Apache ShenYu is an asynchronous, high-performance, cross-language, responsive API gateway.
The Apache ShenYu gateway uses the dubbo plugin to make calls to the dubbo service. You can see the official documentation Dubbo Quick Start to learn how to use the plugin.
This article is based on shenyu-2.4.3 version for source code analysis, please refer to Dubbo Service Access for the introduction of the official website.
1. Service Registration
Take the example provided on the official website shenyu-examples-dubbo. Suppose your dubbo service is defined as follows (spring-dubbo.xml).
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo
https://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="test-dubbo-service"/>
<dubbo:registry address="${dubbo.registry.address}"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20888"/>
<dubbo:service timeout="10000" interface="org.apache.shenyu.examples.dubbo.api.service.DubboTestService" ref="dubboTestService"/>
</beans>
Declare the application service name, register the center address, use the dubbo protocol, declare the service interface, and the corresponding interface implementation class.
@Service("dubboTestService")
public class DubboTestServiceImpl implements DubboTestService {
@Override
@ShenyuDubboClient(path = "/findById", desc = "Query by Id")
public DubboTest findById(final String id) {
return new DubboTest(id, "hello world shenyu Apache, findById");
}
}
In the interface implementation class, use the annotation @ShenyuDubboClient to register the service with shenyu-admin. The role of this annotation and its rationale will be analyzed later.
The configuration information in the configuration file application.yml.
server:
port: 8011
address: 0.0.0.0
servlet:
context-path: /
spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
dubbo:
registry:
address: zookeeper://localhost:2181
shenyu:
register:
registerType: http
serverLists: http://localhost:9095
props:
username: admin
password: 123456
client:
dubbo:
props:
contextPath: /dubbo
appName: dubbo
In the configuration file, declare the registry address used by dubbo. The dubbo service registers with shenyu-admin, using the method http, and the registration address is http://localhost:9095.
See Application Client Access for more information on the use of the registration method.
1.1 Declaration of registration interface
Use the annotation @ShenyuDubboClient to register the service to the gateway. The simple demo is as follows.
@Service("dubboTestService")
public class DubboTestServiceImpl implements DubboTestService {
@Override
@ShenyuDubboClient(path = "/findById", desc = "Query by Id")
public DubboTest findById(final String id) {
return new DubboTest(id, "hello world shenyu Apache, findById");
}
}
annotation definition:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Inherited
public @interface ShenyuDubboClient {
String path();
String ruleName() default "";
String desc() default "";
boolean enabled() default true;
}
Annotation scanning is done through the ApacheDubboServiceBeanListener, which implements the ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> interface and starts executing the event handler method when a context refresh event occurs during the Spring container startup onApplicationEvent().
During constructor instantiation.
- Read property configuration
- Start the thread pool
- Start the registry for registering with
shenyu-admin
public class ApacheDubboServiceBeanListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
public ApacheDubboServiceBeanListener(final PropertiesConfig clientConfig, final ShenyuClientRegisterRepository shenyuClientRegisterRepository) {
Properties props = clientConfig.getProps();
String contextPath = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.CONTEXT_PATH);
String appName = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.APP_NAME);
if (StringUtils.isBlank(contextPath)) {
throw new ShenyuClientIllegalArgumentException("apache dubbo client must config the contextPath or appName");
}
this.contextPath = contextPath;
this.appName = appName;
this.host = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.HOST);
this.port = props.getProperty(ShenyuClientConstants.PORT);
executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("shenyu-apache-dubbo-client-thread-pool-%d").build());
publisher.start(shenyuClientRegisterRepository);
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(final ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
}
- ApacheDubboServiceBeanListener#onApplicationEvent()
Rewritten method logic: read Dubbo service ServiceBean, build metadata object and URI object, and register it with shenyu-admin.
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(final ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
Map<String, ServiceBean> serviceBean = contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext().getBeansOfType(ServiceBean.class);
if (serviceBean.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (!registered.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, ServiceBean> entry : serviceBean.entrySet()) {
handler(entry.getValue());
}
serviceBean.values().stream().findFirst().ifPresent(bean -> {
publisher.publishEvent(buildURIRegisterDTO(bean));
});
}
-
handler()
In the handler() method, read all methods from the serviceBean, determine if there is a ShenyuDubboClient annotation on the method, build a metadata object if it exists, and register the method with shenyu-admin through the registry.
private void handler(final ServiceBean<?> serviceBean) {
Object refProxy = serviceBean.getRef();
Class<?> clazz = refProxy.getClass();
if (AopUtils.isAopProxy(refProxy)) {
clazz = AopUtils.getTargetClass(refProxy);
}
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
ShenyuDubboClient shenyuDubboClient = method.getAnnotation(ShenyuDubboClient.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(shenyuDubboClient)) {
publisher.publishEvent(buildMetaDataDTO(serviceBean, shenyuDubboClient, method));
}
}
}
private MetaDataRegisterDTO buildMetaDataDTO(final ServiceBean<?> serviceBean, final ShenyuDubboClient shenyuDubboClient, final Method method) {
String appName = buildAppName(serviceBean);
String path = contextPath + shenyuDubboClient.path();
String desc = shenyuDubboClient.desc();
String serviceName = serviceBean.getInterface();
String configRuleName = shenyuDubboClient.ruleName();
String ruleName = ("".equals(configRuleName)) ? path : configRuleName;
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypesClazz = method.getParameterTypes();
String parameterTypes = Arrays.stream(parameterTypesClazz).map(Class::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
return MetaDataRegisterDTO.builder()
.appName(appName)
.serviceName(serviceName)
.methodName(methodName)
.contextPath(contextPath)
.host(buildHost())
.port(buildPort(serviceBean))
.path(path)
.ruleName(ruleName)
.pathDesc(desc)
.parameterTypes(parameterTypes)
.rpcExt(buildRpcExt(serviceBean))
.rpcType(RpcTypeEnum.DUBBO.getName())
.enabled(shenyuDubboClient.enabled())
.build();
}
-
buildRpcExt()
dubbo ext information.
private String buildRpcExt(final ServiceBean serviceBean) {
DubboRpcExt build = DubboRpcExt.builder()
.group(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBean.getGroup()) ? serviceBean.getGroup() : "")
.version(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBean.getVersion()) ? serviceBean.getVersion() : "")
.loadbalance(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBean.getLoadbalance()) ? serviceBean.getLoadbalance() : Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE)
.retries(Objects.isNull(serviceBean.getRetries()) ? Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES : serviceBean.getRetries())
.timeout(Objects.isNull(serviceBean.getTimeout()) ? Constants.DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT : serviceBean.getTimeout())
.sent(Objects.isNull(serviceBean.getSent()) ? Constants.DEFAULT_SENT : serviceBean.getSent())
.cluster(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBean.getCluster()) ? serviceBean.getCluster() : Constants.DEFAULT_CLUSTER)
.url("")
.build();
return GsonUtils.getInstance().toJson(build);
}
private URIRegisterDTO buildURIRegisterDTO(final ServiceBean serviceBean) {
return URIRegisterDTO.builder()
.contextPath(this.contextPath)
.appName(buildAppName(serviceBean))
.rpcType(RpcTypeEnum.DUBBO.getName())
.host(buildHost())
.port(buildPort(serviceBean))
.build();
}
The specific registration logic is implemented by the registration center, please refer to Client Access Principles .
