Apache ShenYu is an asynchronous, high-performance, cross-language, responsive API gateway.
background
Recently,when I read the source code of open source project Apache Shenyu API gateway,I find and many core components of the gateway are loaded with the SPI module. Here I will analyzes the source code of SPI module in Shenyu gateway.
what is SPI
SPI means 'Service Provider Interface', which is a dynamic Service discovery mechanism. We can dynamically load the implementation class of the Interface based on the runtime of the Interface (that is, a development mode of Interface programming + strategy pattern + configuration file) with it. The most common is the built-in database Driver interface 'java.sql.Driver' in JDK. Different vendors can implement this interface differently. For example, 'MySQL' ('com.mysql.jdbc.Driver' in the 'MySQL' Driver package),' PostgreSQL' ('org.postgresql.driver' in the 'PostgreSQL' Driver package), etc.
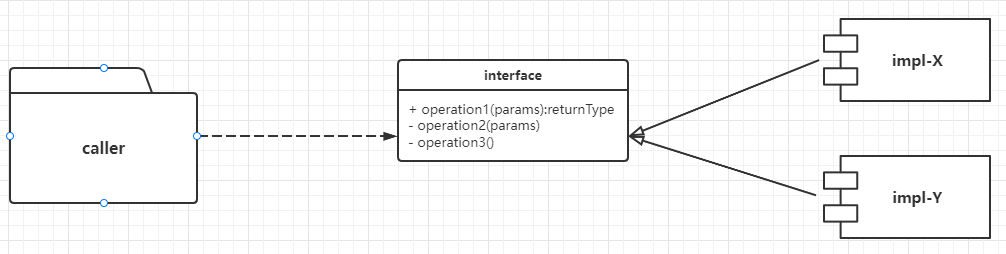
The JDK's built-in 'SPI' can be used as follows:
-
In the 'META-INF/services' directory of the classpath, create a file named with the fully qualified name of the interface (essentially a 'properties' file) whose implementation classes you want the SPI loader to load , for example if you want to load the SQL driver implementation classes mentioned above then create a file named 'java.sql.Driver' since those classes implement the 'java.sql.driver' interface.
-
In this file we can add entries for all the specific implementations of the interface . For example for the above driver class scenario we would add entries as shown in below code snippet in the file META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver
# content of file META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
org.postgresql.Driver
- Finally load the file with 'java.util.ServiceLoader' to instantiate the corresponding implementation class of the interface
ServiceLoader<Driver> loader = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class)
The underlying implementation involves classloading, the parent delegate model, and so on, which I won't expand here. Based on this design idea, many mainstream frameworks self-implemented a set of 'SPI' extension, such as 'Dubbo SPI' extension module, which would read the 'META-INF/services/dubbo' directory file content in the classppath for class loading. The 'shenyu-spi' module also follows this similar design idea.
source code of shenyu-spi
The 'shenyu-spi' module is very concise, and the code structure is as follows:
- shenyu-spi[module]
- org.apache.shenyu.spi[package]
-- ExtensionFactory
-- ExtensionLoader
-- Join
-- SPI
-- SpiExtensionFactory
这些类功能如下:
- 'ExtensionFactory' : 'SPI' loader Factory, used to load an 'ExtensionLoader' instance based on the 'SPI' mechanism and to obtain the default 'SPI' identity implementation based on the 'ExtensionLoader' instance
- 'SpiExtensionFactory' : is an implementation of 'ExtensionFactory'
- 'SPI' : identification annotation, used to identify 'SPI', used on the interface
- 'Join' : identification annotation, used on the implementation class, used to identify the class joining the SPI system
- 'ExtensionLoader' : 'SPI' loader, analogous to 'java.util.ServiceLoader', used to load the implementation class of the interface in 'SPI'
@SPI
org.apache.shenyu.spi.SPI is an identification annotation which is used for identifying an interface as a 'SPI' interface.That is, only interfaces that use '@SPI' annotation can be loaded by 'shenyu-spi'. The class's annotation describes the implementation of Apache Dubbo, a reference to all the SPI systems (which makes sense, since the SPI extension is already a mature scheme with much the same implementation). This annotation has only one method:
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface SPI {
String value() default "";
}
The unique 'value()' method is used to specify the default 'SPI' implementation (optional), as will be shown later when analyzing 'ExtensionLoader'.
