代码......
/**
* The type Nacos listener.
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "shenyu.sync.nacos", name = "url")
@Import(NacosConfiguration.class)
static class NacosListener {
/**
* Data changed listener data changed listener.
*
* @param configService the config service
* @return the data changed listener
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(NacosDataChangedListener.class)
public DataChangedListener nacosDataChangedListener(final ConfigService configService) {
return new NacosDataChangedListener(configService);
}
/**
* Nacos data init zookeeper data init.
*
* @param configService the config service
* @param syncDataService the sync data service
* @return the nacos data init
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(NacosDataInit.class)
public NacosDataInit nacosDataInit(final ConfigService configService, final SyncDataService syncDataService) {
return new NacosDataInit(configService, syncDataService);
}
}
//省略了其他代码......
}
这个配置类是通过SpringBoot条件装配类实现的。在NacosListener类上面有几个注解:
-
@Configuration:配置文件,应用上下文; -
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "shenyu.sync.nacos", name = "url"):属性条件判断,满足条件,该配置类才会生效。也就是说,当我们有如下配置时,就会采用nacos进行数据同步。shenyu:
sync:
nacos:
url: localhost:8848 -
@Import(NacosConfiguration.class):导入另一个配置类NacosConfiguration,NacosConfiguration提供了一个方法ConfigService nacosConfigService(final NacosProperties nacosProp),将Nacos属性转换为ConfigService类型的bean,而Nacos属性是通过@EnableConfigurationProperties(NacosProperties.class)导入的。我们先看ConfigService类型的bean定义。再分析属性配置类和对应的属性配置文件。
/**
* Nacos configuration.
*/
@EnableConfigurationProperties(NacosProperties.class)
public class NacosConfiguration {
/**
* register configService in spring ioc.
*
* @param nacosProp the nacos configuration
* @return ConfigService {@linkplain ConfigService}
* @throws Exception the exception
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ConfigService.class)
public ConfigService nacosConfigService(final NacosProperties nacosProp) throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
if (nacosProp.getAcm() != null && nacosProp.getAcm().isEnabled()) {
// Use aliyun ACM service
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.ENDPOINT, nacosProp.getAcm().getEndpoint());
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.NAMESPACE, nacosProp.getAcm().getNamespace());
// Use subaccount ACM administrative authority
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.ACCESS_KEY, nacosProp.getAcm().getAccessKey());
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.SECRET_KEY, nacosProp.getAcm().getSecretKey());
} else {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.SERVER_ADDR, nacosProp.getUrl());
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(nacosProp.getNamespace())) {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.NAMESPACE, nacosProp.getNamespace());
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(nacosProp.getUsername())) {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.USERNAME, nacosProp.getUsername());
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(nacosProp.getPassword())) {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.PASSWORD, nacosProp.getPassword());
}
}
return NacosFactory.createConfigService(properties);
}
}
这个方法主要分成两步,第一步根据是否使用了aliyun的ACM服务,从NacosProperties中获取不同的nacos路径和鉴权信息,第二步根据获取到的这些属性,使用Nacos官方的工厂方法,使用反射的方式,创建configService。
接下来,让我们分析一下Nacos的属性配置和对应的配置文件。
/**
* The type Nacos config.
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shenyu.sync.nacos")
public class NacosProperties {
private String url;
private String namespace;
private String username;
private String password;
private NacosACMProperties acm;
/**
* Gets the value of url.
*
* @return the value of url
*/
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
/**
* Sets the url.
*
* @param url url
*/
public void setUrl(final String url) {
this.url = url;
}
/**
* Gets the value of namespace.
*
* @return the value of namespace
*/
public String getNamespace() {
return namespace;
}
/**
* Sets the namespace.
*
* @param namespace namespace
*/
public void setNamespace(final String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace;
}
/**
* Gets the value of username.
*
* @return the value of username
*/
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
/**
* Sets the username.
