Data Synchronization Design
Description
This article mainly explains three ways of database synchronization and their principles.
Preface
Gateway is the entrance of request and it is a very important part in micro service architecture, therefore the importance of gateway high availability is self-evident. When we use gateway, we have to change configuration such as flow rule, route rule for satisfying business requirement. Therefore, the dynamic configuration of the gateway is an important factor to ensure the high availability of the gateway. Then, how does Soul support dynamic configuration?
Anyone who has used Soul knows, Soul plugin are hot swap,and the selector, rule of all plugins are dynamic configured, they take effect immediately without restarting service.But during using Soul gateway, users also report many problems
- Rely on
zookeeper, this troubles users who useetcdconsulandnacosregistry - Rely on
redis,influxdb, I have not used the limiting plugin, monitoring plugin, why do I need these
Therefore,we have done a partial reconstruction of Soul,after two months of version iteration,we released version 2.0
- Data Synchronization removes the strong dependence on
zookeeper,and we addhttp long pollingandwebsocket - Limiting plugin and monitoring plugin realize real dynamic configuration,we use
adminbackend for dynamic configuration instead ofymlconfiguration before
Q: Someone may ask me,why don't you use configuration center for synchronization?
First of all, it will add extra costs, not only for maintenance, but also make Soul heavy; In addition, using configuration center, data format is uncontrollable and it is not convenient for soul-admin to do configuration management.
Q: Someone may also ask,dynamic configuration update?Every time I can get latest data from database or redis,why are you making it complicated?
As a gateway, soul cached all the configuration in the HashMap of JVM in order to provide higher response speed and we use local cache for every request, It's very fast. So this article can also be understood as three ways of memory synchronization in a distributed environment.
Principle Analysis
This is a HD uncoded image, it shows the flow of Soul data synchronization, when Soul gateway starts, it will synchronize configuration data from the configuration service and support push-pull mode to obtain configuration change information, and update the local cache.When administrator changes user,rule,plugin,flow configuration in the backend, modified information will synchronize to the Soul gateway through the push-pull mode,whether it is the push mode or the pull mode depends on the configuration.About the configuration synchronization module, it is actually a simplified configuration center.
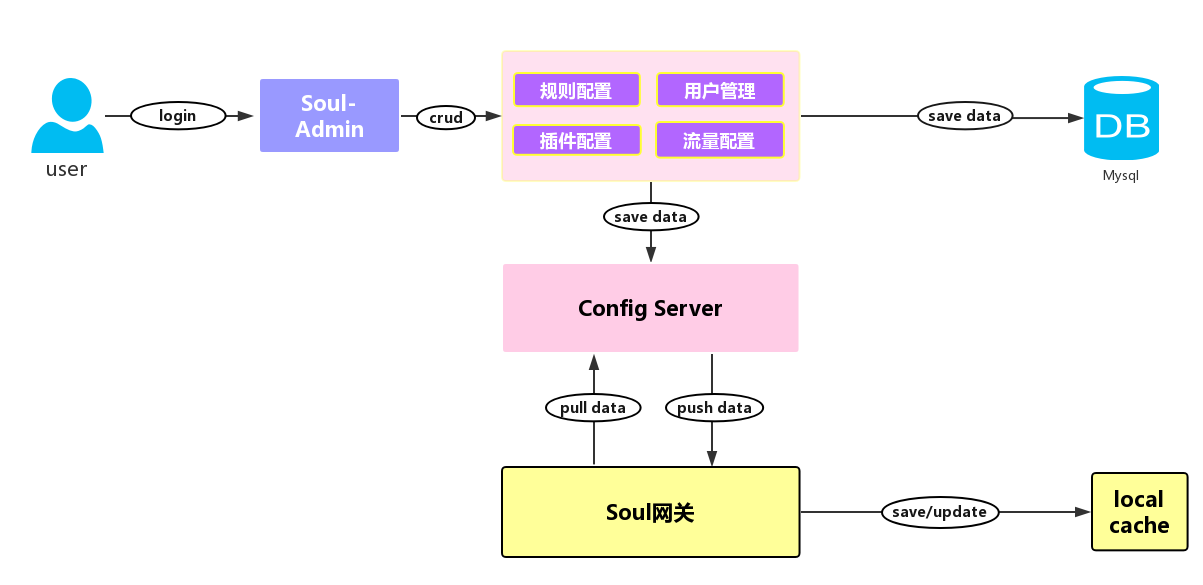
At version 1.x ,configuration service depends on zookeeper,management backend push the modified information to gateway.But version 2.x supports webosocket,http,zookeeper,it can specify the corresponding synchronization strategy through soul.sync.strategy and use webosocket synchronization strategy by default which can achieve second-level data synchronization.But,note that soul-web and soul-admin must use the same synchronization mechanism.