@Join
org.apache.shenyu.spi.Join is an identification annotation too. When this annotation is used on a class it specifies that the class contains 'SPI' implementation and to indicate that the class is added to the SPI system and can be loaded by ExtensionLoader. This annotation has two methods:
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Join {
int order() default 0;
boolean isSingleton() default true;
}
The unique 'order()' method is used to specify the specific sequence number. If a single interface that annotated with '@SPI' has multiple implementation classes that annotated with '@Join', the sequence number determines the order of these implementation class instances (the smaller one comes first).
The isSingleton() method indicates whether the class that the implementation class is a singleton class or not. That is if it is a singleton class it will be instantiated only once else it will create a new instance everytime .
ExtensionLoader
'ExtensionLoader' is the core of the 'SPI' module. Look at it's attributes first:
public final class ExtensionLoader<T> {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExtensionLoader.class);
private static final String SHENYU_DIRECTORY = "META-INF/shenyu/";
private static final Map<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>> LOADERS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Class<T> clazz;
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
private final Holder<Map<String, ClassEntity>> cachedClasses = new Holder<>();
private final Map<String, Holder<Object>> cachedInstances = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<Class<?>, Object> joinInstances = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private String cachedDefaultName;
private final Comparator<Holder<Object>> holderComparator = Comparator.comparing(Holder::getOrder);
private final Comparator<ClassEntity> classEntityComparator = Comparator.comparing(ClassEntity::getOrder);
public static class Holder<T> {
private volatile T value;
private Integer order;
private boolean isSingleton;
}
static final class ClassEntity {
private String name;
private Integer order;
private Boolean isSingleton;
private Class<?> clazz;
private ClassEntity(final String name, final Integer order, final Class<?> clazz, final boolean isSingleton) {
this.name = name;
this.order = order;
this.clazz = clazz;
this.isSingleton = isSingleton;
}
}
}
After analyzing the attributes, it is not difficult to find the following points:
- 'ExtensionLoader' There will be a global static cache 'LOADERS' to cache already created instances of 'ExtensionLoader' to prevent the performance overhead of repeated creation
- Each '@SPI' interface that is loaded using 'ExtensionLoader' generates a new instance of 'ExtensionLoader'
- '@SPI' interfaces that have multiple implementations are eventually acquired in order
Then look at it's constructors and static factory methods:
private ExtensionLoader(final Class<T> clazz, final ClassLoader cl) {
this.clazz = clazz;
this.classLoader = cl;
if (!Objects.equals(clazz, ExtensionFactory.class)) {
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getExtensionClassesEntity();
}
}
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(final Class<T> clazz, final ClassLoader cl) {
Objects.requireNonNull(clazz, "extension clazz is null");
if (!clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("extension clazz (" + clazz + ") is not interface!");
}
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(SPI.class)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("extension clazz (" + clazz + ") without @" + SPI.class + " Annotation");
}
ExtensionLoader<T> extensionLoader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) LOADERS.get(clazz);
if (Objects.nonNull(extensionLoader)) {
return extensionLoader;
}
LOADERS.putIfAbsent(clazz, new ExtensionLoader<>(clazz, cl));
return (ExtensionLoader<T>) LOADERS.get(clazz);
}
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(final Class<T> clazz) {
return getExtensionLoader(clazz, ExtensionLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