*
* @param username username
*/
public void setUsername(final String username) {
this.username = username;
}
/**
* Gets the value of password.
*
* @return the value of password
*/
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
/**
* Sets the password.
*
* @param password password
*/
public void setPassword(final String password) {
this.password = password;
}
/**
* Gets the value of acm.
*
* @return the value of acm
*/
public NacosACMProperties getAcm() {
return acm;
}
/**
* Sets the acm.
*
* @param acm acm
*/
public void setAcm(final NacosACMProperties acm) {
this.acm = acm;
}
public static class NacosACMProperties {
private boolean enabled;
private String endpoint;
private String namespace;
private String accessKey;
private String secretKey;
/**
* Gets the value of enabled.
*
* @return the value of enabled
*/
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
/**
* Sets the enabled.
*
* @param enabled enabled
*/
public void setEnabled(final boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
/**
* Gets the value of endpoint.
*
* @return the value of endpoint
*/
public String getEndpoint() {
return endpoint;
}
/**
* Sets the endpoint.
*
* @param endpoint endpoint
*/
public void setEndpoint(final String endpoint) {
this.endpoint = endpoint;
}
/**
* Gets the value of namespace.
*
* @return the value of namespace
*/
public String getNamespace() {
return namespace;
}
/**
* Sets the namespace.
*
* @param namespace namespace
*/
public void setNamespace(final String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace;
}
/**
* Gets the value of accessKey.
*
* @return the value of accessKey
*/
public String getAccessKey() {
return accessKey;
}
/**
* Sets the accessKey.
*
* @param accessKey accessKey
*/
public void setAccessKey(final String accessKey) {
this.accessKey = accessKey;
}
/**
* Gets the value of secretKey.
*
* @return the value of secretKey
*/
public String getSecretKey() {
return secretKey;
}
/**
* Sets the secretKey.
*
* @param secretKey secretKey
*/
public void setSecretKey(final String secretKey) {
this.secretKey = secretKey;
}
}
}
当我们在配置文件中配置了shenyu.sync.nacos.url属性时,将采用nacos进行数据同步,此时配置类NacosListener会生效,并生成NacosDataChangedListener和NacosDataInit类型的bean。
- 生成
NacosDataChangedListener类型的bean,nacosDataChangedListener,这个bean将ConfigService类型的bean作为成员变量,ConfigService是nacos官方提供的api,当nacosDataChangedListener监听到事件时,进行回调操作,可以通过该api直接与nacos服务器交互,修改配置。 - 生成
NacosDataInit类型的bean,nacosDataInit,这个bean将beanconfigService和beansyncDataService作为成员变量,调用Nacos的apiconfigService判断配置是否未初始化,未初始化则调用syncDataService进行刷新操作,将在下文详述。 根据上文所述,在事件处理方法onApplicationEvent()中,会触发相应的listener的操作。在我们的案例中,是对一条选择器数据进行更新,数据同步采用的是nacos,所以,代码会进入到NacosDataChangedListener进行选择器数据变更处理。
//DataChangedEventDispatcher.java
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void onApplicationEvent(final DataChangedEvent event) {
// 遍历数据变更监听器(一般使用一种数据同步的方式就好了)
for (DataChangedListener listener : listeners) {
// 哪种数据发生变更
switch (event.getGroupKey()) {
// 省略了其他逻辑
case SELECTOR: // 选择器信息
listener.onSelectorChanged((List<SelectorData>) event.getSource(), event.getEventType()); // 在我们的案例中,会进入到NacosDataChangedListener进行选择器数据变更处理
break;
}
}
2.4 Nacos数据变更监听器
-
NacosDataChangedListener.onSelectorChanged()
在
onSelectorChanged()方法中,判断操作类型,是刷新同步还是更新或创建同步。根据当前选择器数据信息判断节点是否在nacos中。
/**
* Use nacos to push data changes.