publisher.publishEvent();
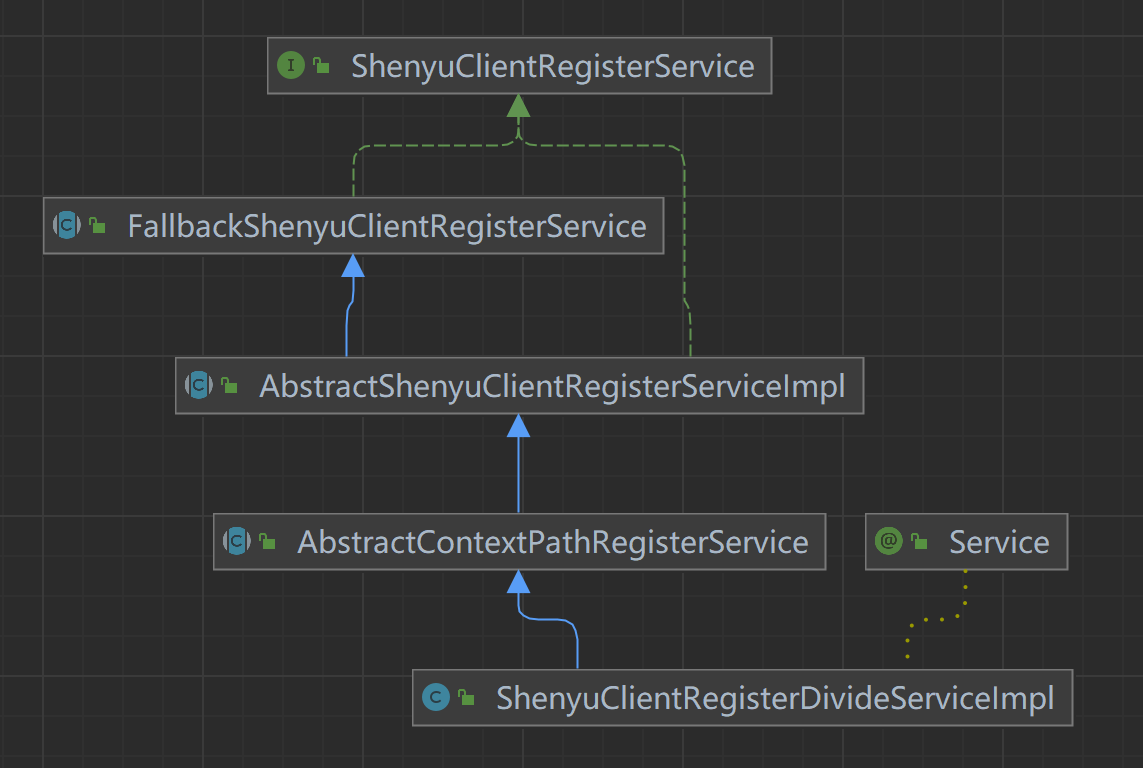
The metadata and URI data registered by the client through the registry are processed at the shenyu-admin end, which is responsible for storing to the database and synchronizing to the shenyu gateway. The client-side registration processing logic of the Dubbo plugin is in the ShenyuClientRegisterDubboServiceImpl. The inheritance relationship is as follows.
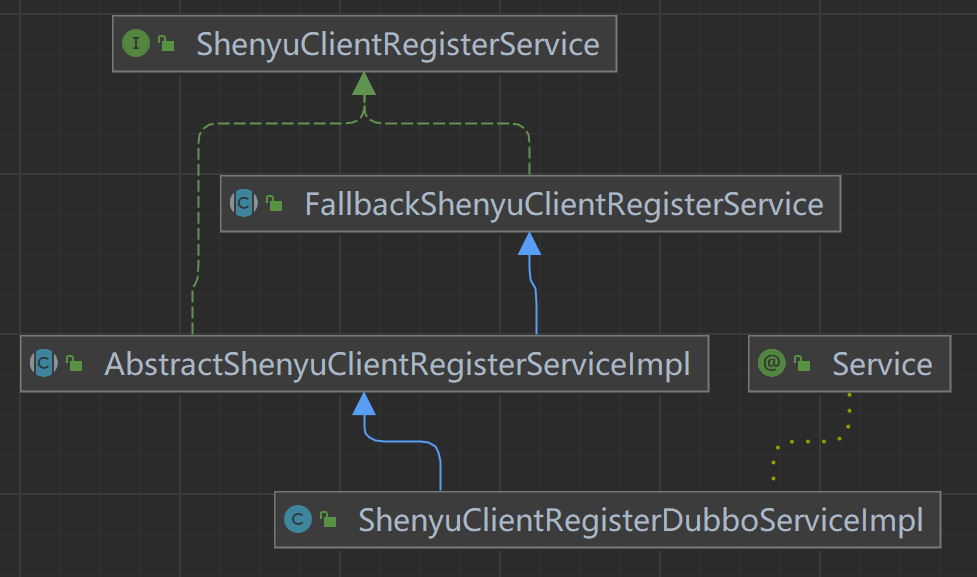
- ShenyuClientRegisterService: client registration service, top-level interface.
- FallbackShenyuClientRegisterService: registration failure, provides retry operation.
- AbstractShenyuClientRegisterServiceImpl: abstract class, implements part of the public registration logic.
- ShenyuClientRegisterDubboServiceImpl: implementation of the
Dubbo plugin registration.
1.3.1 Registration Service
-
org.apache.shenyu.admin.service.register.AbstractShenyuClientRegisterServiceImpl#register()
The metadata MetaDataRegisterDTO object registered by the client through the registry is picked up and dropped in the register() method of shenyu-admin.
@Override
public String register(final MetaDataRegisterDTO dto) {
String selectorHandler = selectorHandler(dto);
String selectorId = selectorService.registerDefault(dto, PluginNameAdapter.rpcTypeAdapter(rpcType()), selectorHandler);
String ruleHandler = ruleHandler();
RuleDTO ruleDTO = buildRpcDefaultRuleDTO(selectorId, dto, ruleHandler);
ruleService.registerDefault(ruleDTO);
registerMetadata(dto);
String contextPath = dto.getContextPath();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(contextPath)) {
registerContextPath(dto);
}
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
1.3.1.1 Register Selector
- org.apache.shenyu.admin.service.impl.SelectorServiceImpl#registerDefault()
Construct contextPath, find if the selector information exists, if it does, return id; if it doesn't, create the default selector information.