As showing picture below,soul-admin will issue a configuration change notification through EventPublisher after users change configuration,EventDispatcher will handle this modification and send configuration to corresponding event handler according to configured synchronization strategy(http,websocket,zookeeper)
- If it is a
websocketsynchronization strategy,it will push modified data tosoul-web,and correspondingWebsocketCacheHandlerhandler will handleadmindata push at the gateway layer - If it is a
zookeepersynchronization strategy,it will push modified data tozookeeper,and theZookeeperSyncCachewill monitor the data changes ofzookeeperand process them - If it is a
httpsynchronization strategy,soul-webproactively initiates long polling requests,90 seconds timeout by default,if there is no modified data insoul-admin,http request will be blocked,if there is a data change, it will respond to the changed data information,if there is no data change after 60 seconds,then respond with empty data,gateway continue to make http request after getting response,this kind of request will repeat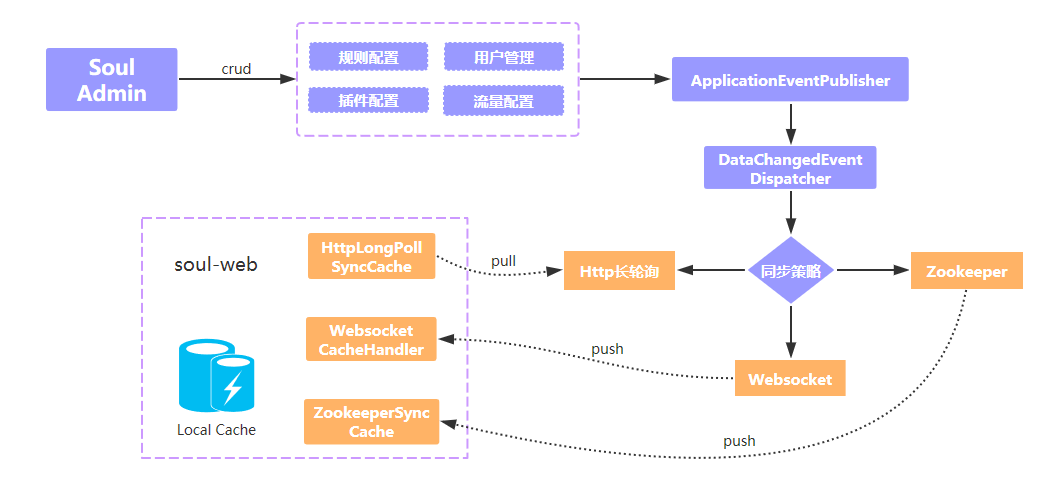
Zookeeper Synchronization