*/
public class NacosDataChangedListener implements DataChangedListener {
// 选择器信息发生改变
@Override
public void onSelectorChanged(final List<SelectorData> changed, final DataEventTypeEnum eventType) {
updateSelectorMap(getConfig(NacosPathConstants.SELECTOR_DATA_ID));
switch (eventType) {
case DELETE:
changed.forEach(selector -> {
List<SelectorData> ls = SELECTOR_MAP
.getOrDefault(selector.getPluginName(), new ArrayList<>())
.stream()
.filter(s -> !s.getId().equals(selector.getId()))
.sorted(SELECTOR_DATA_COMPARATOR)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
SELECTOR_MAP.put(selector.getPluginName(), ls);
});
break;
case REFRESH:
case MYSELF:
SELECTOR_MAP.keySet().removeAll(SELECTOR_MAP.keySet());
changed.forEach(selector -> {
List<SelectorData> ls = SELECTOR_MAP
.getOrDefault(selector.getPluginName(), new ArrayList<>())
.stream()
.sorted(SELECTOR_DATA_COMPARATOR)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
ls.add(selector);
SELECTOR_MAP.put(selector.getPluginName(), ls);
});
break;
default:
changed.forEach(selector -> {
List<SelectorData> ls = SELECTOR_MAP
.getOrDefault(selector.getPluginName(), new ArrayList<>())
.stream()
.filter(s -> !s.getId().equals(selector.getId()))
.sorted(SELECTOR_DATA_COMPARATOR)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
ls.add(selector);
SELECTOR_MAP.put(selector.getPluginName(), ls);
});
break;
}