@Override
public String registerDefault(final MetaDataRegisterDTO dto, final String pluginName, final String selectorHandler) {
String contextPath = ContextPathUtils.buildContextPath(dto.getContextPath(), dto.getAppName());
SelectorDO selectorDO = findByNameAndPluginName(contextPath, pluginName);
if (Objects.isNull(selectorDO)) {
return registerSelector(contextPath, pluginName, selectorHandler);
}
return selectorDO.getId();
}
private String registerSelector(final String contextPath, final String pluginName, final String selectorHandler) {
SelectorDTO selectorDTO = buildSelectorDTO(contextPath, pluginMapper.selectByName(pluginName).getId());
selectorDTO.setHandle(selectorHandler);
return registerDefault(selectorDTO);
}
private SelectorDTO buildSelectorDTO(final String contextPath, final String pluginId) {
SelectorDTO selectorDTO = buildDefaultSelectorDTO(contextPath);
selectorDTO.setPluginId(pluginId);
selectorDTO.setSelectorConditions(buildDefaultSelectorConditionDTO(contextPath));
return selectorDTO;
}
private SelectorDTO buildDefaultSelectorDTO(final String name) {
return SelectorDTO.builder()
.name(name)
.type(SelectorTypeEnum.CUSTOM_FLOW.getCode())
.matchMode(MatchModeEnum.AND.getCode())
.enabled(Boolean.TRUE)
.loged(Boolean.TRUE)
.continued(Boolean.TRUE)
.sort(1)
.build();
}
- Build default selector conditional properties
private List<SelectorConditionDTO> buildDefaultSelectorConditionDTO(final String contextPath) {
SelectorConditionDTO selectorConditionDTO = new SelectorConditionDTO();
selectorConditionDTO.setParamType(ParamTypeEnum.URI.getName());
selectorConditionDTO.setParamName("/");
selectorConditionDTO.setOperator(OperatorEnum.MATCH.getAlias());
selectorConditionDTO.setParamValue(contextPath + AdminConstants.URI_SUFFIX);
return Collections.singletonList(selectorConditionDTO);
}
- Register default selector
@Override
public String registerDefault(final SelectorDTO selectorDTO) {
SelectorDO selectorDO = SelectorDO.buildSelectorDO(selectorDTO);
List<SelectorConditionDTO> selectorConditionDTOs = selectorDTO.getSelectorConditions();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(selectorDTO.getId())) {
selectorMapper.insertSelective(selectorDO);
selectorConditionDTOs.forEach(selectorConditionDTO -> {
selectorConditionDTO.setSelectorId(selectorDO.getId());
selectorConditionMapper.insertSelective(SelectorConditionDO.buildSelectorConditionDO(selectorConditionDTO));
});
}
publishEvent(selectorDO, selectorConditionDTOs);
return selectorDO.getId();
}
1.3.1.2 Registration Rules
In the second step of registering the service, start building the default rules and then register the rules.
@Override
public String register(final MetaDataRegisterDTO dto) {
String ruleHandler = ruleHandler();
RuleDTO ruleDTO = buildRpcDefaultRuleDTO(selectorId, dto, ruleHandler);
ruleService.registerDefault(ruleDTO);
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
@Override
protected String ruleHandler() {
return new DubboRuleHandle().toJson();
}
Dubbo plugin default rule handling properties.
public class DubboRuleHandle implements RuleHandle {
private String version;
private String group;
private Integer retries = 0;
private String loadbalance = LoadBalanceEnum.RANDOM.getName();
private long timeout = Constants.TIME_OUT;
}
private RuleDTO buildRpcDefaultRuleDTO(final String selectorId, final MetaDataRegisterDTO metaDataDTO, final String ruleHandler) {
return buildRuleDTO(selectorId, ruleHandler, metaDataDTO.getRuleName(), metaDataDTO.getPath());
}
private RuleDTO buildRuleDTO(final String selectorId, final String ruleHandler, final String ruleName, final String path) {
RuleDTO ruleDTO = RuleDTO.builder()
.selectorId(selectorId)
.name(ruleName)
.matchMode(MatchModeEnum.AND.getCode())
.enabled(Boolean.TRUE)
.loged(Boolean.TRUE)
.sort(1)
.handle(ruleHandler)
.build();
RuleConditionDTO ruleConditionDTO = RuleConditionDTO.builder()
.paramType(ParamTypeEnum.URI.getName())
.paramName("/")
.paramValue(path)
.build();
if (path.indexOf("*") > 1) {
ruleConditionDTO.setOperator(OperatorEnum.MATCH.getAlias());
} else {
ruleConditionDTO.setOperator(OperatorEnum.EQ.getAlias());
}
ruleDTO.setRuleConditions(Collections.singletonList(ruleConditionDTO));
return ruleDTO;
}
- org.apache.shenyu.admin.service.impl.RuleServiceImpl#registerDefault()
Registration rules: insert records to the database and publish events to the gateway for data synchronization.
@Override
public String registerDefault(final RuleDTO ruleDTO) {
RuleDO exist = ruleMapper.findBySelectorIdAndName(ruleDTO.getSelectorId(), ruleDTO.getName());
if (Objects.nonNull(exist)) {
return "";
}
RuleDO ruleDO = RuleDO.buildRuleDO(ruleDTO);
List<RuleConditionDTO> ruleConditions = ruleDTO.getRuleConditions();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ruleDTO.getId())) {
ruleMapper.insertSelective(ruleDO);
ruleConditions.forEach(ruleConditionDTO -> {
ruleConditionDTO.setRuleId(ruleDO.getId());
ruleConditionMapper.insertSelective(RuleConditionDO.buildRuleConditionDO(ruleConditionDTO));
});
}
publishEvent(ruleDO, ruleConditions);
return ruleDO.getId();
}
Metadata is mainly used for RPC service calls.
@Override
public String register(final MetaDataRegisterDTO dto) {
registerMetadata(dto);
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
@Override
protected void registerMetadata(final MetaDataRegisterDTO dto) {
MetaDataService metaDataService = getMetaDataService();
MetaDataDO exist = metaDataService.findByPath(dto.getPath());
metaDataService.saveOrUpdateMetaData(exist, dto);
}
@Override
public void saveOrUpdateMetaData(final MetaDataDO exist, final MetaDataRegisterDTO metaDataDTO) {
DataEventTypeEnum eventType;
MetaDataDO metaDataDO = MetaDataTransfer.INSTANCE.mapRegisterDTOToEntity(metaDataDTO);
if (Objects.isNull(exist)) {
Timestamp currentTime = new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
metaDataDO.setId(UUIDUtils.getInstance().generateShortUuid());
metaDataDO.setDateCreated(currentTime);
metaDataDO.setDateUpdated(currentTime);
metaDataMapper.insert(metaDataDO);
eventType = DataEventTypeEnum.CREATE;
} else {
metaDataDO.setId(exist.getId());
metaDataMapper.update(metaDataDO);
eventType = DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE;
}
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DataChangedEvent(ConfigGroupEnum.META_DATA, eventType,
Collections.singletonList(MetaDataTransfer.INSTANCE.mapToData(metaDataDO))));
}
1.3.2 Register URI
- org.apache.shenyu.admin.service.register.FallbackShenyuClientRegisterService#registerURI()
The server side receives the URI information registered by the client and processes it.
@Override
public String registerURI(final String selectorName, final List<URIRegisterDTO> uriList) {
String result;
String key = key(selectorName);
try {
this.removeFallBack(key);
result = this.doRegisterURI(selectorName, uriList);
logger.info("Register success: {},{}", selectorName, uriList);
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Register exception: cause:{}", ex.getMessage());
result = "";
this.addFallback(key, new FallbackHolder(selectorName, uriList));
}
return result;
}
- org.apache.shenyu.admin.service.register.AbstractShenyuClientRegisterServiceImpl#doRegisterURI()
Get a valid URI from the URI registered by the client, update the corresponding selector handle property, and send a selector update event to the gateway.