The zookeeper-based synchronization principle is very simple,it mainly depends on zookeeper watch mechanism,soul-web will monitor the configured node,when soul-admin starts,all the data will be written to zookeeper,it will incrementally update the nodes of zookeeper when data changes,at the same time, soul-web will monitor the node for configuration information, and update the local cache once the information changes
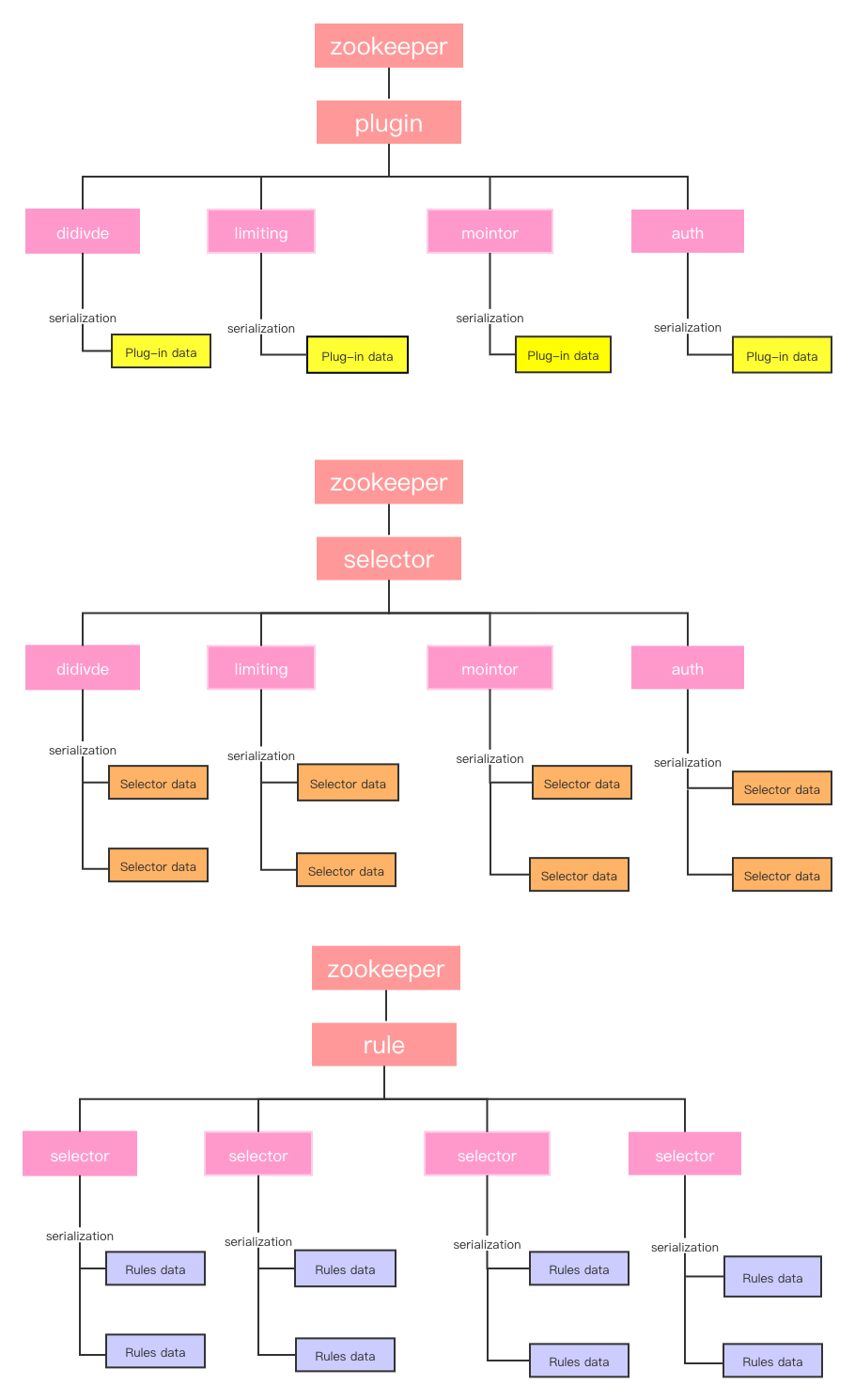
soul writes the configuration information to the zookeeper node,and it is meticulously designed.
WebSocket Synchronization
The mechanism of websocket and zookeeper is similar,when the gateway and the admin establish a websocket connection,admin will push all data at once,it will automatically push incremental data to soul-web through websocket when configured data changes
When we use websocket synchronization,pay attention to reconnect after disconnection,which also called keep heartbeat.soul uses java-websocket ,a third-party library,to connect to websocket.
public class WebsocketSyncCache extends WebsocketCacheHandler {
/**
* The Client.
*/
private WebSocketClient client;
public WebsocketSyncCache(final SoulConfig.WebsocketConfig websocketConfig) {
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1,
SoulThreadFactory.create("websocket-connect", true));
client = new WebSocketClient(new URI(websocketConfig.getUrl())) {
@Override
public void onOpen(final ServerHandshake serverHandshake) {
//....