publishConfig(NacosPathConstants.SELECTOR_DATA_ID, SELECTOR_MAP);
}
}
这部分是核心。changed表示需更新的SelectorData列表,eventType表示事件类型。SELECTOR_MAP的类型是ConcurrentMap<String, List<SelectorData>>,该map的key为selector所属的plugin的名称,value为该plugin下的selector列表。NacosPathConstants.SELECTOR_DATA_ID的值为shenyu.selector.json。操作步骤如下,第一步,使用getConfig方法调用Nacos的api,从Nacos获取group为shenyu.selector.json的配置信息,updateSelectorMap方法使用这些配置信息更新SELECTOR_MAP,这样就同步到了Nacos上最新的selector信息。第二步,再根据事件类型来更新SELECTOR_MAP,最后使用publishConfig方法,调用Nacos的api,将Nacos上,group为shenyu.selector.json的配置进行全量替换。
只要将变动的数据正确写入到Nacos上,admin这边的操作就执行完成了。
在我们当前的案例中,对Divide插件中的一条选择器数据进行更新,将权重更新为90,就会对图中的特定节点更新。
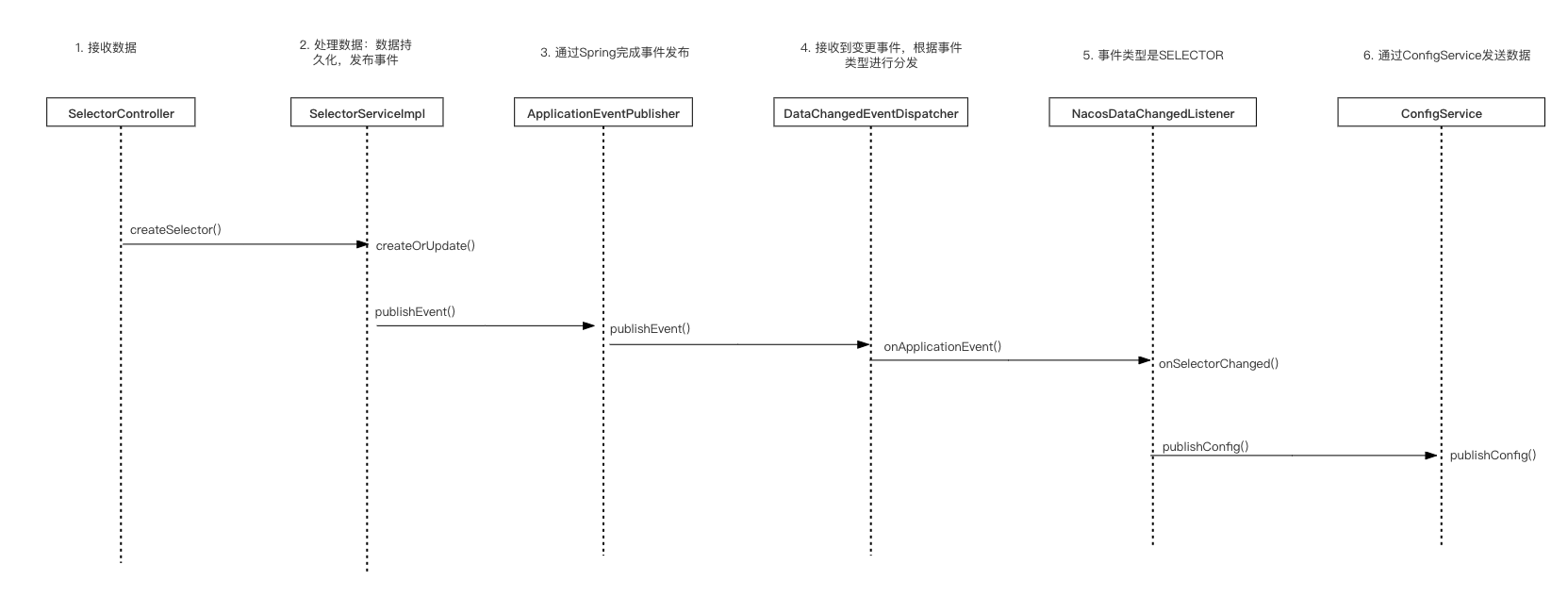
我们用时序图将上面的更新流程串联起来。
3. 网关数据同步
假设ShenYu网关已经在正常运行,使用的数据同步方式也是nacos。那么当在admin端更新选择器数据后,并且向nacos发送了变更的数据,那网关是如何接收并处理数据的呢?接下来我们就继续进行源码分析,一探究竟。
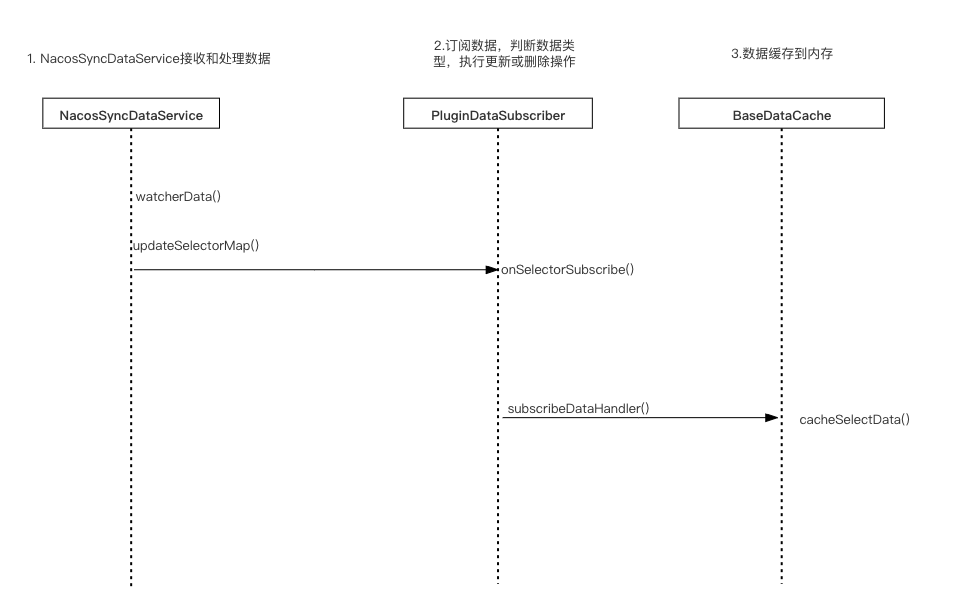
3.1 NacosSyncDataService接收数据
网关是通过NacosSyncDataService对nacos进行监听并获取数据更新的,但是在这部分内容之前,我们先看一下NacosSyncDataService类型的bean是如何生成的。答案是在Spring配置类NacosSyncDataConfiguration中定义的。我们看到NacosSyncDataConfiguration类上的注解,@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "shenyu.sync.nacos", name = "url"),这个注解我们在上文对ShenYu的Admin端中的NacosListener类进行分析时看到过,是一个属性条件判断,满足条件,该配置类才会生效。也就是说,当我们在Shenyu网关端有如下配置时,就表示Shenyu网关端采用nacos进行数据同步,NacosSyncDataConfiguration这个配置类生效。
shenyu:
sync:
nacos:
url: localhost:8848
/**
* Nacos sync data configuration for spring boot.