@Override
public String doRegisterURI(final String selectorName, final List<URIRegisterDTO> uriList) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(uriList)) {
return "";
}
SelectorDO selectorDO = selectorService.findByNameAndPluginName(selectorName, PluginNameAdapter.rpcTypeAdapter(rpcType()));
if (Objects.isNull(selectorDO)) {
throw new ShenyuException("doRegister Failed to execute,wait to retry.");
}
List<URIRegisterDTO> validUriList = uriList.stream().filter(dto -> Objects.nonNull(dto.getPort()) && StringUtils.isNotBlank(dto.getHost())).collect(Collectors.toList());
String handler = buildHandle(validUriList, selectorDO);
if (handler != null) {
selectorDO.setHandle(handler);
SelectorData selectorData = selectorService.buildByName(selectorName, PluginNameAdapter.rpcTypeAdapter(rpcType()));
selectorData.setHandle(handler);
selectorService.updateSelective(selectorDO);
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DataChangedEvent(ConfigGroupEnum.SELECTOR, DataEventTypeEnum.UPDATE, Collections.singletonList(selectorData)));
}
return ShenyuResultMessage.SUCCESS;
}
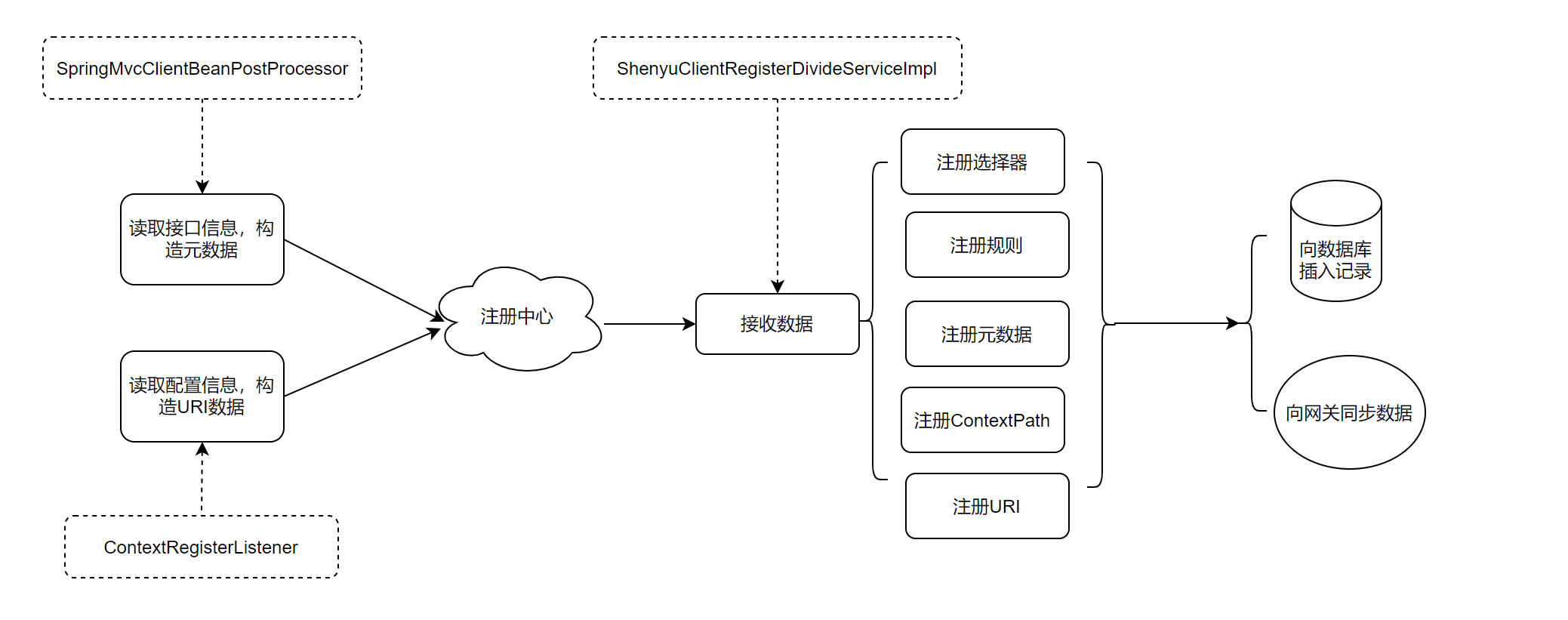
The source code analysis on service registration is completed as well as the analysis flow chart is as follows.
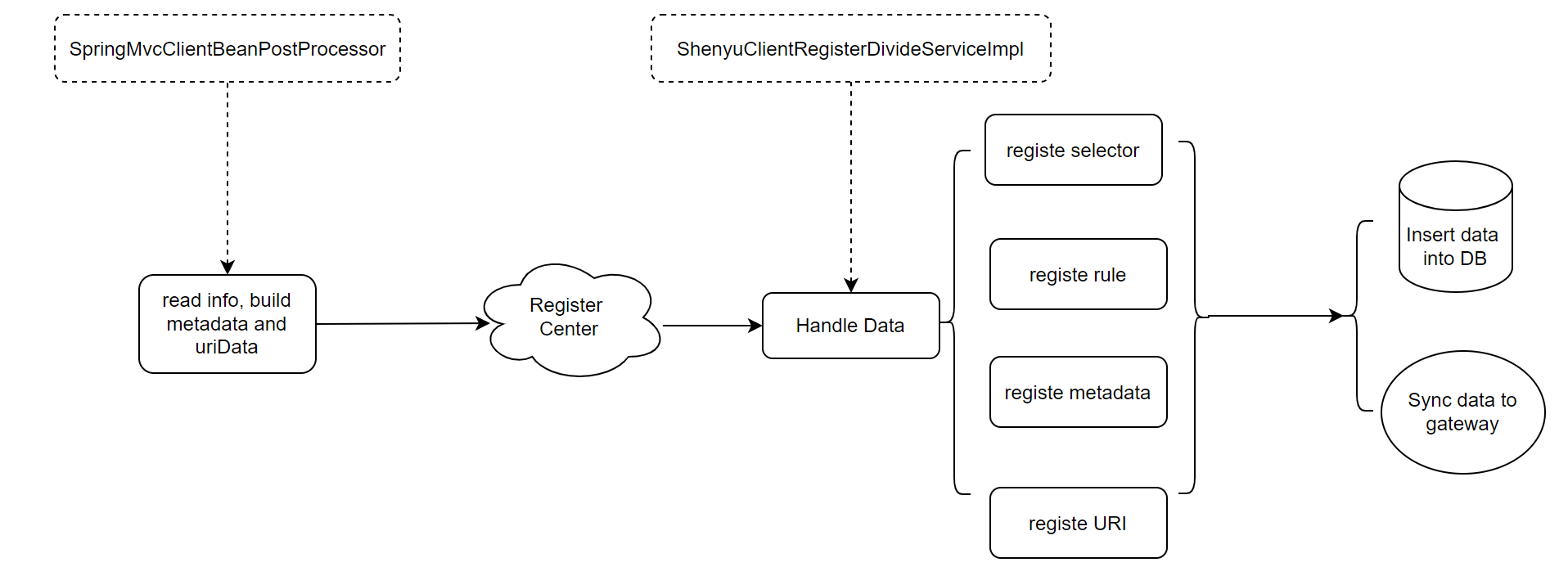
The next step is to analyze how the dubbo plugin initiates calls to the http service based on this information.