}
@Override
public void onMessage(final String result) {
//....
}
};
//connect
client.connectBlocking();
//reconnect after disconnection,using scheduling thread pool,execute every 30 seconds
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
if (client != null && client.isClosed()) {
client.reconnectBlocking();
}
}, 10, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
Http Long Polling
The mechanism of zookeeper and websocket data synchronization is relatively simple,but http synchronization will be relatively complicated.Soul borrows the design ideas of Apollo and Nacos and realizes http long polling data synchronization using their advantages.Note that this is not traditional ajax long polling.

http long polling mechanism as above,soul-web gateway requests admin configuration services,timeout is 90 seconds,it means gateway layer request configuration service will wait at most 90 seconds,this is convenient for admin configuration service to respond modified data in time,and therefore we realize near real-time push.
After the http request reaches soul-admin, it does not respond immediately,but uses the asynchronous mechanism of Servlet3.0 to asynchronously respond to the data.First of all,put long polling request task LongPollingClient into BlocingQueue,and then start scheduling task,execute after 60 seconds,this aims to remove the long polling request from the queue after 60 seconds,even there is no configured data change.Because even if there is no configuration change,gateway also need to know,otherwise it will wait,and there is a 90 seconds timeout when the gateway requests configuration services.
public void doLongPolling(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) {
// since soul-web may not receive notification of a configuration change, MD5 value may be different,so respond immediately
List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroup = compareMD5(request);
String clientIp = getRemoteIp(request);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(changedGroup)) {
this.generateResponse(response, changedGroup);
return;
}
// Servlet3.0 asynchronously responds to http request
final AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync();
asyncContext.setTimeout(0L);
scheduler.execute(new LongPollingClient(asyncContext, clientIp, 60));
}
class LongPollingClient implements Runnable {
LongPollingClient(final AsyncContext ac, final String ip, final long timeoutTime) {
// omit......
}
@Override
public void run() {
// join a scheduled task, if there is no configuration change within 60 seconds, it will be executed after 60 seconds and respond to http requests
this.asyncTimeoutFuture = scheduler.schedule(() -> {
// clients are blocked queue,saved the request from soul-web
clients.remove(LongPollingClient.this);
List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroups = HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener.compareMD5((HttpServletRequest) asyncContext.getRequest());
sendResponse(changedGroups);
}, timeoutTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//
clients.add(this);
}
}
If the administrator changes the configuration data during this period,the long polling requests in the queue will be removed one by one, and respond which group’s data has changed(we distribute plugins, rules, flow configuration , user configuration data into different groups).After gateway receives response,it only knows which Group has changed its configuration,it need to request again to get group configuration data.Someone may ask,why don't you write out the changed data directly?We also discussed this issue deeply during development, because the http long polling mechanism can only guarantee quasi real-time,if gateway layer does not handle it in time,or administrator updates configuration frequently,we probably missed some configuration change push.For security, we only inform that a certain Group information has changed.
// soul-admin configuration changed,remove the requests from the queue one by one and respond to them
class DataChangeTask implements Runnable {
DataChangeTask(final ConfigGroupEnum groupKey) {
this.groupKey = groupKey;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (Iterator<LongPollingClient> iter = clients.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
LongPollingClient client = iter.next();
iter.remove();
client.sendResponse(Collections.singletonList(groupKey));
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error("data change error.", e);
}
}
}
When soul-web gateway layer receives the http response information,pull modified information(if exists),and then request soul-admin configuration service again,this will repeatedly execute.
Storage Address
github: https://github.com/dromara/soul
gitee: https://gitee.com/dromara/soul
There also have video tutorials on the project homepage,you can go to watch it if needed.
At Last
This article introduces that,in order to optimize the response speed, soul as a highly available micro service gateway, its three ways to cache the configuration rule selector data locally.After learning this article,I believe you have a certain understanding of the popular configuration center,it may be easier to learn their codes,I believe you can also write a distributed configuration center.Version 3.0 is already under planning,and I believe it will definitely surprise you.