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(NacosSyncDataService.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "shenyu.sync.nacos", name = "url")
public class NacosSyncDataConfiguration {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NacosSyncDataConfiguration.class);
/**
* Nacos sync data service.
*
* @param configService the config service
* @param pluginSubscriber the plugin subscriber
* @param metaSubscribers the meta subscribers
* @param authSubscribers the auth subscribers
* @return the sync data service
*/
@Bean
public SyncDataService nacosSyncDataService(final ObjectProvider<ConfigService> configService, final ObjectProvider<PluginDataSubscriber> pluginSubscriber,
final ObjectProvider<List<MetaDataSubscriber>> metaSubscribers, final ObjectProvider<List<AuthDataSubscriber>> authSubscribers) {
LOGGER.info("you use nacos sync shenyu data.......");
return new NacosSyncDataService(configService.getIfAvailable(), pluginSubscriber.getIfAvailable(),
metaSubscribers.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList), authSubscribers.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList));
}
/**
* Nacos config service config service.
*
* @param nacosConfig the nacos config
* @return the config service
* @throws Exception the exception
*/
@Bean
public ConfigService nacosConfigService(final NacosConfig nacosConfig) throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
if (nacosConfig.getAcm() != null && nacosConfig.getAcm().isEnabled()) {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.ENDPOINT, nacosConfig.getAcm().getEndpoint());
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.NAMESPACE, nacosConfig.getAcm().getNamespace());
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.ACCESS_KEY, nacosConfig.getAcm().getAccessKey());
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.SECRET_KEY, nacosConfig.getAcm().getSecretKey());
} else {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.SERVER_ADDR, nacosConfig.getUrl());
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(nacosConfig.getNamespace())) {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.NAMESPACE, nacosConfig.getNamespace());
}
if (nacosConfig.getUsername() != null) {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.USERNAME, nacosConfig.getUsername());
}
if (nacosConfig.getPassword() != null) {
properties.put(PropertyKeyConst.PASSWORD, nacosConfig.getPassword());
}
}
return NacosFactory.createConfigService(properties);
}
/**
* Http config http config.