2. Service Invocation
The dubbo plugin is the core processing plugin used by the ShenYu gateway to convert http requests into the dubbo protocol and invoke the dubbo service.
Take the case provided by the official website Quick Start with Dubbo as an example, a dubbo service is registered with shenyu-admin through the registry, and then requested through the ShenYu gateway proxy, the request is as follows.
GET http://localhost:9195/dubbo/findById?id=100
Accept: application/json
The class inheritance relationship in the Dubbo plugin is as follows.
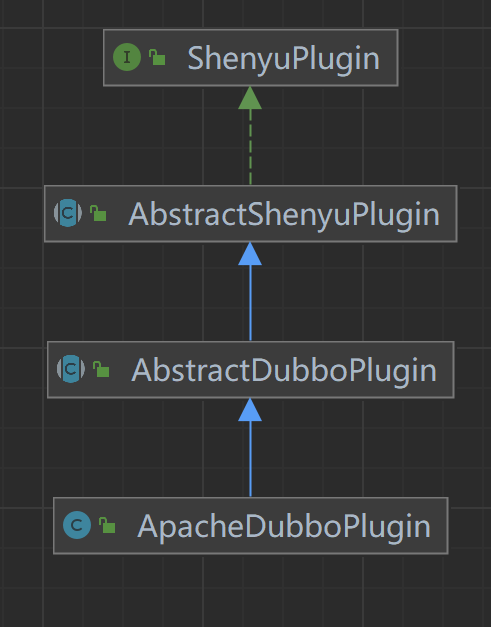
- ShenyuPlugin: top-level interface, defining interface methods.
- AbstractShenyuPlugin: abstract class that implements plugin common logic.
- AbstractDubboPlugin: dubbo plugin abstract class, implementing
dubbo common logic.
- ApacheDubboPlugin: ApacheDubbo plugin.
ShenYu Gateway supports ApacheDubbo and AlibabaDubbo\
2.1 Receive requests
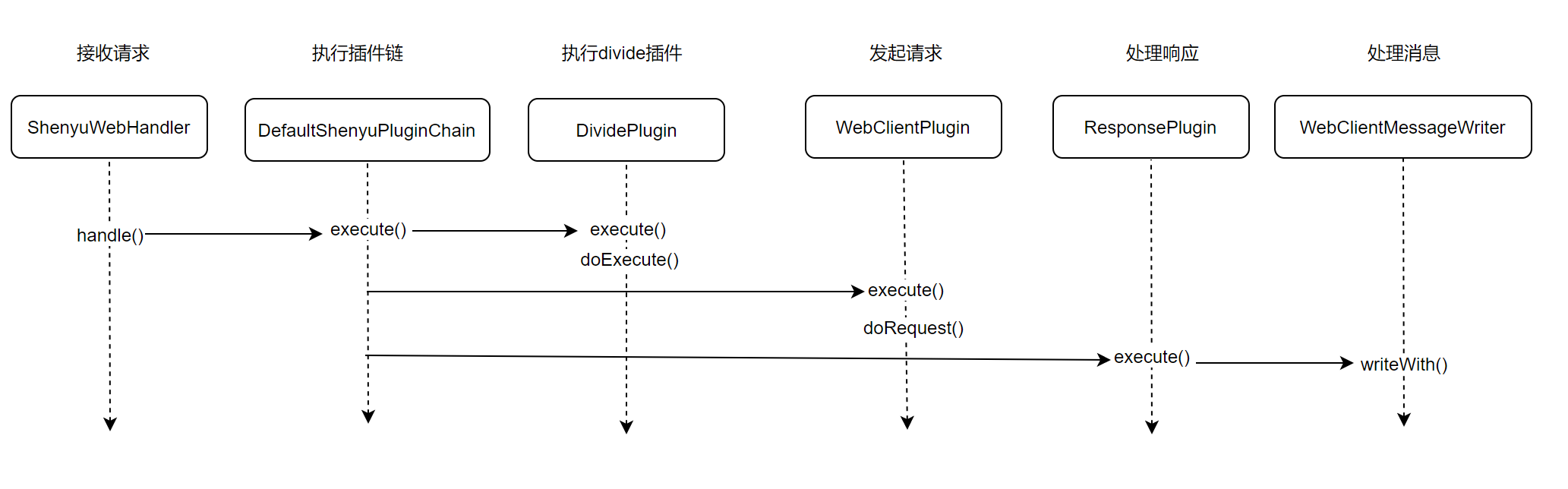
After passing the ShenYu gateway proxy, the request entry is ShenyuWebHandler, which implements the org.springframework.web.server.WebHandler interface.
public final class ShenyuWebHandler implements WebHandler, ApplicationListener<SortPluginEvent> {
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(@NonNull final ServerWebExchange exchange) {
Mono<Void> execute = new DefaultShenyuPluginChain(plugins).execute(exchange);
if (scheduled) {
return execute.subscribeOn(scheduler);
}
return execute;
}
private static class DefaultShenyuPluginChain implements ShenyuPluginChain {
private int index;
private final List<ShenyuPlugin> plugins;
DefaultShenyuPluginChain(final List<ShenyuPlugin> plugins) {
this.plugins = plugins;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> execute(final ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return Mono.defer(() -> {
if (this.index < plugins.size()) {
ShenyuPlugin plugin = plugins.get(this.index++);
boolean skip = plugin.skip(exchange);
if (skip) {
return this.execute(exchange);
}
return plugin.execute(exchange, this);
}
return Mono.empty();
});
}
}
}
2.2 Match Rule
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.base.AbstractShenyuPlugin#execute()
Execute the matching logic for selectors and rules in the execute() method.
- Matching selectors.
- Matching rules.
- Execute the plugin.