'ExtensionLoader' uses a private constructor, static factory methods, and lazy loading mode. Class loading is not triggered after initializing 'ExtensionLoader'. The actual scanning and loading is delayed until the 'getJoin' series methods are called, where the code is swept and all the method call chains that implement class information are loaded:
private Map<String, ClassEntity> getExtensionClassesEntity() {
Map<String, ClassEntity> classes = cachedClasses.getValue();
if (Objects.isNull(classes)) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.getValue();
if (Objects.isNull(classes)) {
classes = loadExtensionClass();
cachedClasses.setValue(classes);
cachedClasses.setOrder(0);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
private Map<String, ClassEntity> loadExtensionClass() {
SPI annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(annotation)) {
String value = annotation.value();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(value)) {
cachedDefaultName = value;
}
}
Map<String, ClassEntity> classes = new HashMap<>(16);
loadDirectory(classes);
return classes;
}
private void loadDirectory(final Map<String, ClassEntity> classes) {
String fileName = SHENYU_DIRECTORY + clazz.getName();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = Objects.nonNull(this.classLoader) ? classLoader.getResources(fileName)
: ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
if (Objects.nonNull(urls)) {
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
loadResources(classes, url);
}
}
} catch (IOException t) {
LOG.error("load extension class error {}", fileName, t);
}
}
private void loadResources(final Map<String, ClassEntity> classes, final URL url) throws IOException {
try (InputStream inputStream = url.openStream()) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
properties.forEach((k, v) -> {
String name = (String) k;
String classPath = (String) v;
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(name) && StringUtils.isNotBlank(classPath)) {
try {
loadClass(classes, name, classPath);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("load extension resources error", e);
}
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("load extension resources error", e);
}
}
private void loadClass(final Map<String, ClassEntity> classes,
final String name, final String classPath) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> subClass = Objects.nonNull(this.classLoader) ? Class.forName(classPath, true, this.classLoader) : Class.forName(classPath);
if (!clazz.isAssignableFrom(subClass)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("load extension resources error," + subClass + " subtype is not of " + clazz);
}
if (!subClass.isAnnotationPresent(Join.class)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("load extension resources error," + subClass + " without @" + Join.class + " annotation");
}
ClassEntity oldClassEntity = classes.get(name);
if (Objects.isNull(oldClassEntity)) {
Join joinAnnotation = subClass.getAnnotation(Join.class);
ClassEntity classEntity = new ClassEntity(name, joinAnnotation.order(), subClass);
classes.put(name, classEntity);
} else if (!Objects.equals(oldClassEntity.getClazz(), subClass)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("load extension resources error,Duplicate class " + clazz.getName() + " name "
+ name + " on " + oldClassEntity.getClazz().getName() + " or " + subClass.getName());
}
}
Processing with the chain of method 'getExtensionClassesEntity - > loadExtensionClass - > loadDirectory - > loadResources - > LoadClass',it will create a mapping of 'alias' to 'implementation class information' for subsequent instantiations, as shown in the 'getJoin()' method:
public T getJoin(final String name) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(name)) {
throw new NullPointerException("get join name is null");
}
Holder<Object> objectHolder = cachedInstances.get(name);
if (Objects.isNull(objectHolder)) {
cachedInstances.putIfAbsent(name, new Holder<>());
objectHolder = cachedInstances.get(name);
}
Object value = objectHolder.getValue();