*
* @return the http config
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shenyu.sync.nacos")
public NacosConfig nacosConfig() {
return new NacosConfig();
}
}
我们重点关注一下上面代码中nacosSyncDataService这个bean的生成:
@Bean
public SyncDataService nacosSyncDataService(final ObjectProvider<ConfigService> configService, final ObjectProvider<PluginDataSubscriber> pluginSubscriber,
final ObjectProvider<List<MetaDataSubscriber>> metaSubscribers, final ObjectProvider<List<AuthDataSubscriber>> authSubscribers) {
LOGGER.info("you use nacos sync shenyu data.......");
return new NacosSyncDataService(configService.getIfAvailable(), pluginSubscriber.getIfAvailable(),
metaSubscribers.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList), authSubscribers.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList));
}
是直接调用NacosSyncDataService的构造方法new了一个该类型的对象。我们继续看构造方法:
public NacosSyncDataService(final ConfigService configService, final PluginDataSubscriber pluginDataSubscriber,
final List<MetaDataSubscriber> metaDataSubscribers, final List<AuthDataSubscriber> authDataSubscribers) {
super(configService, pluginDataSubscriber, metaDataSubscribers, authDataSubscribers);
start();
}
public void start() {
watcherData(NacosPathConstants.PLUGIN_DATA_ID, this::updatePluginMap);
watcherData(NacosPathConstants.SELECTOR_DATA_ID, this::updateSelectorMap);
watcherData(NacosPathConstants.RULE_DATA_ID, this::updateRuleMap);
watcherData(NacosPathConstants.META_DATA_ID, this::updateMetaDataMap);
watcherData(NacosPathConstants.AUTH_DATA_ID, this::updateAuthMap);
}
protected void watcherData(final String dataId, final OnChange oc) {
Listener listener = new Listener() {
@Override
public void receiveConfigInfo(final String configInfo) {
oc.change(configInfo);
}
@Override
public Executor getExecutor() {
return null;
}
};
oc.change(getConfigAndSignListener(dataId, listener));
LISTENERS.computeIfAbsent(dataId, key -> new ArrayList<>()).add(listener);
}
可以看到,在构造方法中调用了start方法,并且通过watcherData方法创建了监听器,并且关联了回调函数oc,由于我们正在分析selector类型组件的变化,对应的回调函数是updateSelectorMap。这个回调函数用于处理数据。
3.2 处理数据
- NacosCacheHandler.updateSelectorMap()
经过判空逻辑之后,缓存选择器数据的操作又交给了PluginDataSubscriber处理。
protected void updateSelectorMap(final String configInfo) {
try {
List<SelectorData> selectorDataList = GsonUtils.getInstance().toObjectMapList(configInfo, SelectorData.class).values().stream().flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toList());
selectorDataList.forEach(selectorData -> Optional.ofNullable(pluginDataSubscriber).ifPresent(subscriber -> {
subscriber.unSelectorSubscribe(selectorData);
subscriber.onSelectorSubscribe(selectorData);
}));
} catch (JsonParseException e) {
LOG.error("sync selector data have error:", e);
}
}
PluginDataSubscriber是一个接口,它只有一个CommonPluginDataSubscriber实现类,负责处理插件、选择器和规则数据。
3.3 通用插件数据订阅者
- PluginDataSubscriber.onSelectorSubscribe()
它没有其他逻辑,直接调用subscribeDataHandler()方法。在方法中,更具数据类型(插件、选择器或规则),操作类型(更新或删除),去执行不同逻辑。
/**
* 通用插件数据订阅者,负责处理所有插件、选择器和规则信息
* The type Common plugin data subscriber.
*/
public class CommonPluginDataSubscriber implements PluginDataSubscriber {
//......