@Override
public Mono<Void> execute(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
String pluginName = named();
PluginData pluginData = BaseDataCache.getInstance().obtainPluginData(pluginName);
if (pluginData != null && pluginData.getEnabled()) {
final Collection<SelectorData> selectors = BaseDataCache.getInstance().obtainSelectorData(pluginName);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(selectors)) {
return handleSelectorIfNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
SelectorData selectorData = matchSelector(exchange, selectors);
if (Objects.isNull(selectorData)) {
return handleSelectorIfNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
selectorLog(selectorData, pluginName);
List<RuleData> rules = BaseDataCache.getInstance().obtainRuleData(selectorData.getId());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(rules)) {
return handleRuleIfNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
RuleData rule;
if (selectorData.getType() == SelectorTypeEnum.FULL_FLOW.getCode()) {
rule = rules.get(rules.size() - 1);
} else {
rule = matchRule(exchange, rules);
}
if (Objects.isNull(rule)) {
return handleRuleIfNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
ruleLog(rule, pluginName);
return doExecute(exchange, chain, selectorData, rule);
}
return chain.execute(exchange);
}
2.3 Execute GlobalPlugin
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.global.GlobalPlugin#execute()
GlobalPlugin is a global plugin that constructs contextual information in the execute() method.
public class GlobalPlugin implements ShenyuPlugin {
private final ShenyuContextBuilder builder;
@Override
public Mono<Void> execute(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
ShenyuContext shenyuContext = builder.build(exchange);
exchange.getAttributes().put(Constants.CONTEXT, shenyuContext);
return chain.execute(exchange);
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.global.DefaultShenyuContextBuilder#build()
Build the default context information.
public class DefaultShenyuContextBuilder implements ShenyuContextBuilder {
@Override
public ShenyuContext build(final ServerWebExchange exchange) {
Pair<String, MetaData> buildData = buildData(exchange);
return decoratorMap.get(buildData.getLeft()).decorator(buildDefaultContext(exchange.getRequest()), buildData.getRight());
}
private Pair<String, MetaData> buildData(final ServerWebExchange exchange) {
MetaData metaData = MetaDataCache.getInstance().obtain(request.getURI().getPath());
if (Objects.nonNull(metaData) && Boolean.TRUE.equals(metaData.getEnabled())) {
exchange.getAttributes().put(Constants.META_DATA, metaData);
return Pair.of(metaData.getRpcType(), metaData);
} else {
return Pair.of(RpcTypeEnum.HTTP.getName(), new MetaData());
}
}
private ShenyuContext buildDefaultContext(final ServerHttpRequest request) {
String appKey = request.getHeaders().getFirst(Constants.APP_KEY);
String sign = request.getHeaders().getFirst(Constants.SIGN);
String timestamp = request.getHeaders().getFirst(Constants.TIMESTAMP);
ShenyuContext shenyuContext = new ShenyuContext();
String path = request.getURI().getPath();
shenyuContext.setPath(path);
shenyuContext.setAppKey(appKey);
shenyuContext.setSign(sign);
shenyuContext.setTimestamp(timestamp);
shenyuContext.setStartDateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
Optional.ofNullable(request.getMethod()).ifPresent(httpMethod -> shenyuContext.setHttpMethod(httpMethod.name()));
return shenyuContext;
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.dubbo.common.context.DubboShenyuContextDecorator#decorator()
wrap ShenyuContext:
public class DubboShenyuContextDecorator implements ShenyuContextDecorator {
@Override
public ShenyuContext decorator(final ShenyuContext shenyuContext, final MetaData metaData) {
shenyuContext.setModule(metaData.getAppName());
shenyuContext.setMethod(metaData.getServiceName());
shenyuContext.setContextPath(metaData.getContextPath());
shenyuContext.setRpcType(RpcTypeEnum.DUBBO.getName());
return shenyuContext;
}
@Override
public String rpcType() {
return RpcTypeEnum.DUBBO.getName();
}
}
The RpcParamTransformPlugin is responsible for reading the parameters from the http request, saving them in the exchange and passing them to the rpc service.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.base.RpcParamTransformPlugin#execute()
In the execute() method, the core logic of the plugin is executed: get the request information from exchange and process the parameters according to the form of content passed in by the request.
public class RpcParamTransformPlugin implements ShenyuPlugin {
@Override
public Mono<Void> execute(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
ShenyuContext shenyuContext = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.CONTEXT);
if (Objects.nonNull(shenyuContext)) {
MediaType mediaType = request.getHeaders().getContentType();
if (MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON.isCompatibleWith(mediaType)) {
return body(exchange, request, chain);
}
if (MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED.isCompatibleWith(mediaType)) {
return formData(exchange, request, chain);
}
return query(exchange, request, chain);
}
return chain.execute(exchange);
}
private Mono<Void> body(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
return Mono.from(DataBufferUtils.join(serverHttpRequest.getBody())
.flatMap(body -> {
exchange.getAttributes().put(Constants.PARAM_TRANSFORM, resolveBodyFromRequest(body));
return chain.execute(exchange);
}));
}
private Mono<Void> formData(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
return Mono.from(DataBufferUtils.join(serverHttpRequest.getBody())
.flatMap(map -> {
String param = resolveBodyFromRequest(map);
LinkedMultiValueMap<String, String> linkedMultiValueMap;
try {
linkedMultiValueMap = BodyParamUtils.buildBodyParams(URLDecoder.decode(param, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
return Mono.error(e);
}
exchange.getAttributes().put(Constants.PARAM_TRANSFORM, HttpParamConverter.toMap(() -> linkedMultiValueMap));
return chain.execute(exchange);
}));
}
private Mono<Void> query(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
exchange.getAttributes().put(Constants.PARAM_TRANSFORM, HttpParamConverter.ofString(() -> serverHttpRequest.getURI().getQuery()));
return chain.execute(exchange);
}
}
2.5 Execute DubboPlugin
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.dubbo.common.AbstractDubboPlugin#doExecute()
In the doExecute() method, the main purpose is to check the metadata and parameters.
public abstract class AbstractDubboPlugin extends AbstractShenyuPlugin {
@Override
public Mono<Void> doExecute(final ServerWebExchange exchange,
final ShenyuPluginChain chain,
final SelectorData selector,
final RuleData rule) {
String param = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.PARAM_TRANSFORM);
ShenyuContext shenyuContext = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.CONTEXT);
assert shenyuContext != null;
MetaData metaData = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.META_DATA);
if (!checkMetaData(metaData)) {
LOG.error(" path is : {}, meta data have error : {}", shenyuContext.getPath(), metaData);
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
Object error = ShenyuResultWrap.error(exchange, ShenyuResultEnum.META_DATA_ERROR, null);
return WebFluxResultUtils.result(exchange, error);
}
if (Objects.nonNull(metaData) && StringUtils.isNoneBlank(metaData.getParameterTypes()) && StringUtils.isBlank(param)) {
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
Object error = ShenyuResultWrap.error(exchange, ShenyuResultEnum.DUBBO_HAVE_BODY_PARAM, null);
return WebFluxResultUtils.result(exchange, error);
}
this.rpcContext(exchange);
return this.doDubboInvoker(exchange, chain, selector, rule, metaData, param);
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.apache.dubbo.ApacheDubboPlugin#doDubboInvoker()
Set special context information in the doDubboInvoker() method, and then start the dubbo generalization call.
public class ApacheDubboPlugin extends AbstractDubboPlugin {
@Override
protected Mono<Void> doDubboInvoker(final ServerWebExchange exchange,
final ShenyuPluginChain chain,
final SelectorData selector,
final RuleData rule,
final MetaData metaData,
final String param) {
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(Constants.DUBBO_SELECTOR_ID, selector.getId());
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(Constants.DUBBO_RULE_ID, rule.getId());
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(Constants.DUBBO_REMOTE_ADDRESS, Objects.requireNonNull(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress()).getAddress().getHostAddress());
final Mono<Object> result = dubboProxyService.genericInvoker(param, metaData, exchange);
return result.then(chain.execute(exchange));
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.apache.dubbo.proxy.ApacheDubboProxyService#genericInvoker()
genericInvoker() method.
- Gets the
ReferenceConfig object.