if (Objects.isNull(value)) {
synchronized (cachedInstances) {
value = objectHolder.getValue();
if (Objects.isNull(value)) {
Holder<T> pair = createExtension(name);
value = pair.getValue();
int order = pair.getOrder();
objectHolder.setValue(value);
objectHolder.setOrder(order);
}
}
}
return (T) value;
}
private Holder<T> createExtension(final String name) {
ClassEntity classEntity = getExtensionClassesEntity().get(name);
if (Objects.isNull(classEntity)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name is error");
}
Class<?> aClass = classEntity.getClazz();
Object o = joinInstances.get(aClass);
if (Objects.isNull(o)) {
try {
joinInstances.putIfAbsent(aClass, aClass.newInstance());
o = joinInstances.get(aClass);
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Extension instance(name: " + name + ", class: "
+ aClass + ") could not be instantiated: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
Holder<T> objectHolder = new Holder<>();
objectHolder.setOrder(classEntity.getOrder());
objectHolder.setValue((T) o);
return objectHolder;
}
As you can see from the 'createExtension()' method, we end up using reflection to instantiate the implementation class. The reflection method 'newInstance()' requires that the class must provide a no-argument constructor because of an implicit convention: The 'SPI' implementation class must provide a no-argument constructor or the instantiation will fail. The rest methods, such as 'getDefaultJoin()' and 'getJoins()' are uncomplicated extensions of 'getJoin()', so we won't analyze them here. In addition, the 'getJoin()' method uses a multilevel cache:
- 'cachedInstances' : Search for the corresponding implementation class instance by alias
- 'joinInstances' : If the alias lookup fails, load all the implementation class information, locate the implementation class type by the alias, and update the' cachedInstances' cache by either finding the implementation class type or creating and caching the implementation class instance
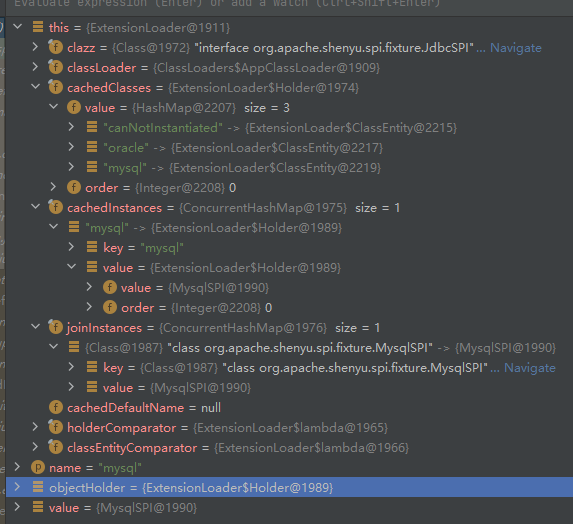
This completes the source code analysis of 'ExtensionLoader'. Here's another example of an 'ExtensionLoader' instance member property memory layout diagram to help you understand:
ExtensionFactory
'ExtensionFactory' is the factory interface inside the factory pattern, which defines a method to get an instance of the 'SPI' implementation (the default implementation, or the only implementation) :
@SPI("spi")
public interface ExtensionFactory {
<T> T getExtension(String key, Class<T> clazz);
}
Let's look the class 'SpiExtensionFactory' :
@Join
public class SpiExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
@Override
public <T> T getExtension(final String key, final Class<T> clazz) {
return Optional.ofNullable(clazz)
.filter(Class::isInterface)
.filter(cls -> cls.isAnnotationPresent(SPI.class))
.map(ExtensionLoader::getExtensionLoader)
.map(ExtensionLoader::getDefaultJoin)
.orElse(null);
}
}
It's worth noting here that the 'ExtensionFactory' itself is part of the 'SPI' system. So when using 'ExtensionFactory' you can instantiate it directly:
ExtensionFactory extensionFactory = new SpiExtensionFactory();
It can also be loaded based on an 'ExtensionLoader':
# the content of META-INF/services/shenyu/org.apache.shenyu.spi.ExtensionFactory
spi=org.apache.shenyu.spi.SpiExtensionFactory
# then load it with ExtensionLoader
ExtensionFactory extensionFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getDefaultJoin();
Once you have an 'ExtensionFactory' instance, you can load an instance of its default implementation class based on the '@SPI' interface.
The 'SPI' extension framework based on the design idea of 'Java' native 'SPI' has the characteristics of loose coupling, high usability and high scalability, a loading instance cache system, concurrency security and other features to fill some defects of 'SPI' in the native 'JDK', Shenyu SPI module is the same. Base on this powerful 'SPI' module, other modules in 'Shenyu' such as the 'Plugin' module can be configured quickly and pluggable, making it easier to load a newly developed Plugin instance.