// 处理选择器数据
@Override
public void onSelectorSubscribe(final SelectorData selectorData) {
subscribeDataHandler(selectorData, DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE);
}
// 订阅数据处理器,处理数据的更新或删除
private <T> void subscribeDataHandler(final T classData, final DataEventTypeEnum dataType) {
Optional.ofNullable(classData).ifPresent(data -> {
// 插件数据
if (data instanceof PluginData) {
PluginData pluginData = (PluginData) data;
if (dataType == DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE) { // 更新操作
// 将数据保存到网关内存
BaseDataCache.getInstance().cachePluginData(pluginData);
// 如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理
Optional.ofNullable(handlerMap.get(pluginData.getName())).ifPresent(handler -> handler.handlerPlugin(pluginData));
} else if (dataType == DataEventTypeEnum.DELETE) { // 删除操作
// 从网关内存移除数据
BaseDataCache.getInstance().removePluginData(pluginData);
// 如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理
Optional.ofNullable(handlerMap.get(pluginData.getName())).ifPresent(handler -> handler.removePlugin(pluginData));
}
} else if (data instanceof SelectorData) { // 选择器数据
SelectorData selectorData = (SelectorData) data;
if (dataType == DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE) { // 更新操作
// 将数据保存到网关内存
BaseDataCache.getInstance().cacheSelectData(selectorData);
// 如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理 Optional.ofNullable(handlerMap.get(selectorData.getPluginName())).ifPresent(handler -> handler.handlerSelector(selectorData));
} else if (dataType == DataEventTypeEnum.DELETE) { // 删除操作
// 从网关内存移除数据
BaseDataCache.getInstance().removeSelectData(selectorData);
// 如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理
Optional.ofNullable(handlerMap.get(selectorData.getPluginName())).ifPresent(handler -> handler.removeSelector(selectorData));
}
} else if (data instanceof RuleData) { // 规则数据
RuleData ruleData = (RuleData) data;
if (dataType == DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE) { // 更新操作
// 将数据保存到网关内存
BaseDataCache.getInstance().cacheRuleData(ruleData);
// 如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理
Optional.ofNullable(handlerMap.get(ruleData.getPluginName())).ifPresent(handler -> handler.handlerRule(ruleData));
} else if (dataType == DataEventTypeEnum.DELETE) { // 删除操作
// 从网关内存移除数据
BaseDataCache.getInstance().removeRuleData(ruleData);
// 如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理
Optional.ofNullable(handlerMap.get(ruleData.getPluginName())).ifPresent(handler -> handler.removeRule(ruleData));
}
}
});
}
}
3.4 数据缓存到内存
那么更新一条选择器数据,会进入下面的逻辑:
// 将数据保存到网关内存
BaseDataCache.getInstance().cacheSelectData(selectorData);
// 如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理
Optional.ofNullable(handlerMap.get(selectorData.getPluginName())).ifPresent(handler -> handler.handlerSelector(selectorData));
一是将数据保存到网关的内存中。BaseDataCache是最终缓存数据的类,通过单例模式实现。选择器数据就存到了SELECTOR_MAP这个Map中。在后续使用的时候,也是从这里拿数据。
public final class BaseDataCache {
// 私有变量
private static final BaseDataCache INSTANCE = new BaseDataCache();
// 私有构造器
private BaseDataCache() {
}
/**
* Gets instance.
* 公开方法
* @return the instance
*/
public static BaseDataCache getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
/**
* 缓存选择器数据的Map
* pluginName -> SelectorData.
*/
private static final ConcurrentMap<String, List<SelectorData>> SELECTOR_MAP = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
public void cacheSelectData(final SelectorData selectorData) {
Optional.ofNullable(selectorData).ifPresent(this::selectorAccept);
}
/**
* cache selector data.
* 缓存选择器数据
* @param data the selector data
*/
private void selectorAccept(final SelectorData data) {
String key = data.getPluginName();
if (SELECTOR_MAP.containsKey(key)) { // 更新操作,先删除再插入
List<SelectorData> existList = SELECTOR_MAP.get(key);
final List<SelectorData> resultList = existList.stream().filter(r -> !r.getId().equals(data.getId())).collect(Collectors.toList());
resultList.add(data);
final List<SelectorData> collect = resultList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(SelectorData::getSort)).collect(Collectors.toList());
SELECTOR_MAP.put(key, collect);
} else { // 新增操作,直接放到Map中
SELECTOR_MAP.put(key, Lists.newArrayList(data));
}
}
}
二是如果每个插件还有自己的处理逻辑,那么就去处理。 通过idea编辑器可以看到,当新增一条选择器后,有如下的插件还有处理。这里我们就不再展开了。
经过以上的源码追踪,并通过一个实际的案例,在admin端新增更新一条选择器数据,就将nacos数据同步的流程分析清楚了。
我们还是通过时序图将网关端的数据同步流程串联一下:
数据同步的流程已经分析完了,为了不让同步流程被打断,在分析过程中就忽略了其他逻辑。网关同步操作初始化的流程在NacosSyncDataService的start方法中,我们在上文分析网关数据同步时分析过了,下面分析Admin的同步数据初始化。
4. Admin同步数据初始化
admin端,NacosDataInit类型的bean,在NacosListener中进行定义和生成,如果admin的配置中指定了使用nacos进行数据同步,当admin启动后,会将当前的数据信息全量同步到nacos中,实现逻辑如下:
/**
* The type Nacos data init.