- Gets the generalization service
GenericService object.
- Constructs the request parameter
pair object.
- Initiates an asynchronous generalization invocation.
public class ApacheDubboProxyService {
public Mono<Object> genericInvoker(final String body, final MetaData metaData, final ServerWebExchange exchange) throws ShenyuException {
ReferenceConfig<GenericService> reference = ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().get(metaData.getPath());
if (Objects.isNull(reference) || StringUtils.isEmpty(reference.getInterface())) {
ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().invalidate(metaData.getPath());
reference = ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().initRef(metaData);
}
GenericService genericService = reference.get();
Pair<String[], Object[]> pair;
if (StringUtils.isBlank(metaData.getParameterTypes()) || ParamCheckUtils.dubboBodyIsEmpty(body)) {
pair = new ImmutablePair<>(new String[]{}, new Object[]{});
} else {
pair = dubboParamResolveService.buildParameter(body, metaData.getParameterTypes());
}
return Mono.fromFuture(invokeAsync(genericService, metaData.getMethodName(), pair.getLeft(), pair.getRight()).thenApply(ret -> {
if (Objects.isNull(ret)) {
ret = Constants.DUBBO_RPC_RESULT_EMPTY;
}
exchange.getAttributes().put(Constants.RPC_RESULT, ret);
exchange.getAttributes().put(Constants.CLIENT_RESPONSE_RESULT_TYPE, ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getName());
return ret;
})).onErrorMap(exception -> exception instanceof GenericException ? new ShenyuException(((GenericException) exception).getExceptionMessage()) : new ShenyuException(exception));
}
private CompletableFuture<Object> invokeAsync(final GenericService genericService, final String method, final String[] parameterTypes, final Object[] args) throws GenericException {
genericService.$invoke(method, parameterTypes, args);
Object resultFromFuture = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture();
return resultFromFuture instanceof CompletableFuture ? (CompletableFuture<Object>) resultFromFuture : CompletableFuture.completedFuture(resultFromFuture);
}
}
Calling the dubbo service at the gateway can be achieved by generalizing the call.
The ReferenceConfig object is the key object to support generalization calls , and its initialization operation is done during data synchronization. There are two parts of data involved here, one is the synchronized plugin handler information and the other is the synchronized plugin metadata information.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.dubbo.common.handler.AbstractDubboPluginDataHandler#handlerPlugin()
When the plugin data is updated, the data synchronization module synchronizes the data from shenyu-admin to the gateway. The initialization operation is performed in handlerPlugin().
public abstract class AbstractDubboPluginDataHandler implements PluginDataHandler {
protected abstract void initConfigCache(DubboRegisterConfig dubboRegisterConfig);
@Override
public void handlerPlugin(final PluginData pluginData) {
if (Objects.nonNull(pluginData) && Boolean.TRUE.equals(pluginData.getEnabled())) {
DubboRegisterConfig dubboRegisterConfig = GsonUtils.getInstance().fromJson(pluginData.getConfig(), DubboRegisterConfig.class);
DubboRegisterConfig exist = Singleton.INST.get(DubboRegisterConfig.class);
if (Objects.isNull(dubboRegisterConfig)) {
return;
}
if (Objects.isNull(exist) || !dubboRegisterConfig.equals(exist)) {
this.initConfigCache(dubboRegisterConfig);
}
Singleton.INST.single(DubboRegisterConfig.class, dubboRegisterConfig);
}
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.apache.dubbo.handler.ApacheDubboPluginDataHandler#initConfigCache()
Perform initialization operations.
public class ApacheDubboPluginDataHandler extends AbstractDubboPluginDataHandler {
@Override
protected void initConfigCache(final DubboRegisterConfig dubboRegisterConfig) {
ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().init(dubboRegisterConfig);
ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().invalidateAll();
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.apache.dubbo.cache.ApacheDubboConfigCache#init()
In the initialization, set registryConfig and consumerConfig.
public final class ApacheDubboConfigCache extends DubboConfigCache {
public void init(final DubboRegisterConfig dubboRegisterConfig) {
if (Objects.isNull(applicationConfig)) {
applicationConfig = new ApplicationConfig("shenyu_proxy");
}
if (needUpdateRegistryConfig(dubboRegisterConfig)) {
RegistryConfig registryConfigTemp = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfigTemp.setProtocol(dubboRegisterConfig.getProtocol());
registryConfigTemp.setId("shenyu_proxy");
registryConfigTemp.setRegister(false);
registryConfigTemp.setAddress(dubboRegisterConfig.getRegister()); Optional.ofNullable(dubboRegisterConfig.getGroup()).ifPresent(registryConfigTemp::setGroup);
registryConfig = registryConfigTemp;
}
if (Objects.isNull(consumerConfig)) {
consumerConfig = ApplicationModel.getConfigManager().getDefaultConsumer().orElseGet(() -> {
ConsumerConfig consumerConfig = new ConsumerConfig();
consumerConfig.refresh();
return consumerConfig;
});
Optional.ofNullable(dubboRegisterConfig.getThreadpool()).ifPresent(consumerConfig::setThreadpool);
Optional.ofNullable(dubboRegisterConfig.getCorethreads()).ifPresent(consumerConfig::setCorethreads);
Optional.ofNullable(dubboRegisterConfig.getThreads()).ifPresent(consumerConfig::setThreads);
Optional.ofNullable(dubboRegisterConfig.getQueues()).ifPresent(consumerConfig::setQueues);
}
}
private boolean needUpdateRegistryConfig(final DubboRegisterConfig dubboRegisterConfig) {
if (Objects.isNull(registryConfig)) {
return true;
}
return !Objects.equals(dubboRegisterConfig.getProtocol(), registryConfig.getProtocol())
|| !Objects.equals(dubboRegisterConfig.getRegister(), registryConfig.getAddress())
|| !Objects.equals(dubboRegisterConfig.getProtocol(), registryConfig.getProtocol());
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.apache.dubbo.subscriber.ApacheDubboMetaDataSubscriber#onSubscribe()
When the metadata is updated, the data synchronization module synchronizes the data from shenyu-admin to the gateway. The metadata update operation is performed in the onSubscribe() method.
public class ApacheDubboMetaDataSubscriber implements MetaDataSubscriber {
private static final ConcurrentMap<String, MetaData> META_DATA = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
public void onSubscribe(final MetaData metaData) {
if (RpcTypeEnum.DUBBO.getName().equals(metaData.getRpcType())) {
MetaData exist = META_DATA.get(metaData.getPath());
if (Objects.isNull(exist) || Objects.isNull(ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().get(metaData.getPath()))) {
ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().initRef(metaData);
} else {
if (!Objects.equals(metaData.getServiceName(), exist.getServiceName())
|| !Objects.equals(metaData.getRpcExt(), exist.getRpcExt())
|| !Objects.equals(metaData.getParameterTypes(), exist.getParameterTypes())
|| !Objects.equals(metaData.getMethodName(), exist.getMethodName())) {
ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().build(metaData);
}
}
META_DATA.put(metaData.getPath(), metaData);
}
}
public void unSubscribe(final MetaData metaData) {
if (RpcTypeEnum.DUBBO.getName().equals(metaData.getRpcType())) {
ApacheDubboConfigCache.getInstance().invalidate(metaData.getPath());
META_DATA.remove(metaData.getPath());
}
}
}
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.apache.dubbo.cache.ApacheDubboConfigCache#initRef()
Build ReferenceConfig objects from metaData.
public final class ApacheDubboConfigCache extends DubboConfigCache {
public ReferenceConfig<GenericService> initRef(final MetaData metaData) {
try {
ReferenceConfig<GenericService> referenceConfig = cache.get(metaData.getPath());
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(referenceConfig.getInterface())) {
return referenceConfig;
}
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
LOG.error("init dubbo ref exception", e);
}
return build(metaData);
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public ReferenceConfig<GenericService> build(final MetaData metaData) {
if (Objects.isNull(applicationConfig) || Objects.isNull(registryConfig)) {
return new ReferenceConfig<>();
}
ReferenceConfig<GenericService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<>();
reference.setGeneric("true");
reference.setAsync(true);
reference.setApplication(applicationConfig);
reference.setRegistry(registryConfig);
reference.setConsumer(consumerConfig);
reference.setInterface(metaData.getServiceName());
reference.setProtocol("dubbo");
reference.setCheck(false);
reference.setLoadbalance("gray");
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<>(2);
parameters.put("dispatcher", "direct");
reference.setParameters(parameters);
String rpcExt = metaData.getRpcExt();
DubboParam dubboParam = parserToDubboParam(rpcExt);
if (Objects.nonNull(dubboParam)) {
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(dubboParam.getVersion())) {
reference.setVersion(dubboParam.getVersion());
}
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(dubboParam.getGroup())) {
reference.setGroup(dubboParam.getGroup());
}
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(dubboParam.getUrl())) {
reference.setUrl(dubboParam.getUrl());
}
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(dubboParam.getCluster())) {
reference.setCluster(dubboParam.getCluster());
}
Optional.ofNullable(dubboParam.getTimeout()).ifPresent(reference::setTimeout);
Optional.ofNullable(dubboParam.getRetries()).ifPresent(reference::setRetries);
Optional.ofNullable(dubboParam.getSent()).ifPresent(reference::setSent);
}
try {
Object obj = reference.get();
if (Objects.nonNull(obj)) {
LOG.info("init apache dubbo reference success there meteData is :{}", metaData);
cache.put(metaData.getPath(), reference);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("init apache dubbo reference exception", e);
}
return reference;
}
}
2.6 Execute ResponsePlugin
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.response.ResponsePlugin#execute()
The response results are handled by the ResponsePlugin plugin.
@Override
public Mono<Void> execute(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
ShenyuContext shenyuContext = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.CONTEXT);
assert shenyuContext != null;
return writerMap.get(shenyuContext.getRpcType()).writeWith(exchange, chain);
}
The processing type is determined by MessageWriter and the class inheritance relationship is as follows.
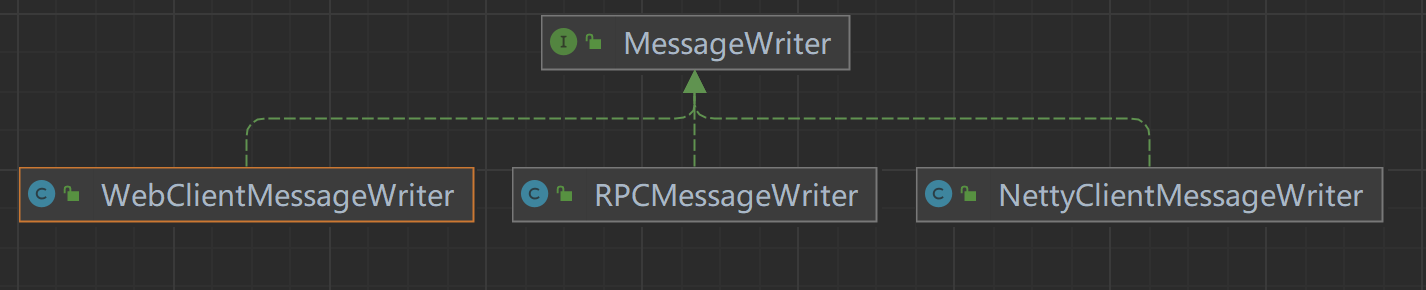
- MessageWriter: interface, defining message processing methods.
- NettyClientMessageWriter: processing of
Netty call results.
- RPCMessageWriter: processing the results of
RPC calls.
- WebClientMessageWriter: processing the results of
WebClient calls.
Dubbo service call, the processing result is RPCMessageWriter of course.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.response.strategy.RPCMessageWriter#writeWith()
Process the response results in the writeWith() method.
public class RPCMessageWriter implements MessageWriter {
@Override
public Mono<Void> writeWith(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final ShenyuPluginChain chain) {
return chain.execute(exchange).then(Mono.defer(() -> {
Object result = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.RPC_RESULT);
if (Objects.isNull(result)) {
Object error = ShenyuResultWrap.error(exchange, ShenyuResultEnum.SERVICE_RESULT_ERROR, null);
return WebFluxResultUtils.result(exchange, error);
}
return WebFluxResultUtils.result(exchange, result);
}));
}
}
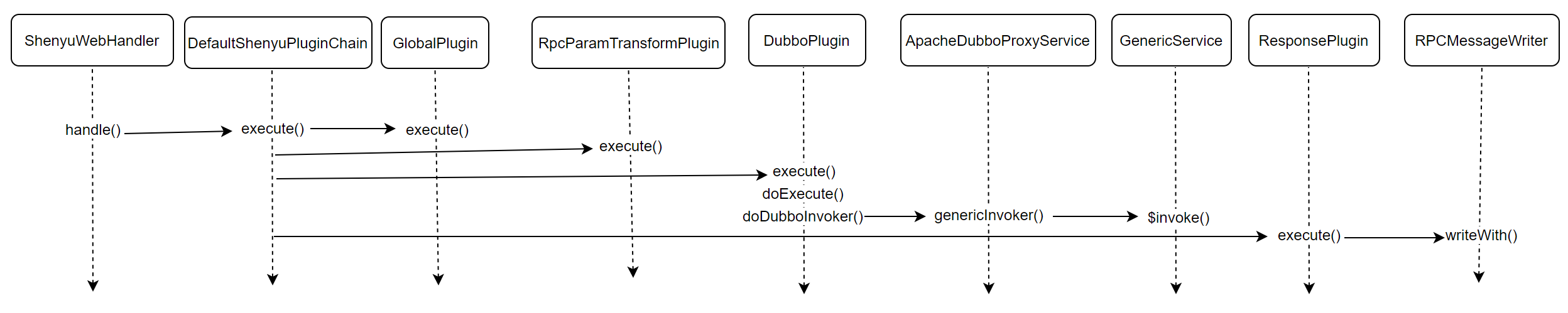
At this point in the analysis, the source code analysis of the Dubbo plugin is complete, and the analysis flow chart is as follows.
3. Summary
The source code analysis in this article starts from Dubbo service registration to Dubbo plug-in service calls. The Dubbo plugin is mainly used to handle the conversion of http requests to the dubbo protocol, and the main logic is implemented through generalized calls.