*/
public class NacosDataInit implements CommandLineRunner {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NacosDataInit.class);
private final ConfigService configService;
private final SyncDataService syncDataService;
/**
* Instantiates a new Nacos data init.
* @param configService the nacos config service
* @param syncDataService the sync data service
*/
public NacosDataInit(final ConfigService configService, final SyncDataService syncDataService) {
this.configService = configService;
this.syncDataService = syncDataService;
}
@Override
public void run(final String... args) {
String pluginDataId = NacosPathConstants.PLUGIN_DATA_ID;
String authDataId = NacosPathConstants.AUTH_DATA_ID;
String metaDataId = NacosPathConstants.META_DATA_ID;
if (dataIdNotExist(pluginDataId) && dataIdNotExist(authDataId) && dataIdNotExist(metaDataId)) {
syncDataService.syncAll(DataEventTypeEnum.REFRESH);
}
}
private boolean dataIdNotExist(final String pluginDataId) {
try {
String group = NacosPathConstants.GROUP;
long timeout = NacosPathConstants.DEFAULT_TIME_OUT;
return configService.getConfig(pluginDataId, group, timeout) == null;
} catch (NacosException e) {
LOG.error("Get data from nacos error.", e);
throw new ShenyuException(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
判断nacos中是否存在数据,如果不存在,则进行同步。
NacosDataInit实现了CommandLineRunner接口。它是springboot提供的接口,会在所有 Spring Beans初始化之后执行run()方法,常用于项目中初始化的操作。
- SyncDataService.syncAll()
从数据库查询数据,然后进行全量数据同步,所有的认证信息、插件信息、选择器信息、规则信息和元数据信息。主要是通过eventPublisher发布同步事件。这里就跟前面提到的同步逻辑就又联系起来了,eventPublisher通过publishEvent()发布完事件后,有ApplicationListener执行事件变更操作,在ShenYu中就是前面提到的DataChangedEventDispatcher。
@Service
public class SyncDataServiceImpl implements SyncDataService {
// 事件发布
private final ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
/***
* 全量数据同步
* @param type the type
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean syncAll(final DataEventTypeEnum type) {
// 同步认证信息
appAuthService.syncData();
// 同步插件信息
List<PluginData> pluginDataList = pluginService.listAll();
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DataChangedEvent(ConfigGroupEnum.PLUGIN, type, pluginDataList));
// 同步选择器信息
List<SelectorData> selectorDataList = selectorService.listAll();
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DataChangedEvent(ConfigGroupEnum.SELECTOR, type, selectorDataList));
// 同步规则信息
List<RuleData> ruleDataList = ruleService.listAll();
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DataChangedEvent(ConfigGroupEnum.RULE, type, ruleDataList));
// 同步元数据信息
metaDataService.syncData();
return true;
}
}
5. 总结
本文通过一个实际案例,对nacos的数据同步原理进行了源码分析。涉及到的主要知识点如下:
- 基于
nacos的数据同步,主要是通过watch机制实现; - 通过
Spring完成事件发布和监听; - 通过抽象
DataChangedListener接口,支持多种同步策略,面向接口编程; - 使用单例设计模式实现缓存数据类
BaseDataCache; - 通过
SpringBoot的条件装配和starter加载机制实现配置类的加载。